CNC Milling Machines Market Accelerates with Industry 4.0 Adoption and Smart Manufacturing Advancements – openPR.com
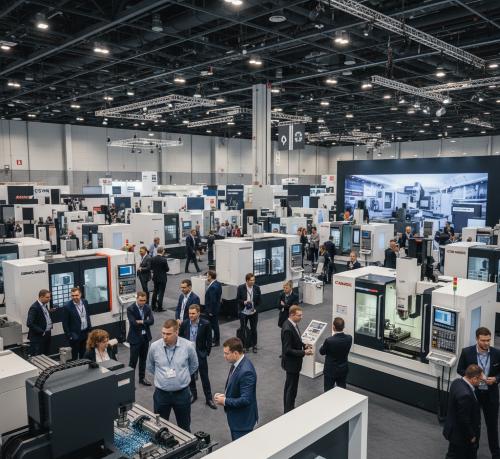

Global CNC Milling Machines Market: A Sustainable Development Perspective
Market Overview and Projections
The Global CNC (Computer Numerical Control) Milling Machines Market was valued at US$83.09 billion in 2024. It is projected to reach US$103.92 billion by 2032, demonstrating a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 2.99% during the 2025-2032 forecast period. This growth reflects the market’s critical role in advancing industrial capabilities and supporting global sustainability objectives.
CNC milling machines are integral to modern manufacturing, enabling high-precision, efficient, and consistent production across vital sectors such as automotive, aerospace, medical, and energy. The market’s expansion is closely linked to the global push for automation and Industry 4.0, which aligns with several United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
Contribution to Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
The evolution of the CNC milling machines market is a significant contributor to achieving key SDGs:
- SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure): By providing the foundational technology for smart manufacturing, CNC machines build resilient infrastructure, promote inclusive and sustainable industrialization, and foster innovation.
- SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production): Advanced CNC systems promote resource efficiency by minimizing material waste through high-precision machining. The integration of energy-efficient components and smart power management supports sustainable production patterns.
- SDG 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy): The development of energy-efficient drives and eco-friendly machining practices contributes to reducing the carbon footprint of industrial operations.
- SDG 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth): The market’s growth stimulates economic productivity and supports the creation of high-skilled jobs in advanced manufacturing sectors worldwide.
Key Growth Drivers Aligned with SDGs
The market’s robust growth is propelled by several factors that directly support sustainable development:
- Industrial Automation and Smart Manufacturing: The increasing integration of CNC milling systems into modern production lines enhances industrial efficiency and technological capability, a core target of SDG 9.
- Demand for Precision Engineering: Sectors like aerospace and medical devices require high-tolerance components. CNC machines meet these stringent quality requirements, reducing defects and material waste, thereby advancing SDG 12.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations such as AI-based predictive maintenance and cloud-connected systems improve operational uptime and productivity. This fosters technological upgrading under SDG 9 while reducing resource consumption.
- Emphasis on Sustainability: A primary driver is the industry’s shift towards sustainable practices. Modern CNC systems with energy-efficient drives and intelligent power management directly support SDG 7 and SDG 12 by reducing energy consumption and carbon emissions.
- Flexible and Customized Production: The rise of mass customization necessitates flexible CNC machines capable of quick setups for small-batch production. This model reduces overproduction and waste, aligning with the principles of responsible consumption (SDG 12).
Recent Developments in Sustainable and Innovative Manufacturing
United States
- June 2025: Haas Automation Inc. announced a manufacturing plant expansion to meet rising domestic demand, reinforcing industrial infrastructure and promoting local economic growth (SDG 8 & SDG 9).
- Early 2025: Hurco Companies, Inc. launched 5-axis CNC machines with AI-assisted controls, an innovation that enhances precision and reduces cycle times, contributing to resource efficiency (SDG 9 & SDG 12).
Japan
- 2025: Yamazaki Mazak Corporation introduced hybrid CNC machines combining additive and subtractive manufacturing. This technology fosters innovation and resource efficiency, particularly in high-value sectors (SDG 9 & SDG 12).
- 2025: Okuma Corporation announced strategic investments in sustainable and smart machining centers, directly targeting the development of carbon-neutral production facilities in line with SDG 7 and SDG 12.
Market Segmentation Analysis
By Type
- Vertical Milling Machines
- Horizontal Milling Machines
- Universal Milling Machines
- Others (Gantry, 5-axis systems)
Multi-axis systems are gaining traction for their ability to produce complex components efficiently, reducing waste and energy use per part, which supports SDG 12.
By Axis Type
- 3-Axis
- 4-Axis
- 5-Axis
- Multi-Axis Machines
The growth in 5-axis machines highlights a move towards more efficient manufacturing processes that minimize setups and improve precision, contributing to sustainable industrialization (SDG 9).
By Application
- Automotive
- Aerospace & Defense
- Electronics
- Medical Devices
- Industrial Equipment
Growth in the aerospace and medical sectors underscores the need for high-quality, reliable components, which is essential for building resilient infrastructure and ensuring public well-being.
By Control Type
- Conventional CNC Systems
- AI-Integrated Smart CNC Systems
The emergence of AI-integrated systems is a key enabler of SDG 9, facilitating enhanced automation, data-driven process optimization, and predictive maintenance to ensure responsible production (SDG 12).
Regional Analysis: Fostering Sustainable Industrialization
North America
The region’s market is driven by advanced manufacturing sectors adopting Industry 4.0 technologies. Investments in automation and sustainable production methods accelerate progress towards SDG 9 and SDG 12.
Europe
With a strong focus on precision engineering and smart, energy-efficient solutions, Europe is a leader in sustainable manufacturing. Nations like Germany are pioneering green machining practices, aligning with SDG 7 and SDG 12.
Asia-Pacific
Dominating the global market, this region’s growth is fueled by rapid industrialization and government support for smart factories. This investment in modern infrastructure is a direct contribution to SDG 9.
South America
Market growth is supported by the modernization of industrial facilities. Investment in CNC technology enhances manufacturing efficiency and competitiveness, promoting sustained economic growth (SDG 8).
Middle East & Africa
The region is adopting CNC technologies as part of industrial diversification strategies. These initiatives support the development of resilient infrastructure and new economic sectors (SDG 9).
Key Industry Stakeholders
- GROB-WERKE GmbH & Co. KG
- FILL Gesellschaft m.b.H.
- Tirupati CNC Products
- DMG MORI
- DN SOLUTIONS
- Doosan Precision Engineering Ltd
- Hwacheon
- Makino Inc
- GF Machining Solutions Management SA
Analysis of Sustainable Development Goals in the Article
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
- SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure: This is the most prominent SDG in the article. The text focuses on the CNC Milling Machines Market, which is a core component of modern industrial infrastructure. It discusses advancements in manufacturing technology, industrial automation, the integration of Industry 4.0 and AI, and investments in upgrading production capabilities. The article highlights how these innovations are driving growth in key industrial sectors like automotive, aerospace, and electronics.
- SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production: The article directly addresses sustainability in manufacturing. It mentions a growing emphasis on “sustainable and smart machining centers,” “eco-friendly machining practices,” and the development of systems with “energy-efficient drives and smart power management.” These efforts are aimed at reducing material waste and carbon emissions, which aligns with the principles of responsible production.
- SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth: The article discusses the significant economic growth of the CNC Milling Machines Market, projecting an increase from US$83.09 billion in 2024 to US$103.92 billion by 2032. This growth signifies economic activity and investment. Furthermore, the article emphasizes how technological advancements like AI-based systems and 5-axis machines improve “operational efficiency,” “productivity,” and “reduce cycle times,” which are key factors in achieving higher levels of economic productivity.
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
- Target 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable. The article provides clear examples of this target in action. It describes how manufacturers are adopting modern CNC systems that “incorporate energy-efficient drives and smart power management.” A specific instance is Okuma Corporation’s strategic investment “to develop sustainable and smart machining centers aimed at carbon-neutral production facilities,” which directly supports the goal of retrofitting industries with cleaner and more environmentally sound technologies.
- Target 9.5: Enhance scientific research, upgrade the technological capabilities of industrial sectors. The article is replete with examples of technological upgrades and innovation. It mentions Hurco Companies, Inc. introducing “a new series of 5-axis CNC milling machines equipped with AI-assisted control systems” and Yamazaki Mazak Corporation launching “hybrid CNC milling machines combining additive and subtractive manufacturing.” These developments represent an enhancement of technological capabilities within the industrial sector.
- Target 12.2: Achieve the sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources. The article connects to this target through its discussion of “eco-friendly machining practices to reduce material waste.” By improving precision and efficiency, advanced CNC machines minimize the amount of raw material that is discarded during the production process, contributing to more efficient resource use.
- Target 8.2: Achieve higher levels of economic productivity through diversification, technological upgrading and innovation. The entire premise of the market’s growth is based on technological upgrading. The article states that advancements such as “AI-based predictive maintenance and cloud-connected CNC systems, are improving operational efficiency and uptime” and “enhancing productivity across manufacturing facilities.” This directly aligns with achieving higher economic productivity through innovation.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
- Indicator for Target 9.4: Progress can be measured by the adoption rate of sustainable technologies. The article implies this through Okuma Corporation’s investment in “carbon-neutral production facilities” and the general trend of manufacturers adopting “energy-efficient drives and smart power management.” The “Sustainability Outlook” section of the report mentioned in the article would likely contain data to track this.
- Indicator for Target 9.5: The introduction of new, advanced technologies serves as a direct indicator. The article provides specific examples, such as the launch of “AI-assisted control systems” and “hybrid CNC milling machines.” The market segmentation by “AI-Integrated Smart CNC Systems” also suggests that the adoption of these advanced systems is a measurable trend.
- Indicator for Target 12.2: An implied indicator is the reduction of industrial waste. The article states that a key driver is the adoption of “eco-friendly machining practices to reduce material waste.” Measuring the volume of material waste saved per unit produced using these new technologies would be a way to quantify progress.
- Indicator for Target 8.2: The article provides a clear economic indicator: the projected market growth at a “CAGR of 2.99%” from US$83.09 billion to US$103.92 billion. Additionally, operational improvements like “reduced cycle times” and enhanced “productivity,” which are mentioned as benefits of new CNC technologies, are measurable indicators of increased economic productivity.
4. Table of SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure | 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable, with increased resource-use efficiency and greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies. | Investment in and development of “sustainable and smart machining centers aimed at carbon-neutral production facilities”; Adoption of “energy-efficient drives and smart power management.” |
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure | 9.5: Enhance scientific research, upgrade the technological capabilities of industrial sectors in all countries. | Launch of new technologies like “AI-assisted control systems” and “hybrid CNC milling machines”; Growth of the “AI-Integrated Smart CNC Systems” market segment. |
| SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production | 12.2: By 2030, achieve the sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources. | Implementation of “eco-friendly machining practices to reduce material waste.” |
| SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth | 8.2: Achieve higher levels of economic productivity through diversification, technological upgrading and innovation. | Projected market growth (CAGR of 2.99%); Technological advancements leading to “reduced cycle times” and enhanced “productivity.” |
Source: openpr.com

What is Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0