US energy storage set a new record in Q1 2025 but the future looks shaky – Electrek
US Energy Storage Market Achieves Record Growth in Q1 2025

The United States energy storage market recorded its strongest first quarter ever in 2025, adding over 2 gigawatts (GW) of capacity across all segments. This milestone was reported by the US Energy Storage Monitor, a collaboration between Wood Mackenzie and the American Clean Power Association (ACP).
This unprecedented growth in Q1 2025 marks the largest first quarter for energy storage in US history, demonstrating significant progress towards sustainable energy infrastructure aligned with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly SDG 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy) and SDG 13 (Climate Action).
Utility-Scale Projects Lead Growth
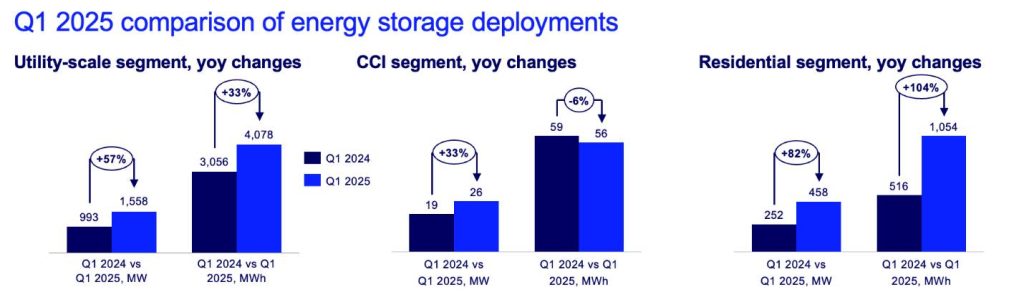
Utility-scale energy storage projects were the primary drivers of this surge, contributing over 1.5 GW of new capacity. This represents a 57% increase compared to Q1 2024, highlighting the expanding role of large-scale storage solutions in supporting grid reliability and renewable energy integration.
John Hensley, Senior Vice President of Markets and Policy Analysis at ACP, emphasized the importance of energy storage in addressing increasing energy demand and grid strain: “The energy storage market is responding to help keep the lights on and support this unprecedented growth in an affordable and reliable way.” This development supports SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure) by enhancing resilient infrastructure.
Emerging Markets Showcase Expansion Potential
Energy storage deployment is expanding beyond traditional early-adopter states such as California and Texas. Indiana exemplifies this trend, having added 256 megawatts (MW) of new energy storage capacity in Q1 2025, quadrupling its total installed capacity. Indiana now holds more than 10 GW of new storage projects in its interconnection queue, ranking fifth nationally.
Key factors driving Indiana’s growth include:
- Availability of land
- Clear and efficient permitting processes
Noah Roberts, Vice President of Energy Storage at ACP, noted, “We’re now seeing significant deployment in emerging markets like Indiana, while states across the Southwest such as Nevada and Arizona continue to expand their energy storage portfolios.” This geographic diversification promotes SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities) by supporting localized clean energy solutions.
Residential Energy Storage Experiences Record Growth
The residential energy storage sector also achieved a new milestone, with 458 MW installed in Q1 2025—the highest ever recorded in a single quarter. California and Puerto Rico led this growth, accounting for 74% of new residential storage capacity, while states like Illinois and other emerging markets showed increasing adoption rates.
Policy Challenges Threaten Future Growth
Despite strong near-term prospects, the long-term outlook for energy storage growth faces uncertainty due to potential changes in federal policy. Proposed amendments to the Investment Tax Credit (ITC) within the House’s reconciliation bill could significantly reduce future capacity additions.
- Distributed Storage Impact: Projected to decline by 46%, representing the largest segment reduction.
- Utility-Scale Storage Impact: Potential contraction by 16 GW over five years.
Additionally, the community, commercial, and industrial (CCI) segment has already experienced a 42% reduction in its five-year forecast, influenced by tariff risks and slow adoption of California’s NEM 3.0 regulations.
Allison Weis, Global Head of Energy Storage at Wood Mackenzie, highlighted the critical juncture faced by the industry: “The Q1 2025 results demonstrate the demand for energy storage in the US to serve a grid with both growing renewables and growing load. However, the industry stands at a crossroads, with potential policy changes threatening to disrupt this momentum.”
Forecast and Implications for Sustainable Development
The report projects that in 2025, approximately 15 GW (49 GWh) of new energy storage capacity will be installed across all segments, with utility-scale installations expected to grow by 22% year-over-year. However, policy uncertainty could lead to a 29% contraction in utility-scale storage in 2026.
This energy storage expansion is essential for achieving multiple SDGs, including:
- SDG 7: Ensuring access to affordable, reliable, sustainable, and modern energy.
- SDG 13: Taking urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts by enabling higher renewable energy penetration.
- SDG 9: Building resilient infrastructure and fostering innovation in energy technologies.
Continued growth in energy storage capacity supports the transition to a low-carbon economy and enhances energy security and resilience across communities.
Recommendations for Consumers and Stakeholders
For individuals living in regions prone to natural disasters and power outages, adopting solar energy combined with battery storage systems can improve home resilience and energy independence. Services such as EnergySage provide access to trusted solar installers offering competitive pricing and high-quality solutions.
- EnergySage connects consumers with hundreds of pre-vetted solar installers.
- Users can compare personalized solar quotes online with support from unbiased Energy Advisers.
- The platform helps save 20-30% compared to independent purchasing and ensures no sales calls until an installer is selected.
These consumer options align with SDG 7 by promoting clean energy adoption at the household level and enhancing community resilience.
Further Reading: This new San Diego battery can power 200,000 homes during peak hours
1. Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) Addressed or Connected
- SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
- The article discusses the rapid growth in energy storage capacity in the US, which supports the integration of renewable energy and enhances grid reliability.
- SDG 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure
- Expansion of utility-scale and residential energy storage reflects innovation in energy infrastructure and technology deployment.
- SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
- Energy storage contributes to resilient and sustainable urban energy systems, especially in areas prone to natural disasters.
- SDG 13: Climate Action
- By enabling greater use of renewable energy and reducing reliance on fossil fuels, energy storage supports climate change mitigation efforts.
2. Specific Targets Under the Identified SDGs
- SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
- Target 7.2: Increase substantially the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix.
- Target 7.3: Double the global rate of improvement in energy efficiency.
- SDG 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure
- Target 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable, with increased resource-use efficiency and greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies.
- SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
- Target 11.5: Reduce the number of deaths and the number of people affected by disasters, including water-related disasters.
- Target 11.b: Increase the number of cities adopting and implementing integrated policies and plans towards inclusion, resource efficiency, mitigation and adaptation to climate change.
- SDG 13: Climate Action
- Target 13.2: Integrate climate change measures into national policies, strategies and planning.
3. Indicators Mentioned or Implied to Measure Progress
- Installed Energy Storage Capacity (GW and MW)
- The article provides data on gigawatts (GW) and megawatts (MW) of new energy storage capacity installed in various segments (utility-scale, residential, distributed), which can be used as an indicator of progress towards clean energy targets.
- Growth Rate of Energy Storage Installations
- Year-over-year percentage increases in energy storage capacity (e.g., 57% jump in utility-scale projects) serve as indicators of market expansion and adoption of clean technologies.
- Policy Impact on Storage Deployment
- Projected changes in storage buildout due to policy shifts (e.g., 27% reduction if ITC changes pass) imply indicators related to policy environment and its effect on sustainable infrastructure development.
- Geographic Distribution of Storage Capacity
- Data on energy storage growth in emerging markets like Indiana and states like California and Puerto Rico indicate progress in regional sustainable energy adoption.
4. SDGs, Targets and Indicators Table
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy |
|
|
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure |
|
|
| SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities |
|
|
| SDG 13: Climate Action |
|
|
Source: electrek.co








