EVI Industries: A Founder-Led Engine of Industrial Growth and Shareholder Value – AInvest
EVI Industries: A Report on Strategic Growth and Alignment with Sustainable Development Goals
EVI Industries, Inc. (NASDAQ: EVI) has established itself as North America’s foremost value-added distributor of commercial laundry products through a disciplined consolidation strategy. This report analyzes the company’s operational model, financial performance, and strategic initiatives through the lens of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly focusing on SDG 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth), SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure), and SDG 17 (Partnerships for the Goals).
Strategic Execution and Contribution to SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
EVI’s growth model is directly aligned with the principles of SDG 8, promoting sustained, inclusive, and sustainable economic growth, full and productive employment, and decent work for all. This is achieved through a founder-led governance structure and a strategic acquisition methodology.
Founder-Led Governance for Long-Term Value
- Leadership Stability: The company is led by its founder, Chairman, and CEO, Henry M. Nahmad, who, along with key executives, holds over 60% of the company. This structure ensures a long-term vision focused on sustainable value creation rather than short-term returns.
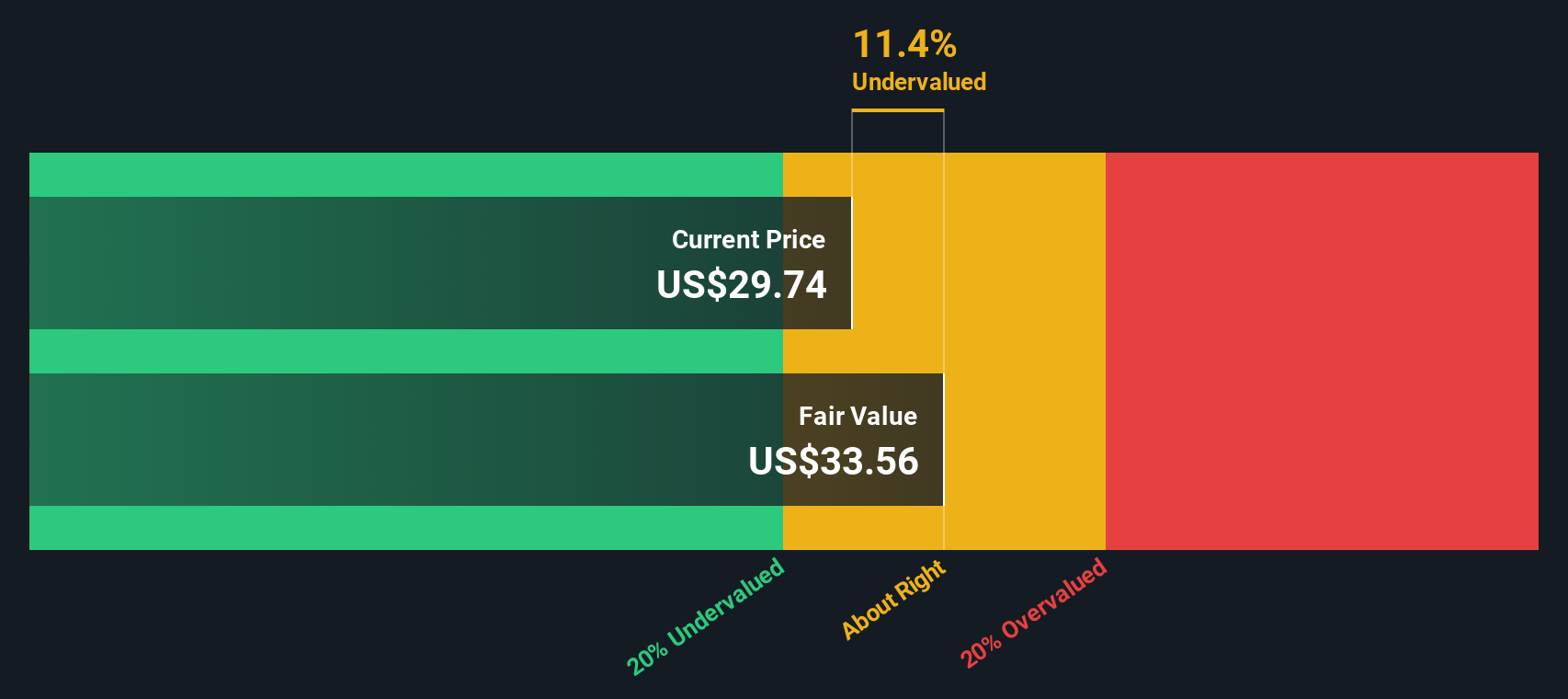
- Economic Growth: This strategic coherence has driven a 31% compound annual growth rate (CAGR) in revenue since 2016, contributing significantly to economic expansion within its sector.
The “Buy-and-Build” Strategy: Fostering Local Economies
EVI’s acquisition strategy supports local economic stability and job preservation by integrating regional distributors into its network while maintaining their operational autonomy.
- Acquisition and Integration: Since 2016, EVI has completed 31 acquisitions, expanding its geographic footprint and market share.
- Preservation of Local Expertise: The company employs a decentralized model where acquired management teams, such as that of Girbau North America (GNA) with an average of 25 years of industry experience, retain operational control. This approach secures local jobs and leverages regional expertise, directly supporting SDG 8.
- Organic Growth: By providing acquired companies with enhanced financial resources and technology, EVI fosters further organic growth at the local level.
Fostering Innovation and Resilient Infrastructure (SDG 9)
EVI’s commitment to technological modernization and capital efficiency is central to building resilient infrastructure and promoting inclusive and sustainable industrialization, in line with SDG 9.
Technological Advancement in a Traditional Industry
EVI is transforming the fragmented and low-digital-penetration commercial laundry sector into a tech-enabled service platform.
- Investment in Digital Platforms: The company is implementing a Field Service Management (FSM) platform, a next-generation CRM system, and an e-commerce solution.
- Efficiency and Sustainability Gains: These technological investments are projected to reduce service costs by 15-20%, improving operational efficiency and contributing to more sustainable industrial practices.
Capital Efficiency for Sustainable Growth
A robust and sustainable financial structure enables long-term investment in innovation and infrastructure.
- Strengthened Financial Position: In March 2025, EVI amended its credit facility, extending maturity to 2030 and increasing liquidity to $200 million (including a $50 million accordion feature).
- Low-Leverage Model: The company maintains a net leverage ratio below 2.5x, a conservative figure compared to industry peers. This financial prudence ensures stability and the capacity for continued investment in sustainable technologies and accretive acquisitions without exposing the organization to undue risk.
Partnerships for Sustainable Industrial Transformation (SDG 17)
EVI’s consolidation model exemplifies SDG 17 by creating robust partnerships that strengthen the means of implementation for sustainable development within the industrial distribution sector.
A Partnership-Based Consolidation Model
- Synergistic Acquisitions: EVI’s strategy targets distributors with strong local relationships and recurring revenue. The acquisitions are structured as partnerships, preserving brand equity and local leadership while integrating them into a larger, more efficient network.
- Building a Collaborative Network: By connecting over 1,000 fragmented distributors through its platform, EVI is creating a North American network that can collectively adopt more sustainable and technologically advanced practices, thereby strengthening the entire industry.
Conclusion: An Integrated Model for Sustainable Growth
EVI Industries presents a compelling model of industrial growth that is intrinsically aligned with key Sustainable Development Goals. Its founder-led vision fosters long-term economic stability (SDG 8), while its investments in technology build resilient and innovative infrastructure (SDG 9). Furthermore, its “buy-and-build” strategy serves as a powerful example of creating partnerships for sustainable goals (SDG 17). The company’s disciplined execution, which has resulted in a 31% revenue CAGR since 2016, demonstrates that financial success and contributions to sustainable development can be mutually reinforcing objectives.
Analysis of Sustainable Development Goals in the Article
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
-
SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
The article extensively discusses EVI Industries’ significant economic growth, exemplified by its “31% compound annual growth rate (CAGR) in revenue since 2016.” This focus on sustained economic expansion, operational efficiency, and value creation directly aligns with the core principles of SDG 8.
-
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
The article highlights EVI’s role in transforming the “fragmented world of industrial distribution” through a “buy-and-build strategy.” Its investments in “technological modernization,” including a “Field Service Management (FSM) platform, a next-generation CRM system, and an e-commerce solution,” point directly to innovation and upgrading industrial infrastructure.
-
SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
This goal is implicitly connected through the company’s drive for efficiency. The article states that investments in technology are “expected to reduce service costs by 15–20%.” Such significant cost reductions in service delivery imply more efficient use of resources (e.g., fuel, time, materials), which is a key component of sustainable production patterns.
-
SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals
EVI’s entire business model is built on partnerships. The “31 acquisitions since 2016” represent a series of private-private partnerships. The strategy of acquiring companies while retaining their local management under a “decentralized model” showcases a collaborative approach to achieving growth and strengthening the industry.
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
-
SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
- Target 8.2: Achieve higher levels of economic productivity through diversification, technological upgrading and innovation. The article details EVI’s strategy of “reinvesting in technology” and transforming into a “tech-enabled service platform” to drive productivity and efficiency, which directly supports this target.
-
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
- Target 9.3: Increase the access of small-scale industrial and other enterprises… to financial services… and their integration into value chains and markets. EVI’s strategy of acquiring “niche distributors” and integrating them into its “unified platform” provides these smaller enterprises with capital, technology, and access to a larger market, aligning with this target.
- Target 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable, with increased resource-use efficiency. EVI’s focus on “operational integration and technological modernization” of the acquired companies serves to upgrade the industry’s infrastructure. The goal of reducing service costs by 15-20% through technology is a direct move towards increased resource-use efficiency.
-
SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
- Target 12.2: By 2030, achieve the sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources. The article implies progress towards this target through EVI’s technology-driven productivity gains. The FSM platform, for instance, can optimize service routes, leading to lower fuel consumption and more efficient use of resources.
-
SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals
- Target 17.17: Encourage and promote effective public, public-private and civil society partnerships. EVI’s “buy-and-build” strategy, which involves acquiring and partnering with numerous private companies (31 since 2016), is a clear example of effective private-private partnerships aimed at achieving shared economic goals.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
-
For SDG 8 (Target 8.2):
The “31% compound annual growth rate (CAGR) in revenue since 2016” is a direct quantitative indicator of economic growth and productivity at the company level.
-
For SDG 9 (Targets 9.3 & 9.4):
The investment in a “Field Service Management (FSM) platform, a next-generation CRM system, and an e-commerce solution” serves as an indicator of technological upgrading. The expected “15–20% reduction in service costs” is a specific metric for measuring increased efficiency and resource productivity.
-
For SDG 12 (Target 12.2):
The “15–20% reduction in service costs” is an implied indicator of more efficient resource use, as lower costs in logistics and field service are often correlated with reduced consumption of fuel and other resources.
-
For SDG 17 (Target 17.17):
The “31 acquisitions since 2016” is a clear, quantifiable indicator of the number of partnerships formed to execute the company’s consolidation strategy.
4. Summary Table of SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth | 8.2: Achieve higher levels of economic productivity through technological upgrading and innovation. | 31% compound annual growth rate (CAGR) in revenue since 2016. |
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure | 9.3: Increase the access of small-scale industrial enterprises to financial services and their integration into value chains. | Acquisition of niche distributors and integration into a unified platform. |
| 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries for increased resource-use efficiency. | Investment in FSM, CRM, and e-commerce platforms; Expected 15–20% reduction in service costs. | |
| SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production | 12.2: Achieve the sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources. | Implied indicator: 15–20% reduction in service costs suggests more efficient resource use. |
| SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals | 17.17: Encourage and promote effective private-private partnerships. | Execution of 31 acquisitions since 2016. |
Source: ainvest.com

What is Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0















































:focal(1500,1000)/https://media.globalcitizen.org/a6/9a/a69a4720-d8a1-4715-b596-18738d03c05c/rotary_polio_hero_image.jpg?#)







/countries/sri-lanka/photo-credit---dmc-sri-lanka.tmb-1200v.jpg?sfvrsn=dc298bcc_1#)