Addressing Gender Disparities for Inclusive and Equitable Development in Lao PDR – Asian Development Bank

Demography and Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in Lao PDR
Population Overview
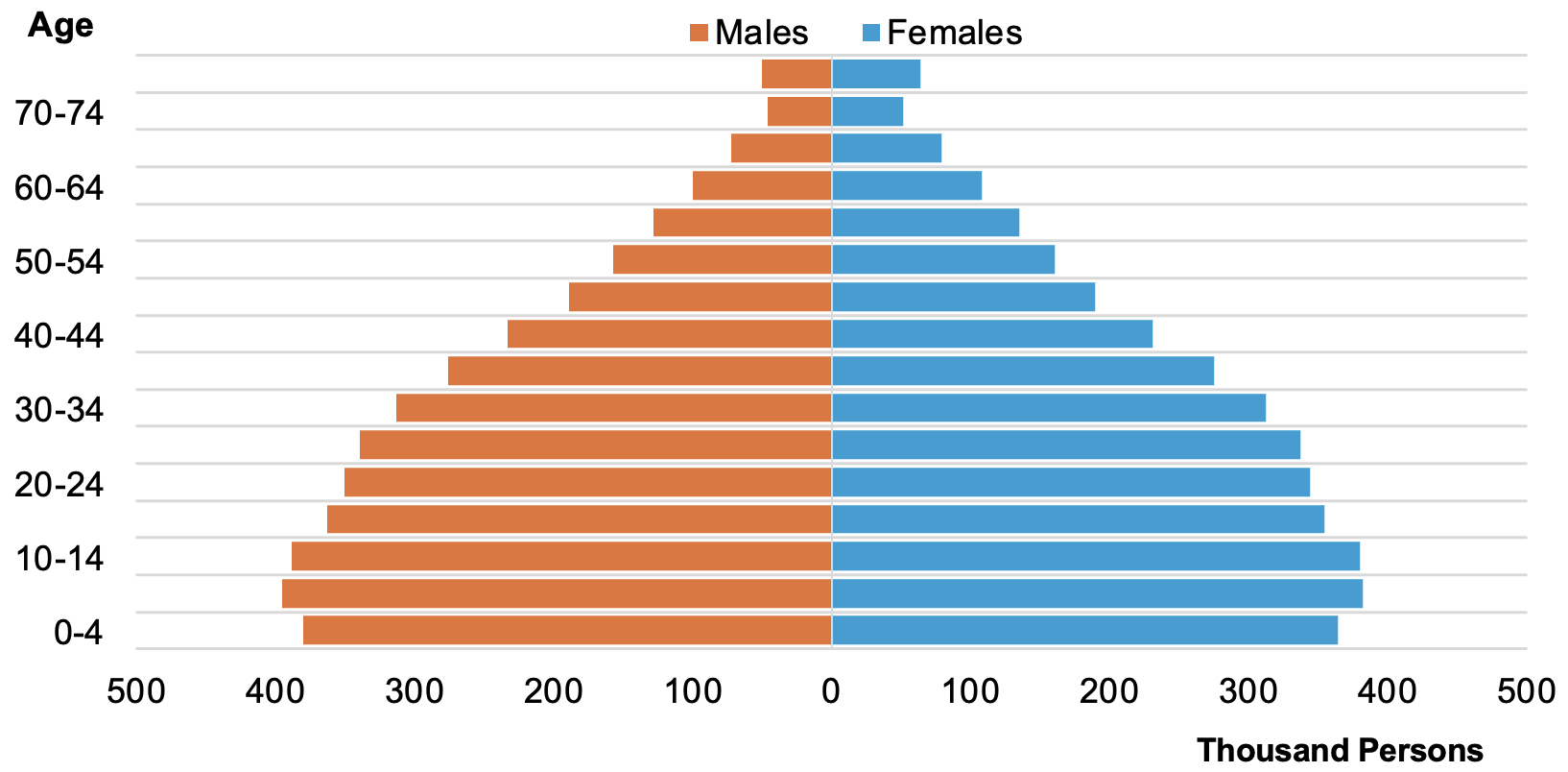
The Lao People’s Democratic Republic (Lao PDR) recorded a population of 6.67 million with an almost equal gender distribution as of 2015.[1] Projections indicate the population will reach 9.4 million by 2045. The population structure is youthful, with 41.4% under a young age and only 4.5% elderly. The sex ratio is projected at 100.4 males per 100 females in 2023. Female-headed households constitute 17.7%, with lower proportions in rural areas. The total fertility rate is expected to decline from 3.0 in 2015 to 1.8 by 2045, while life expectancy is increasing, with females living longer than males.
Figure 1: Distribution of Population by Age Group and Sex
Education and Gender Equality (SDG 4 and SDG 5)
Gender Disparities in Education
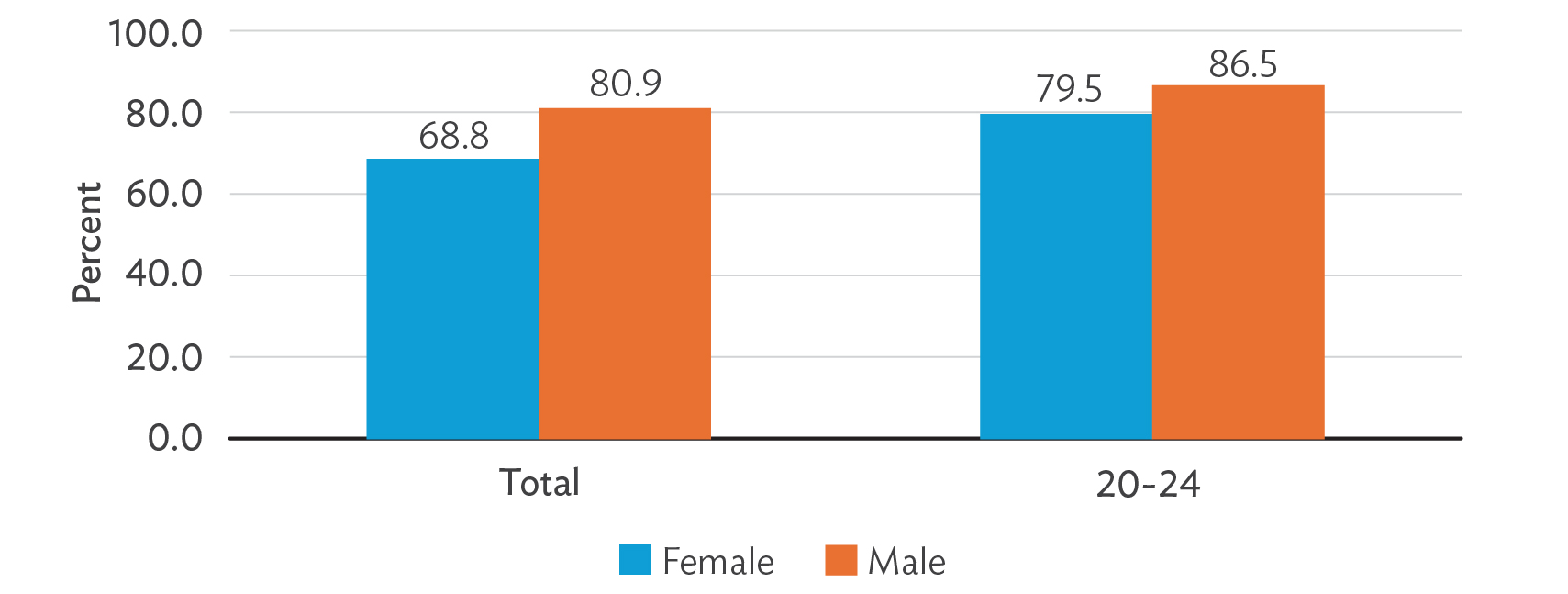
Gender inequalities persist in education within Lao PDR. Males generally have higher literacy rates than females, although this gap is narrowing among younger generations. Early childhood education attendance is low, with 34% of girls and 30% of boys aged 3 to 4 years enrolled. Girls outperform boys slightly in early childhood development indices, particularly in literacy–numeracy and social–emotional development.
Figure 2: Percentage of Adult Population Reporting Ability to Read and Write, by Sex
Teacher and Enrollment Statistics
- Over 99% of pre-primary teachers are female.
- Female teachers predominate in primary and secondary education.
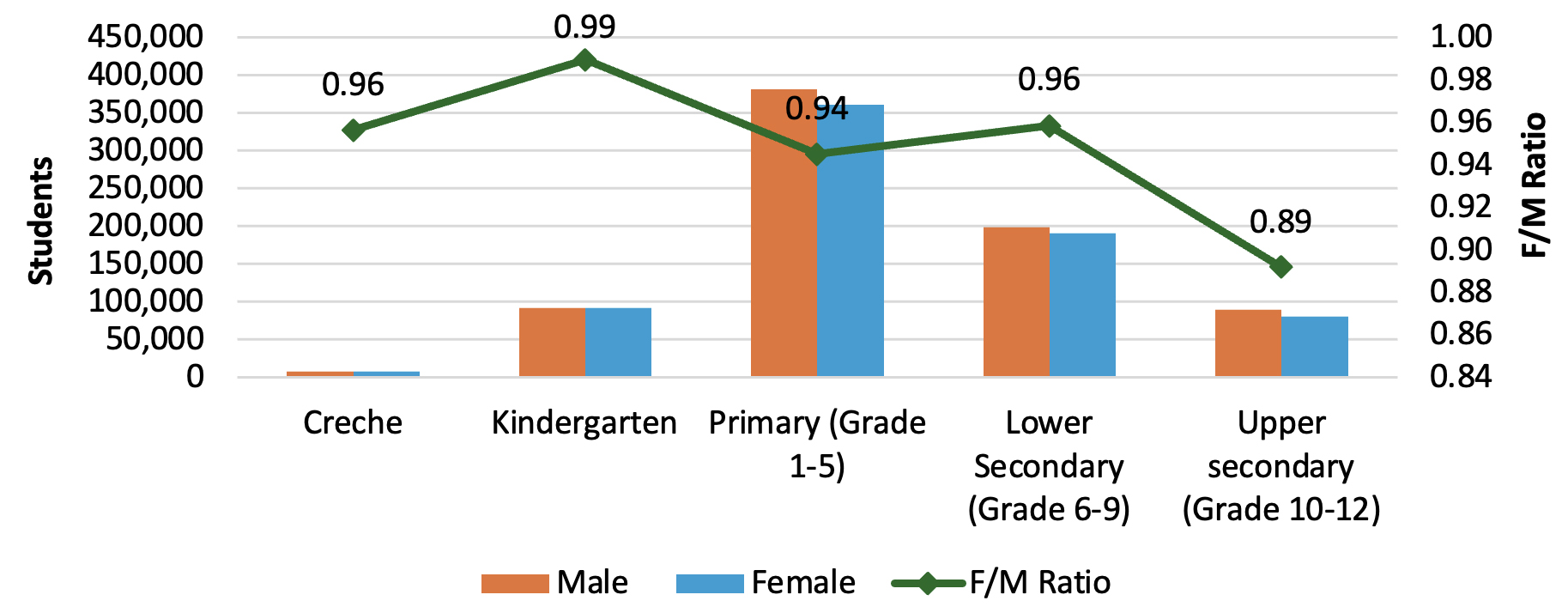
- More males are enrolled at preschool and primary levels, with a significant male majority in upper secondary school.
- Out-of-school rates are higher for boys across all education levels, especially in upper secondary education.
Digital access shows similar mobile usage between males and females (84%), but men have higher computer (13% vs. 9%) and internet usage (61% vs. 57%) and digital skills proficiency (10.9% vs. 8.1%).
Figure 3: Number of Students by Sex and Female–Male Ratio for Enrolment, 2023
Strategies to Reduce Gender Gaps in Education
- Expand early childhood education programs, especially targeting rural areas and girls, including subsidizing enrollment costs.
- Implement targeted interventions to reduce out-of-school rates through community engagement and scholarship programs.
- Develop gender-sensitive curricula to eliminate stereotypes and promote gender equality.
- Provide regular gender-sensitivity training for teachers.
- Enhance digital literacy for women and girls by offering training and improving access to digital tools and internet connectivity.
- Engage communities actively in promoting gender equality.
- Establish monitoring and evaluation mechanisms with regular data collection and feedback from students and parents.
Labor and Employment: Gender Disparities (SDG 8 and SDG 5)
Labor Market Overview
Significant gender disparities exist in the labor market. A majority of women (58.1%) are outside the labor force compared to 47.4% of men, primarily due to family care responsibilities. The unemployment rate in 2022 was 1.9% for women and 2.8% for men.[2] Women led 36% of enterprises in 2020, mainly microenterprises in trade, manufacturing, and hospitality sectors. Informal employment is higher among women, and a persistent gender pay gap exists across agriculture, industry, and services sectors. In public administration, 45% of women occupy the lowest salary level compared to 33% of men. Women spend 48% of their day on unpaid domestic and care work, while men spend less than 40%.
Measures to Promote Gender Equality in Employment
- Empower women in business through leadership training, mentorship programs, and gender diversity quotas, particularly in the public sector.
- Promote female entrepreneurship via financial support such as grants, low-interest loans, and networking opportunities.
- Address the gender pay gap by encouraging transparent pay scales, mandatory gender pay audits, equal pay policies, and public reporting of pay disparities.
Health and Well-being (SDG 3 and SDG 5)
Health Improvements and Challenges
Between 2000 and 2020, Lao PDR achieved significant reductions in maternal mortality and infant mortality rates, with narrowing gender gaps. Under-five child mortality rates have also improved. In 2023, 53.1% of women used contraception, with 75% opting for modern methods.
Urban areas show better maternal and newborn health care access: 95% of urban women had skilled birth attendance versus 75% in rural areas; 77% of urban women accessed maternal and postnatal checkups compared to 59% in rural areas.
Food insecurity increased from 2019 to 2020, disproportionately affecting females. Anemia remains a concern, especially among pregnant women. Child malnutrition is significant, with 25.1% of boys and 23.4% of girls underweight, and 34.6% of boys and 31% of girls stunted.
Tobacco and alcohol use are higher among men (36.8% and 74.5%, respectively) than women (3.8% and 48.6%). Traffic accidents involve more male drivers and passengers, though females also experience injuries and fatalities.
Health Sector Recommendations
- Enhance maternal and child health services in rural areas by increasing access through mobile health units and specialized training.
- Promote modern contraceptive use via awareness campaigns and subsidized contraceptives.
- Improve nutrition programs targeting anemia and malnutrition through school feeding and community initiatives.
- Increase food security for women through agricultural support and microfinancing.
- Implement public health campaigns to reduce tobacco and alcohol consumption.
- Improve road safety with education programs and infrastructure enhancements such as safer pedestrian crossings and traffic signals.
Political and Public Life Representation (SDG 5 and SDG 16)
Gender Representation in Civil Service
Gender representation in political and public life remains uneven. In 2022, Lao PDR had 78,110 male and 72,103 female civil servants, with a male-to-female ratio of 1.08. Women dominate in the Ministry of Public Health (M/F ratio 0.53) and Ministry of Education and Sports (M/F ratio 0.91), while men dominate in the Ministry of Public Works and Transport (M/F ratio 3.31) and Ministry of Energy and Mines (M/F ratio 3.18).
Strategies to Achieve Gender Parity in Governance
- Eliminate barriers to female participation through gender bias training and support networks involving the Lao Women’s Organization.
- Implement gender quotas legislated to ensure balanced representation in ministries and the National Assembly.
- Promote female candidates via leadership training programs organized by development partners in collaboration with the Ministry of Education and Sports.
Family and Relationships: Addressing Early Marriage and Gender-Based Violence (SDG 5)
Current Situation
Early marriage remains prevalent, with one-third of women aged 20–24 married before 18. Rates are higher in rural (36.3%) and economically disadvantaged (48.5%) populations. In 2023, adolescent birth rates were 83 live births per 1,000 females aged 15–19, rising to 136 in rural areas. Additionally, 7% of women reported experiencing intimate partner violence in 2014.
Intervention Measures
- Enforce existing laws against child marriage and provide free legal aid to victims of gender-based violence.
- Engage communities, including men and boys, in gender equality initiatives promoting respect and positive masculinity.
- Conduct educational campaigns through schools and media highlighting benefits of girls’ education.
- Ensure safe school environments with improved infrastructure and sanitation to retain girls in education.
- Provide economic opportunities through vocational training to promote financial independence and reduce early marriages.
1. Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) Addressed in the Article
- SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being
- Maternal and child health improvements
- Reduction in infant and under-5 mortality rates
- Contraceptive use and reproductive health
- Nutrition and anemia concerns
- Tobacco and alcohol use reduction
- Road safety improvements
- SDG 4: Quality Education
- Gender disparities in literacy and education enrollment
- Early childhood education attendance
- Digital skills and access to technology
- Teacher gender balance and training
- Reducing out-of-school rates
- SDG 5: Gender Equality
- Gender disparities in education, labor force participation, and political representation
- Early marriage and intimate partner violence
- Gender pay gap and unpaid domestic work
- Empowerment of women in business and leadership
- SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
- Labor market gender disparities
- Female entrepreneurship and employment quality
- Pay equity and labor force participation
- SDG 10: Reduced Inequalities
- Addressing rural-urban disparities in health and education
- Reducing inequalities in digital access and skills
- Economic and social inequalities affecting women and disadvantaged groups
- SDG 16: Peace, Justice and Strong Institutions
- Legal enforcement against child marriage and gender violence
- Gender parity in political and public life representation
- Community engagement and gender equality initiatives
2. Specific Targets Under the Identified SDGs
- SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being
- Target 3.1: Reduce the global maternal mortality ratio
- Target 3.2: End preventable deaths of newborns and children under 5 years
- Target 3.7: Ensure universal access to sexual and reproductive health-care services
- Target 3.4: Reduce premature mortality from non-communicable diseases (tobacco and alcohol use)
- Target 3.6: Halve the number of global deaths and injuries from road traffic accidents
- SDG 4: Quality Education
- Target 4.1: Ensure all girls and boys complete free, equitable and quality primary and secondary education
- Target 4.2: Ensure access to quality early childhood development and pre-primary education
- Target 4.3: Equal access to affordable technical, vocational and higher education
- Target 4.4: Increase the number of youth and adults with relevant skills for employment
- Target 4.5: Eliminate gender disparities in education
- SDG 5: Gender Equality
- Target 5.1: End all forms of discrimination against women and girls
- Target 5.2: Eliminate all forms of violence against women and girls
- Target 5.3: Eliminate harmful practices such as child marriage
- Target 5.4: Recognize and value unpaid care and domestic work
- Target 5.5: Ensure women’s full participation and equal opportunities in leadership
- SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
- Target 8.5: Achieve full and productive employment and decent work for all women and men
- Target 8.3: Promote development-oriented policies that support productive activities and entrepreneurship
- Target 8.8: Protect labor rights and promote safe working environments
- SDG 10: Reduced Inequalities
- Target 10.2: Empower and promote social, economic and political inclusion of all
- Target 10.3: Ensure equal opportunity and reduce inequalities of outcome
- SDG 16: Peace, Justice and Strong Institutions
- Target 16.3: Promote rule of law and ensure equal access to justice
- Target 16.7: Ensure responsive, inclusive, participatory and representative decision-making
3. Indicators Mentioned or Implied in the Article
- Demography and Population
- Population size and growth projections (6.67 million in 2023 to 9.4 million by 2045)
- Sex ratio (100.4 males per 100 females)
- Total fertility rate (declining from 3.0 to 1.8)
- Life expectancy by sex
- Education
- Literacy rates by sex
- Early childhood education attendance rates (34% girls, 30% boys)
- School enrollment and out-of-school rates by sex and education level
- Digital skills proficiency percentages (men 10.9%, women 8.1%)
- Teacher gender composition
- Labor and Employment
- Labor force participation rates by sex (women 41.9%, men 52.6%)
- Unemployment rates by sex (women 1.9%, men 2.8%)
- Percentage of women-led enterprises (36%)
- Informal employment rates by sex
- Gender pay gap data in sectors and salary levels
- Time spent on unpaid domestic and care work
- Health
- Maternal mortality rate trends
- Infant and under-5 mortality rates by sex
- Contraceptive prevalence rate (53.1% women, 75% modern methods)
- Skilled birth attendance rates (urban 95%, rural 75%)
- Nutrition indicators: underweight and stunting rates among children under 5
- Tobacco and alcohol use prevalence by sex
- Traffic accident injury and fatality rates by sex
- Political and Public Life
- Number and ratio of male to female civil servants
- Gender representation ratios in ministries
- Family and Relationships
- Prevalence of early marriage (one-third of women 20–24 married before 18)
- Adolescent birth rates (83 per 1,000 females 15–19)
- Reported intimate partner violence rates (7%)
4. Table of SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being |
|
|
| SDG 4: Quality Education |
|
|
| SDG 5: Gender Equality |
|
|
| SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth |
|
|
| SDG 10: Reduced Inequalities |
|
|
| SDG 16: Peace, Justice and Strong Institutions |
|
|
Source: adb.org