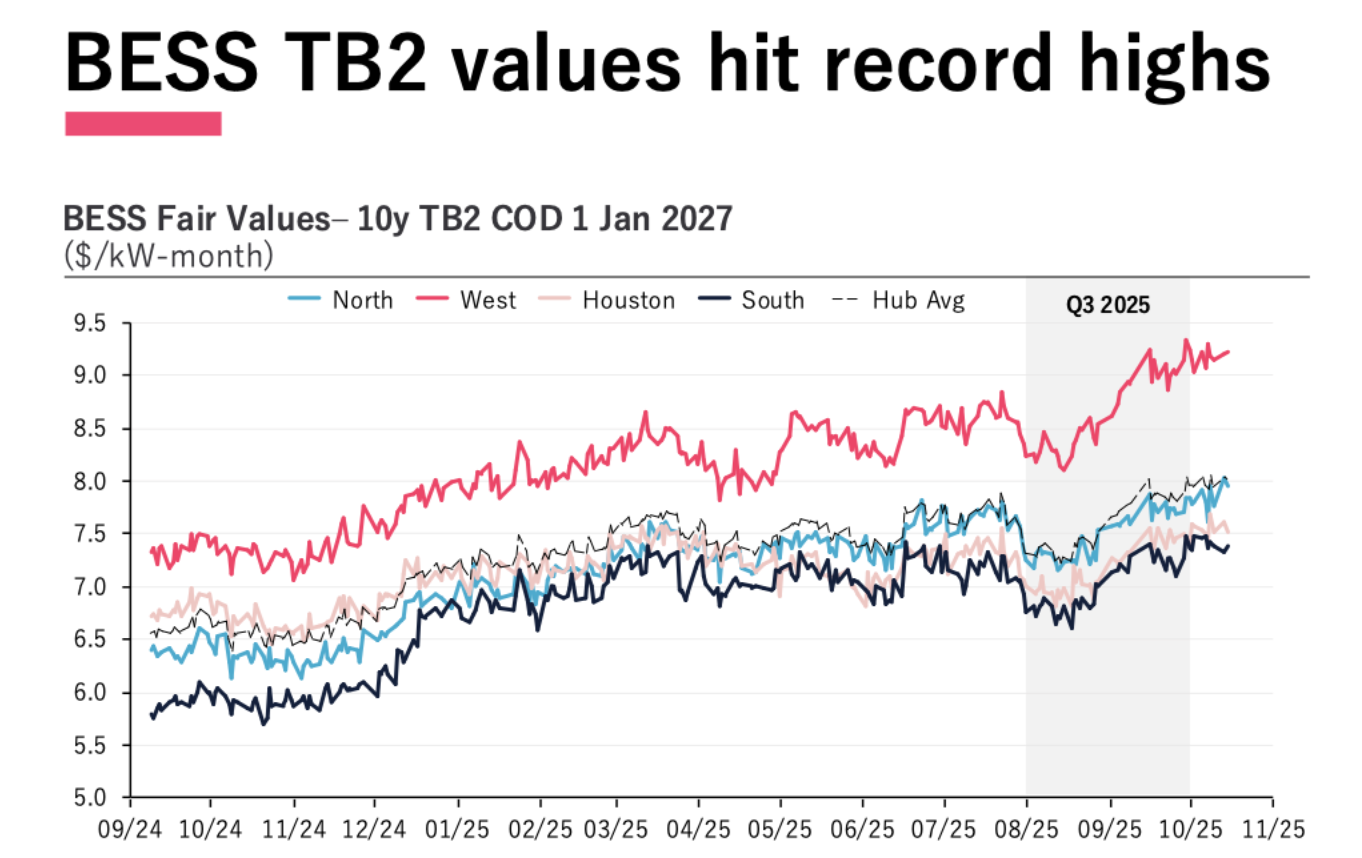
Behind Risen Energy’s integrated PV, storage and energy management solutions – PV Tech

Report on Risen Energy’s Integrated Solutions and Contribution to Sustainable Development Goals
Executive Summary
This report analyzes the contributions of Risen Energy’s integrated photovoltaic (PV), energy storage, and energy management solutions toward achieving the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The company’s focus on technological innovation, particularly in Heterojunction (HJT) module technology, directly supports global efforts to ensure sustainable energy access, combat climate change, and build resilient infrastructure.
Alignment with Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
Risen Energy’s strategic focus on integrated energy systems provides a multi-faceted approach to addressing several key SDGs.
SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
The core of Risen Energy’s mission is to expand access to affordable, reliable, and modern energy. This is achieved through:
- Integrated PV and Storage: Combining solar power generation with energy storage systems ensures a consistent and reliable power supply, overcoming the intermittency of solar energy. This is crucial for grid stability and off-grid communities.
- Advanced HJT Module Technology: Developments in HJT technology increase module efficiency and power output, lowering the Levelized Cost of Energy (LCOE) and making solar power more economically competitive with fossil fuels.
- Energy Management Systems: Intelligent management solutions optimize energy generation, storage, and consumption, maximizing efficiency and reducing waste, thereby enhancing affordability.
SDG 13: Climate Action
By providing clean energy alternatives, Risen Energy’s solutions are instrumental in taking urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts. The deployment of their solar and storage systems directly contributes to:
- Reducing global dependence on fossil fuels.
- Lowering greenhouse gas emissions from the power sector.
- Facilitating the transition to a low-carbon economy.
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure & SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
Risen Energy promotes the development of resilient, sustainable, and innovative energy infrastructure.
- Innovation in Manufacturing: The continuous improvement and scaling of HJT module technology represent significant industrial innovation (SDG 9), creating more efficient and durable products for sustainable infrastructure.
- Building Resilient Communities: Integrated PV and storage solutions support the development of decentralized energy grids, enhancing the energy security and resilience of cities and communities against climate-related disruptions (SDG 11).
- Smart Energy Management: The company’s energy management platforms are a key component of smart city infrastructure, enabling efficient resource management and contributing to more sustainable urban environments.
Technological Advancements: HJT Modules
Key Developments and Impact
Recent developments in Risen Energy’s HJT module technology are a primary driver of its contribution to the SDGs. The advantages of this technology include:
- Higher conversion efficiency, generating more power per unit area.
- Superior performance in low-light conditions and high temperatures.
- Lower degradation rates, ensuring long-term reliability and energy yield.
These technological enhancements make solar installations more productive and cost-effective, accelerating the adoption of clean energy in alignment with the objectives of SDG 7 and SDG 13.
Analysis of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in the Article
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
Based on the article’s title, “Behind Risen Energy’s integrated PV, storage and energy management solutions,” and its description, the following SDGs are addressed:
-
SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
This is the most directly relevant SDG. The article focuses on photovoltaic (PV) technology, energy storage, and energy management, which are all core components of providing clean, modern, and affordable energy.
-
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
The article discusses “recent developments in HJT module technology” and “integrated energy solutions.” This highlights innovation within the renewable energy industry and the development of sustainable and resilient energy infrastructure.
-
SDG 13: Climate Action
The development and deployment of solar PV and energy storage solutions are critical strategies for mitigating climate change by reducing dependence on fossil fuels and lowering greenhouse gas emissions. The technologies discussed are a direct response to the need for climate action.
-
SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
Integrated energy solutions, particularly those combining solar generation with storage, contribute to creating more sustainable and resilient energy systems for communities, which is essential for sustainable urban development.
-
SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
The shift towards renewable energy sources like solar PV is a fundamental aspect of establishing sustainable patterns of production. Furthermore, the mention of “energy management solutions” directly relates to promoting resource and energy efficiency.
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
The article’s focus on advanced solar technology and integrated systems points to several specific SDG targets:
-
SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
- Target 7.2: “By 2030, increase substantially the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix.” The article’s entire subject is solar PV technology, a key renewable energy source, and its advancement contributes directly to this target.
- Target 7.a: “By 2030, enhance international cooperation to facilitate access to clean energy research and technology… and promote investment in energy infrastructure and clean energy technology.” The discussion of “recent developments in HJT module technology” by a company like Risen Energy exemplifies the promotion and advancement of clean energy technology.
-
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
- Target 9.4: “By 2030, upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable, with increased resource-use efficiency and greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies…” The development of “integrated PV, storage and energy management solutions” is a direct contribution to upgrading energy infrastructure with clean and efficient technology.
-
SDG 13: Climate Action
- Target 13.2: “Integrate climate change measures into national policies, strategies and planning.” The technologies discussed in the article are the types of solutions that are integrated into national and corporate strategies to combat climate change.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
The article does not provide explicit numerical data, but it implies indicators that are used to measure progress towards the identified targets:
-
For Target 7.2 (Increase renewable energy share):
- Implied Indicator: The article’s focus on the production and technological advancement of solar PV modules implies progress related to Indicator 7.2.1: Renewable energy share in the total final energy consumption. The availability of more efficient and integrated solutions, as discussed, is a driver for increasing this share.
-
For Target 9.4 (Upgrade infrastructure with clean technologies):
- Implied Indicator: The mention of “recent developments in HJT module technology” serves as a qualitative indicator of innovation and technological improvement. This relates to the goal of adopting cleaner technologies and can be quantitatively measured by Indicator 9.4.1: CO2 emission per unit of value added. Advanced PV solutions directly help in reducing this metric.
-
For Target 7.a (Promote investment in clean energy technology):
- Implied Indicator: The article itself, by reporting on a company’s “integrated energy solutions,” points to activity and investment in the clean energy sector. This relates to Indicator 7.a.1: International financial flows to developing countries in support of clean energy research and development and renewable energy production. The development of such technologies is a prerequisite for these financial flows and investments.
4. Table of SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators (Implied from the article) |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy | 7.2: Increase substantially the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix. | 7.2.1: The development of “integrated PV, storage and energy management solutions” contributes to the renewable energy share in total final energy consumption. |
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure | 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable… with greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies. | 9.4.1: “Recent developments in HJT module technology” imply progress in creating cleaner technologies that reduce CO2 emissions per unit of value added. |
| SDG 13: Climate Action | 13.2: Integrate climate change measures into national policies, strategies and planning. | The availability of advanced PV and storage solutions enables the integration of climate mitigation measures into policy and action plans. |
Source: pv-tech.org

What is Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0