Tuberculosis drug development; fluoroquinolone structural tailoring – Nature
Report on Tuberculosis Drug Development: Emphasizing Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
Introduction
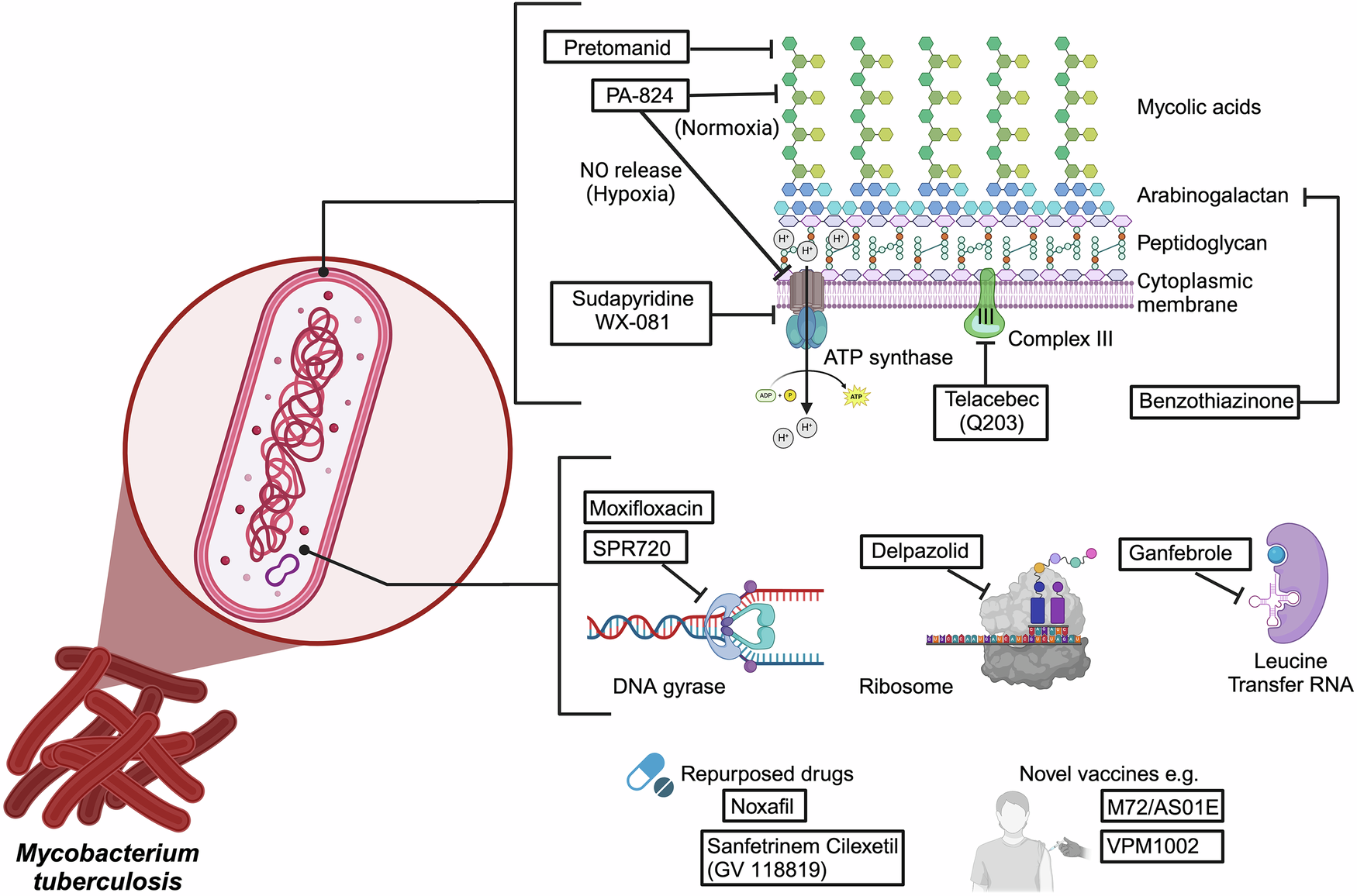
Tuberculosis (TB) remains a significant global health challenge, caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb). Transmission occurs via airborne particles expelled by infected individuals, posing a high risk of infection to new hosts. Despite advances in medicine, TB continues to be a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, exacerbated by the rise of multidrug-resistant (MDR) strains of Mtb. Addressing TB aligns closely with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goal 3 (SDG 3) — ensuring healthy lives and promoting well-being for all at all ages.
Challenges in Tuberculosis Control
- Multidrug Resistance: The emergence of MDR-TB strains complicates treatment and control efforts.
- Diagnosis and Prophylaxis: There is a critical need for effective diagnostic methods and preventive measures.
- Pharmacological Therapies: Development of new drugs is essential to overcome resistance and improve treatment outcomes.
Role of Fluoroquinolones in TB Treatment
Fluoroquinolones (FQs) are synthetic broad-spectrum antibiotics effective against Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria, including M. tuberculosis. Their significance in managing drug-resistant TB highlights their contribution to SDG 3 by combating infectious diseases.
Generations and Structural Modifications
- Four generations of fluoroquinolones have been developed, each with enhanced antibacterial properties.
- Structural modifications have improved tissue penetration and reduced side effects.
- These advancements address bacterial resistance, supporting the goal of sustainable health interventions.
Current Research Trends
Recent research focuses on novel synthetic approaches to fluoroquinolones, aiming to tackle the global issue of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. This innovation supports SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure) by fostering research and development in health technologies.
Implications for Sustainable Development Goals
- SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-being): Effective TB control reduces disease burden and mortality, improving population health.
- SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure): Advances in drug synthesis and development promote innovation in healthcare.
- SDG 10 (Reduced Inequalities): Improved TB treatments can reduce health disparities, particularly in vulnerable populations.
- SDG 17 (Partnerships for the Goals): Collaborative research and knowledge sharing are essential for global TB eradication efforts.
Conclusion
The ongoing development and structural tailoring of fluoroquinolones represent a critical strategy in the fight against tuberculosis, especially multidrug-resistant forms. These efforts contribute significantly to achieving the Sustainable Development Goals by promoting health, innovation, and equity worldwide. Continued investment in research, diagnosis, and treatment is imperative to control TB and improve global health outcomes.
1. Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) Addressed or Connected
- SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being
- The article focuses on tuberculosis (TB), a major infectious disease causing morbidity and mortality worldwide.
- It discusses diagnosis, prophylaxis, and new pharmacological therapies to control TB, including drug-resistant strains.
- SDG 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure
- The article highlights research and development of new fluoroquinolone antibiotics and synthetic approaches to combat multidrug-resistant TB.
- SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals
- The article references global strategies and reports by the World Health Organization (WHO), indicating international collaboration in TB control.
2. Specific Targets Under Those SDGs Identified
- SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being
- Target 3.3: By 2030, end the epidemics of AIDS, tuberculosis, malaria and neglected tropical diseases and combat hepatitis, water-borne diseases and other communicable diseases.
- Target 3.b: Support the research and development of vaccines and medicines for the communicable and non-communicable diseases that primarily affect developing countries.
- SDG 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure
- Target 9.5: Enhance scientific research, upgrade the technological capabilities of industrial sectors, including pharmaceutical research and development.
- SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals
- Target 17.6: Enhance North-South, South-South and triangular regional and international cooperation on and access to science, technology and innovation.
3. Indicators Mentioned or Implied to Measure Progress
- Incidence and Mortality Rates of Tuberculosis
- The article mentions TB as a major cause of morbidity and mortality, implying the use of incidence and mortality rates as indicators to measure progress in TB control (related to Target 3.3).
- Prevalence of Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis (MDR-TB)
- The emergence of multidrug-resistant strains of Mtb is highlighted, implying monitoring the prevalence of MDR-TB as an indicator.
- Development and Availability of New Medicines
- The article discusses new fluoroquinolones and pharmacological therapies, implying indicators related to the number of new TB drugs developed and approved (related to Target 3.b and 9.5).
- Research and Innovation Outputs
- The focus on synthetic approaches and drug development implies indicators such as research publications, patents, and clinical trials related to TB drugs.
- Global Cooperation and Implementation of Strategies
- References to WHO reports and strategies imply indicators measuring international cooperation effectiveness and implementation of global TB control programs (related to Target 17.6).
4. Table of SDGs, Targets and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being |
|
|
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure |
|
|
| SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals |
|
|
Source: nature.com








