Can Apple’s Product Innovation and Strategic Pricing Drive a 2025 Stock Rebound? – AInvest
Apple Inc. 2025 Strategic Outlook: An Analysis of Innovation, Market Dynamics, and Alignment with Sustainable Development Goals
A comprehensive review of Apple’s strategic direction for 2025 reveals a pivotal period defined by product innovation, services expansion, and significant regulatory challenges. The company’s performance is increasingly intertwined with its ability to navigate these factors while contributing to global sustainability objectives. This report analyzes Apple’s product pipeline, services growth, and operational strategies through the lens of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
Product Innovation and Contribution to Sustainable Development
Apple’s 2025 product strategy centers on enhancing its hardware portfolio with a focus on design, performance, and accessibility, which directly aligns with several key SDGs.
The iPhone 17 Series and Digital Inclusion
- iPhone 17 Air: This new model, featuring a 6.6-inch display and a slim 5.5mm profile, is strategically priced to bridge the gap between base and Pro models. Its introduction aims to stimulate market growth and upgrade cycles.
- Contribution to SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure): The integration of the advanced A19 chip, Wi-Fi 7, and enhanced on-device AI capabilities in iOS 26 represents a significant contribution to technological innovation and the development of resilient digital infrastructure.
- Contribution to SDG 10 (Reduced Inequalities): By offering a premium-featured device at a mid-tier price point, Apple enhances access to cutting-edge technology for a broader consumer base.
The MacBook Lineup and Educational Empowerment
- M4 MacBook Air: The model’s 20-35% performance increase over its predecessor, coupled with a price reduction, has already spurred a 21.4% year-over-year growth in Mac shipments. This demonstrates a commitment to energy efficiency, a core tenet of SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production).
- Forthcoming A18 MacBook: A planned $799 entry-level model for 2026 is poised to expand market share in the budget-conscious segment.
- Contribution to SDG 4 (Quality Education): The strategy of making powerful computing devices more affordable directly supports educational objectives by equipping students and first-time buyers with essential tools for learning and digital literacy.
Services Division Growth and Economic Enablement
The Services division has become a critical driver of revenue and a stabilizing force against hardware market volatility, fostering economic growth and digital participation.
Financial Performance and Ecosystem Monetization
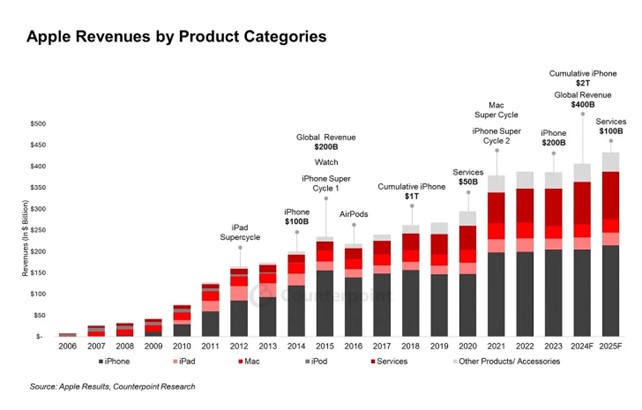
- In Q2 2025, Services revenue reached $26.65 billion, a 12% year-over-year increase, now constituting 28% of total company revenue.
- Growth is primarily driven by Apple Pay, iCloud, and various subscription services, which leverage the company’s extensive installed user base.
Contribution to Sustainable Economic Growth
- Contribution to SDG 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth): The App Store ecosystem provides a global platform for developers and entrepreneurs, creating jobs and fostering economic activity. Payment systems like Apple Pay facilitate secure digital commerce, further supporting small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
- Contribution to SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure): The expansion of services like iCloud builds upon and strengthens global digital infrastructure, providing essential tools for businesses and individuals.
Navigating Regulatory and Ethical AI Challenges
Apple faces significant regulatory scrutiny and intense competition in the field of artificial intelligence. Its response to these challenges reflects a strategic focus on user privacy and institutional integrity.
Regulatory Compliance and Fair Competition
- The company is addressing an antitrust case from the U.S. Department of Justice and enforcement actions under the EU’s Digital Markets Act (DMA), including a €500 million fine for “anti-steering” practices.
- Contribution to SDG 16 (Peace, Justice and Strong Institutions): By engaging with regulatory bodies and adapting its business practices to comply with legal frameworks, Apple contributes to the development of accountable and transparent institutions governing the digital economy.
A Privacy-Centric Approach to Artificial Intelligence
- Apple’s strategy prioritizes on-device processing for AI tasks to protect user data, differentiating it from competitors reliant on large-scale cloud-based models.
- Potential collaborations, such as with Alibaba’s Qwen3 AI, indicate a hybrid approach to remain competitive while upholding privacy principles.
- Contribution to SDG 16: This focus on privacy is a direct contribution to protecting fundamental freedoms in the digital age, a key target within SDG 16.
Strategic Supply Chain Management and Global Partnerships
Apple’s “China Plus One” supply chain strategy is a proactive measure to mitigate geopolitical risks and enhance operational resilience, with significant implications for global economic development.
Diversification and Resilience
- The company is actively shifting production, with a target of moving 15% of iPhone manufacturing to India and Vietnam.
- This diversification reduces dependency on a single region, mitigating risks from trade tensions and tariffs, and aligns with principles of building resilient infrastructure under SDG 9.
Contribution to Global Economic Development
- Contribution to SDG 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth): By investing in manufacturing capabilities in India and Vietnam, Apple is directly fostering job creation, promoting industrialization, and contributing to economic growth in these nations.
- Contribution to SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production): A diversified supply chain allows for greater oversight and the potential to implement sustainable production practices across a wider geographic footprint.
Conclusion and Forward Outlook
Apple’s trajectory in 2025 is contingent on its successful execution across three core pillars, each with embedded connections to sustainable development.
- Sustainable Product Differentiation: Success depends on delivering innovative products like the iPhone 17 Air and M4 MacBook Air that are not only technologically superior but also more accessible and energy-efficient, aligning with SDGs 9, 10, and 12.
- Inclusive Services Momentum: Continued growth in the high-margin Services division is crucial for financial stability and for its role in enabling economic growth and digital participation, supporting SDG 8.
- Ethical and Regulatory Navigation: Proactive compliance with global regulations and a steadfast commitment to user privacy in AI development are essential for mitigating risk and reinforcing the company’s commitment to strong, just institutions under SDG 16.
For stakeholders, Apple’s long-term value creation is increasingly dependent on its ability to balance market leadership with a tangible commitment to sustainable and equitable business practices. The company’s robust financial position provides a foundation for navigating near-term challenges, but its continued success will be measured by its capacity to innovate responsibly and contribute positively to global development goals.
SDGs Addressed in the Article
SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
The article connects to SDG 8 by focusing on Apple’s economic performance, productivity, and innovation as drivers of growth. The discussion on revenue, market share, and strategic pricing reflects the goal of sustaining economic growth.
- Explanation: The article details Apple’s financial health, such as the Services division’s revenue hitting “$26.65 billion, a 12% year-over-year increase,” and its role in the company’s overall economic stability. The strategy to drive “higher average selling prices (ASPs) and boost replacement rates by 10–15% in 2025” directly relates to achieving higher levels of economic productivity. Furthermore, shifting production to India and Vietnam contributes to economic activity in those nations.
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
This is a central theme of the article. It extensively covers Apple’s commitment to technological innovation, research and development, and building resilient infrastructure through supply chain diversification.
- Explanation: The text is replete with examples of innovation, including the “iPhone 17 Air” with its “advanced A19 chip, Wi-Fi 7 support, and AI-enhanced features,” and the “M4 MacBook Air” with a “20–35% performance boost.” The “China Plus One” strategy, which involves “shifting 15% of iPhone production to India and Vietnam,” is a direct example of building resilient infrastructure and promoting industrialization in developing countries.
SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
The article touches upon SDG 12 through its mention of supply chain diversification, which is framed as a move towards more sustainable and resilient production patterns.
- Explanation: The article explicitly states that Apple’s strategy to diversify its supply chain away from China “not only stabilizes margins but also aligns with global ESG trends.” This alignment with Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) trends implies a move towards more responsible and sustainable production patterns, a core concept of SDG 12.
SDG 16: Peace, Justice and Strong Institutions
The article addresses SDG 16 by highlighting the complex regulatory landscape Apple must navigate, which involves legal challenges and the enforcement of laws by strong national and international institutions.
- Explanation: The text details several legal and regulatory challenges, such as the “U.S. Department of Justice’s antitrust case,” the “EU’s Digital Markets Act enforcement,” and “French investigations into privacy tools.” The mention of the “EU’s €500 million fine for breaching ‘anti-steering’ rules” is a clear example of institutions enforcing laws to ensure corporate accountability.
SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals
The article alludes to SDG 17 through its discussion of strategic collaborations that are crucial for Apple’s future, particularly in the field of AI and manufacturing.
- Explanation: The article mentions a “rumored collaboration with Alibaba’s Qwen3 AI” as a way for Apple to mitigate its gap in generative AI. This represents a private-private partnership to achieve a technological goal. Additionally, the “China Plus One” strategy inherently relies on establishing manufacturing partnerships in India and Vietnam.
Identified Targets
SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
- Target 8.2: Achieve higher levels of economic productivity through diversification, technological upgrading and innovation.
- Evidence: The article’s focus on the “M4 MacBook Air” with its “20–35% performance boost” and the development of the “advanced A19 chip” and “AI-enhanced features” directly supports the goal of achieving productivity through technological upgrading and innovation.
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
- Target 9.2: Promote inclusive and sustainable industrialization.
- Evidence: The strategy of “shifting 15% of iPhone production to India and Vietnam” contributes to the industrialization and economic infrastructure of those developing countries.
- Target 9.5: Enhance scientific research, upgrade the technological capabilities of industrial sectors…encouraging innovation.
- Evidence: The entire article is a testament to this target, detailing how Apple’s R&D efforts are yielding innovations like the “iPhone 17 Air,” “M4 MacBook Air,” and “Apple Intelligence” to maintain a competitive edge. The text notes that Services revenue is used to “fund R&D in AI and other innovations.”
- Target 9.b: Support domestic technology development, research and innovation in developing countries.
- Evidence: By moving parts of its advanced manufacturing supply chain to India and Vietnam, Apple indirectly supports the development of technological capabilities in those countries.
SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
- Target 12.a: Support developing countries to strengthen their scientific and technological capacity to move towards more sustainable patterns of consumption and production.
- Evidence: The “China Plus One” strategy, which shifts advanced manufacturing to India and Vietnam, helps build the technological capacity in these nations for production that the article notes “aligns with global ESG trends.”
SDG 16: Peace, Justice and Strong Institutions
- Target 16.3: Promote the rule of law at the national and international levels.
- Evidence: The article discusses Apple’s need for “Compliance with antitrust rulings” from institutions like the U.S. Department of Justice and the EU, which demonstrates the application of the rule of law to multinational corporations.
- Target 16.6: Develop effective, accountable and transparent institutions at all levels.
- Evidence: The enforcement actions described, such as the “EU’s Digital Markets Act enforcement” and the resulting “€500 million fine,” are examples of institutional mechanisms designed to hold powerful entities like Apple accountable for their practices.
SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals
- Target 17.17: Encourage and promote effective public, public-private and civil society partnerships.
- Evidence: The “rumored collaboration with Alibaba’s Qwen3 AI” is a clear example of a private-private partnership aimed at advancing technology and market position.
Implied Indicators
Indicators for SDG 8 & 9
- Revenue from a specific sector: “In Q2 2025, Services revenue hit $26.65 billion, a 12% year-over-year increase.” This measures economic performance and diversification.
- Growth in shipments: A “21.4% year-over-year surge in Mac shipments” serves as an indicator of market demand and production output.
- Investment in R&D: While no specific number is given, the article implies this is a key indicator, stating that Services growth will “fund R&D in AI and other innovations.”
Indicators for SDG 9 & 12
- Proportion of production shifted to new regions: “shifting 15% of iPhone production to India and Vietnam” is a quantifiable indicator of supply chain diversification and building resilient infrastructure.
Indicators for SDG 16
- Number and value of regulatory fines: The “EU’s €500 million fine” is a specific indicator of the enforcement of laws and regulations against a corporation.
- Number of antitrust cases or investigations: The mention of the “U.S. Department of Justice’s antitrust case” and “French investigations” serves as an indicator of institutional oversight and the promotion of justice.
Indicators for SDG 17
- Number of strategic partnerships: The “rumored collaboration with Alibaba’s Qwen3 AI” is an indicator of partnership formation to achieve strategic goals.
Summary of Findings
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth | 8.2: Achieve higher levels of economic productivity through diversification, technological upgrading and innovation. |
|
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure |
9.2: Promote inclusive and sustainable industrialization. 9.5: Enhance scientific research, upgrade technological capabilities, and encourage innovation. 9.b: Support domestic technology development in developing countries. |
|
| SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production | 12.a: Support developing countries to strengthen their scientific and technological capacity for sustainable production. |
|
| SDG 16: Peace, Justice and Strong Institutions |
16.3: Promote the rule of law. 16.6: Develop effective, accountable and transparent institutions. |
|
| SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals | 17.17: Encourage and promote effective public-private and civil society partnerships. |
|
Source: ainvest.com

What is Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0












































































