Bio-based Phase Change Material Market Expected to Grow at 9.2% CAGR from 2025 to 2032 – openPR.com
Market Analysis of Bio-based Phase Change Materials and Contribution to Sustainable Development Goals
Market Overview and Projections
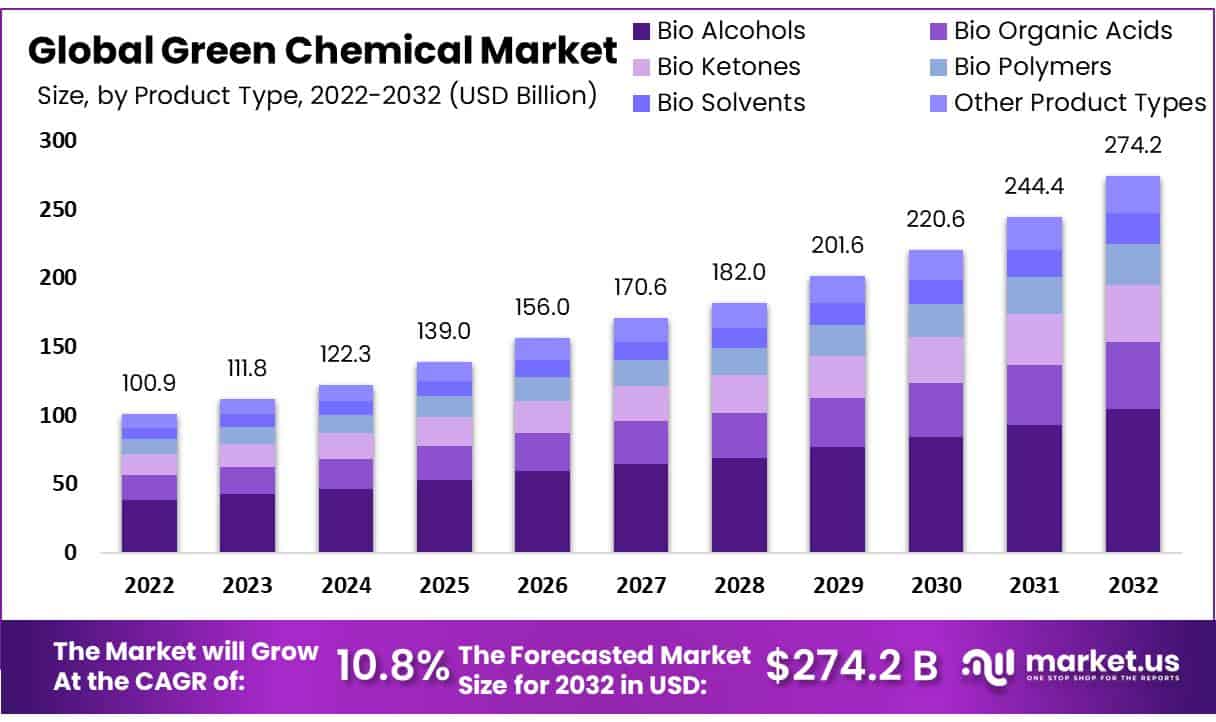
The global market for Bio-based Phase Change Materials (PCMs) is projected to experience significant growth, with market valuation estimated at USD 1.5 billion in 2024. The market is forecast to expand at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 9.2% from 2025 to 2031, reaching an anticipated value of USD 3.2 billion by 2031. This growth is attributed to the increasing industrial adoption of sustainable thermal energy storage solutions, which are critical for enhancing energy efficiency and reducing environmental impact.
Alignment with Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
The expansion of the Bio-based PCM market is intrinsically linked to the advancement of several United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The technology’s core function of efficient thermal management directly supports global sustainability targets.
- SDG 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy): By improving thermal energy storage in applications like building insulation and electronics cooling, bio-based PCMs reduce the energy required for heating and cooling, thus lowering overall energy consumption and promoting energy efficiency.
- SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure): The market thrives on innovation in materials science and encapsulation technologies. Its products are integral to developing resilient and sustainable infrastructure, particularly green buildings and energy-efficient industrial processes.
- SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities): Bio-based PCMs are a key component in the construction of energy-efficient buildings, which helps reduce the carbon footprint of urban areas and contributes to the creation of sustainable and resilient cities.
- SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production): The shift from petroleum-based PCMs to bio-based alternatives promotes the use of renewable resources, aligning with sustainable production patterns. Enhanced energy efficiency also contributes to more responsible consumption of resources.
- SDG 13 (Climate Action): By significantly decreasing energy demand for thermal regulation, the use of bio-based PCMs directly contributes to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions, supporting global climate action initiatives.
Key Market Drivers
- Technological Advancements and Innovation: Continuous R&D in encapsulation and thermal conductivity is enhancing the performance and expanding the applications of bio-based PCMs. These innovations support SDG 9 by fostering technological progress in sustainable materials.
- Expanding Applications Across End-Use Sectors: The integration of PCMs in diverse sectors such as construction, automotive, and electronics is driving demand. This cross-industry adoption promotes energy efficiency in line with SDG 7 and SDG 11.
- Favorable Government Policies and Infrastructure Initiatives: Government incentives, green building standards, and stringent environmental regulations are compelling industries to adopt sustainable solutions. Public-private partnerships for smart cities and Industry 4.0 initiatives further accelerate market growth, reinforcing SDG 11 and SDG 13.
- Increased Investment in Research & Development: Growing investment from public and private entities is focused on developing next-generation PCMs with greater efficiency and environmental sustainability, directly contributing to the innovation targets of SDG 9.
Market Segmentation
By Type
- Microencapsulated Phase Change Materials
- Macroencapsulated Phase Change Materials
- Bulk Phase Change Materials
By Application
- Building & Construction
- Textiles
- Electronics
- Packaging
- Chilled Beverages
By End-Use Industry
- Construction
- Textile
- Food & Beverage
- Electronics
- Automotive
Regional Analysis
- North America: This region holds a significant market share due to advanced technological infrastructure, high investment, and early adoption of PCM technologies. Regulatory frameworks promoting energy efficiency support continued growth in alignment with SDG 7 and SDG 13.
- Europe: As a leading market, Europe’s growth is driven by strong environmental regulations and a focus on sustainability. Countries like Germany and the UK are at the forefront of adopting green solutions, heavily influenced by commitments to SDG 12 and SDG 13.
- Asia-Pacific: This region is identified as having the highest growth potential. Rapid industrialization, urbanization, and infrastructure development in economies like China and India are creating substantial demand for energy-efficient solutions, contributing to progress on SDG 9 and SDG 11.
- Rest of the World: Latin America, the Middle East, and Africa are demonstrating moderate market growth. Expanding industrial activities and developing infrastructure present future opportunities for the adoption of bio-based PCMs to meet regional sustainability goals.
Key Industry Players
The market includes several key players focused on innovation and strategic expansion:
- BASF SE
- Honeywell International Inc.
- Phase Change Energy Solutions Inc.
- Climator Sweden AB
- PCM Products
- RGEES
- Sustainable Innovations LLC
- Cold Chain Technologies
- ECO-Phase
- Xiongxing New Material Technology Co. Ltd.
- TACONIC
- Ecovative Design
Analysis of Sustainable Development Goals in the Article
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
The article on the Bio-based Phase Change Material market connects to several Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) by focusing on sustainable technology, energy efficiency, and industrial innovation. The primary SDGs addressed are:
- SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy – The core function of phase change materials is thermal energy storage, which directly contributes to energy efficiency and conservation.
- SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure – The article is centered on market growth driven by technological innovation, R&D, and the application of these materials in various industries and infrastructure projects like green buildings.
- SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities – The use of these materials in “building insulation” and adherence to “green building standards” helps create more energy-efficient and sustainable buildings, which are key components of sustainable cities.
- SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production – The emphasis on “bio-based” materials as an “eco-friendly” alternative to “petroleum-based counterparts” promotes sustainable production patterns and a shift away from fossil-fuel-based resources.
- SDG 13: Climate Action – By improving energy efficiency and enabling “low-carbon thermal management systems,” the adoption of these materials helps reduce energy consumption and, consequently, greenhouse gas emissions.
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
Based on the article’s discussion, the following specific SDG targets can be identified:
- Target 7.3: By 2030, double the global rate of improvement in energy efficiency.
- Explanation: The article repeatedly highlights that the demand for bio-based phase change materials is driven by the need for “energy-efficient systems” and “energy conservation.” Their primary application is to “store and release thermal energy efficiently,” which directly supports the goal of improving energy efficiency in sectors like construction and electronics.
- Target 9.4: By 2030, upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable, with increased resource-use efficiency and greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies.
- Explanation: The article describes the adoption of these materials in “building & construction,” “automotive,” and “industrial manufacturing.” The shift towards “eco-friendly PCM alternatives” and “low-carbon thermal management systems” represents the adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies to make industries more sustainable.
- Target 9.5: Enhance scientific research, upgrade the technological capabilities of industrial sectors…, and encourage innovation.
- Explanation: The text explicitly states that “Technological Advancements and Innovation” and “Increased Investment and Focus on Research & Development” are key growth drivers. It mentions “cutting-edge innovations,” “next-generation products,” and R&D efforts by companies to improve efficiency and create new applications.
- Target 11.6: By 2030, reduce the adverse per capita environmental impact of cities, including by paying special attention to air quality and municipal and other waste management.
- Explanation: The article’s emphasis on “green building standards” and the use of these materials for “building insulation” directly contributes to reducing the energy consumption of buildings. This lowers the overall environmental footprint of cities.
- Target 12.2: By 2030, achieve the sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources.
- Explanation: The core subject is “bio-based” materials, which are presented as a sustainable alternative to “petroleum-based counterparts.” This shift signifies a move towards using renewable resources over finite fossil fuels, aligning with sustainable resource management.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
The article provides several quantitative and qualitative indicators that can be used to measure progress:
- Market Growth and Size: The projection of the global market reaching “USD 3.2 billion by 2031” with a “CAGR of 9.2%” serves as a direct indicator for the adoption rate of this energy-efficient and sustainable technology (Indicator for Targets 7.3 and 9.4).
- Investment in R&D: The mention of a “surge in investment from both private and public entities” and companies dedicating “substantial resources to research and development” is a qualitative indicator of progress towards innovation (Indicator for Target 9.5).
- Adoption in Key Sectors: The increasing integration of these materials in sectors like “Building & Construction,” “Textiles,” “Electronics,” and “Automotive” indicates the retrofitting of industries with sustainable technologies (Indicator for Target 9.4).
- Policy and Regulatory Support: The article points to “stringent environmental regulations and incentives for sustainable construction practices” in Europe and North America and “Favorable Government Policies” as drivers. This serves as an indicator of national integration of climate and sustainability measures (Indicator for SDG 13).
- Shift to Bio-Based Materials: The growth of the “Bio-based Phase Change Material market” itself is an indicator of the shift away from petroleum-based products, measuring progress towards sustainable resource use (Indicator for Target 12.2).
4. Table of SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators Identified in the Article |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy | 7.3: Double the global rate of improvement in energy efficiency. | Market growth (CAGR of 9.2%) of materials designed for “energy-efficient systems” and “energy conservation.” |
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure | 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable and adopt clean technologies. | Adoption of “eco-friendly PCM alternatives” in sectors like construction, automotive, and electronics; Market size projected to reach USD 3.2 billion by 2031. |
| 9.5: Enhance scientific research and encourage innovation. | Mention of “Increased Investment and Focus on Research & Development”; “Technological Advancements and Innovation” cited as a primary market driver. | |
| SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities | 11.6: Reduce the adverse per capita environmental impact of cities. | Application of materials in “building insulation” to meet “green building standards.” |
| SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production | 12.2: Achieve the sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources. | Market growth of “bio-based” materials as an alternative to “petroleum-based counterparts.” |
| SDG 13: Climate Action | 13.2: Integrate climate change measures into national policies, strategies and planning. | Existence of “stringent environmental regulations,” “incentives for sustainable construction,” and “favorable government policies” driving market adoption. |
Source: openpr.com

What is Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0




































































![Lancaster homeowner’s energy-efficient renovation sparks clash over historic preservation [Lancaster Watchdog] – LancasterOnline](https://bloximages.newyork1.vip.townnews.com/lancasteronline.com/content/tncms/assets/v3/editorial/9/ed/9ed03d32-c902-44d2-a461-78ad888eec38/69050b156baeb.image.png?resize=150,75#)








