Emergency Mental Health Services – Market.us
Report Overview
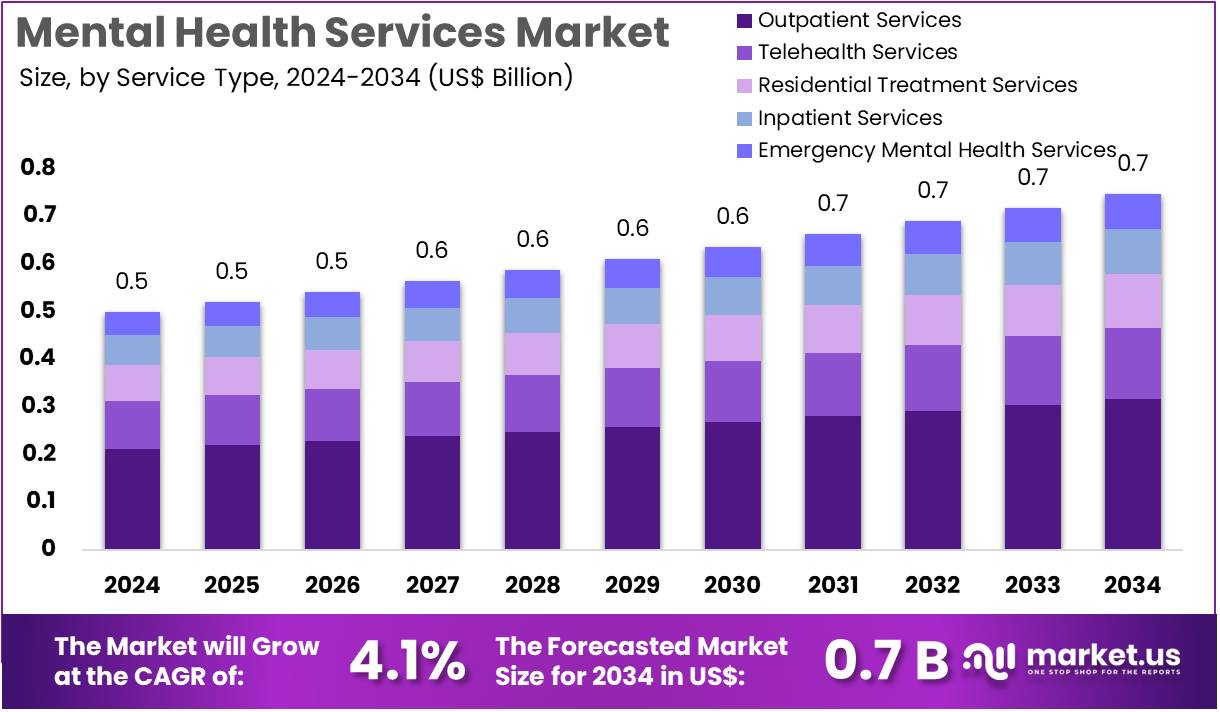
The Mental Health Services Market is projected to grow from US$ 0.5 billion in 2024 to approximately US$ 0.7 billion by 2034, exhibiting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.1% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. This growth aligns closely with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being, by enhancing access to mental health care globally.
Increasing awareness of mental health issues and the rising prevalence of conditions such as depression, anxiety, and stress are key drivers of market expansion. The reduction of stigma surrounding mental health encourages more individuals to seek care, supporting SDG 3’s target of promoting mental health and well-being for all ages.
Advancements in telehealth technologies have improved accessibility, especially for remote populations, contributing to SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure. Initiatives like the establishment of new behavioral health hospitals, such as the 96-bed facility planned by Acadia Healthcare and Nebraska Methodist Health System in Iowa, further enhance service availability and support equitable health services.
Key Takeaways
- Market revenue reached US$ 0.5 billion in 2024, with a forecasted CAGR of 4.1%, expected to attain US$ 0.7 billion by 2034.
- Outpatient services dominate the service type segment with a 42.3% market share in 2023, reflecting a preference for accessible and flexible care.
- Hospitals and clinics represent the largest end-user segment, holding 48.6% of the market share, emphasizing institutional roles in mental health service delivery.
- North America leads the market with a 38.5% share in 2023, highlighting regional advancements in mental health awareness and infrastructure.
Service Type Analysis
Outpatient services are the leading segment, accounting for 42.3% of the market share. This trend supports SDG 3 by providing less invasive, cost-effective, and flexible mental health care options that improve patient access and outcomes. The growth in outpatient services is driven by increased recognition of mental health importance and the diminishing stigma associated with seeking treatment.
End-User Analysis
Hospitals and clinics constitute the largest end-user group with a 48.6% market share. These institutions provide comprehensive mental health services, including emergency care, inpatient treatment, and long-term management, aligning with SDG 3’s objective to ensure healthy lives and promote well-being. Expansion of mental health departments within hospitals enhances service quality and accessibility, addressing the growing global mental health burden.
Key Market Segments
By Service Type
- Outpatient Services
- Telehealth Services
- Residential Treatment Services
- Inpatient Services
- Emergency Mental Health Services
By End-User
- Hospitals & Clinics
- Home Healthcare
- Educational Institutions
- Corporate Sector
- Community Centers
Drivers
Increasing Prevalence of Mental Health Conditions
The global rise in mental health disorders, including depression and anxiety, is a primary market driver. Approximately one in eight people worldwide live with a mental disorder, according to WHO 2024 data, underscoring the urgent need for expanded mental health services. This trend supports SDG 3 by emphasizing universal access to mental health care and reducing disease burden.
In the United States, nearly 25% of adults reported experiencing mental illness in 2023, reflecting increased demand for therapeutic and support services.
Restraints
Shortage of Qualified Mental Health Professionals
A significant challenge is the shortage of trained mental health professionals, which limits service accessibility, especially in rural and underserved areas. Over one-third of the U.S. population resides in Mental Health Professional Shortage Areas, as reported by HRSA in 2024. Addressing this gap is essential to achieving SDG 3 targets related to health workforce strengthening and equitable healthcare access.
Opportunities
Expansion of Telehealth Services
Telehealth presents a major opportunity to enhance mental health service delivery by overcoming geographic and mobility barriers, thus promoting SDG 9 through innovation and infrastructure development. Programs like India’s National Tele Mental Health Programme (Tele MANAS) have demonstrated significant impact, handling over 1.8 million calls by early 2025, expanding mental health support across diverse populations.
Impact of Macroeconomic and Geopolitical Factors
Economic stability influences healthcare funding and insurance coverage, affecting mental health service accessibility. While steady global growth projected by the IMF supports investment in health systems, economic downturns may restrict resources, challenging SDG 3 progress.
Geopolitical events such as conflicts and refugee crises increase demand for mental health services, necessitating international cooperation aligned with SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals. Tariff policies affecting medical technology imports may impact operational costs but also encourage domestic innovation, supporting SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth.
Trends
Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) for Early Intervention
AI and machine learning are increasingly utilized for early detection, personalized treatment, and enhanced diagnostics in mental health care. These technologies contribute to SDG 3 by improving the quality and responsiveness of mental health services. AI applications analyze behavioral data to identify at-risk individuals, facilitating timely interventions and scalable support solutions.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America leads the market with a 38.5% share, driven by high public awareness, reduced stigma, and substantial government investment. The U.S. CDC reported increased prevalence of anxiety and depression symptoms in adults, highlighting the need for expanded services. Funding such as the US$ 8.1 billion SAMHSA budget in 2024 supports SDG 3 by enhancing mental health and substance use disorder services. Digital platforms like Teladoc Health’s BetterHelp segment generated over US$ 1 billion in 2024, illustrating the growing role of telehealth.
Asia Pacific
The Asia Pacific region is expected to register the highest CAGR, supported by urbanization, changing societal attitudes, and government initiatives. The OECD’s 2024 report notes mental and neurological conditions constitute a significant disease burden, emphasizing the need for expanded care aligned with SDG 3. Programs such as India’s Tele MANAS and China’s mental health policy enhancements demonstrate regional commitment to improving mental health infrastructure and access.
Key Regions and Countries
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Russia
- Netherlands
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- New Zealand
- Singapore
- Thailand
- Vietnam
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- South Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Leading companies in the mental health services market are adopting strategic initiatives to foster growth and innovation. These include expanding service portfolios, investing in automation and high-throughput technologies, and forming partnerships with biotechnology firms and research institutions. Such collaborations accelerate the integration of advanced therapies, supporting SDG 3 by enhancing treatment quality and accessibility.
Geographic expansion of facilities and distribution networks improves service delivery and reduces waiting times, promoting equitable access aligned with SDG 10: Reduced Inequalities.
Acadia Healthcare, a prominent U.S. player, operates a broad network of behavioral health facilities offering inpatient and outpatient services focused on patient-centered care, contributing significantly to nationwide mental health service availability.
Top Key Players
- Teladoc Health
- Talkspace
- Pfizer
- Lundbeck
- Johnson & Johnson
- Modern Health
- Headspace
- Bristol Myers Squibb
Recent Developments
- May 2024: Modern Health launched a new suite of services integrating physical and mental health care, advancing holistic wellness approaches consistent with SDG 3.
- September 2023: Headspace partnered with One Medical to combine mindfulness and meditation with primary care, enhancing preventive health and mental well-being.
1. Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) Addressed or Connected to the Issues Highlighted in the Article
- SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being
- The article focuses extensively on mental health services, addressing the increasing prevalence of mental health conditions such as depression, anxiety, and PTSD.
- It discusses expanding access to mental health care, integration of telehealth, and innovations in treatment, all contributing to ensuring healthy lives and promoting well-being for all ages.
- SDG 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure
- The article highlights the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and telehealth technologies in mental health services, fostering innovation in healthcare delivery.
- It also mentions the development of infrastructure such as new behavioral health hospitals and telehealth cells.
- SDG 10: Reduced Inequalities
- By emphasizing telehealth services and efforts to reach remote and underserved areas, the article addresses reducing inequalities in access to mental health care.
- SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals
- The article notes collaborations between healthcare providers, biotechnology firms, and research institutions to accelerate innovation and improve mental health services.
2. Specific Targets Under Those SDGs Identified Based on the Article’s Content
- Under SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being
- Target 3.4: By 2030, reduce by one third premature mortality from non-communicable diseases through prevention and treatment and promote mental health and well-being.
- Target 3.8: Achieve universal health coverage, including financial risk protection and access to quality essential health-care services, including mental health services.
- Target 3.c: Substantially increase health financing and recruitment, development, training, and retention of the health workforce in developing countries, including mental health professionals.
- Under SDG 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure
- Target 9.5: Enhance scientific research, upgrade the technological capabilities of health sectors, including the adoption of AI and telehealth technologies.
- Target 9.b: Support domestic technology development and innovation in healthcare infrastructure.
- Under SDG 10: Reduced Inequalities
- Target 10.2: Empower and promote the social, economic and political inclusion of all, including marginalized populations with limited access to mental health services.
- Under SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals
- Target 17.16: Enhance the global partnership for sustainable development, including multi-stakeholder partnerships in mental health innovation and service delivery.
3. Indicators Mentioned or Implied in the Article to Measure Progress Towards the Identified Targets
- Prevalence and Incidence Rates of Mental Health Conditions
- Statistics such as “one in eight people worldwide lives with a mental disorder” and percentages of adults experiencing anxiety or depression are indicators of mental health burden.
- Access to Mental Health Services
- Number and capacity of mental health facilities (e.g., new 96-bed behavioral health hospital in Iowa).
- Number of telehealth service users and tele-mental health calls handled (e.g., 1.8 million calls to Tele MANAS Cells).
- Market share percentages of service types and end-users indicating service availability and utilization.
- Health Workforce Availability
- Data on shortage of qualified mental health professionals, such as the population living in Mental Health Professional Shortage Areas (Mental Health HPSA).
- Financial Investment and Market Growth
- Budgets allocated to mental health services (e.g., US$ 8.1 billion SAMHSA budget).
- Market size and CAGR growth rates indicating expansion of mental health services.
- Technology Adoption Metrics
- Integration of AI and telehealth platforms, measured by usage rates and revenue generated (e.g., Teladoc Health’s US$ 1.04 billion revenue from virtual mental health services).
4. Table: SDGs, Targets and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being |
|
|
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure |
|
|
| SDG 10: Reduced Inequalities |
|
|
| SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals |
|
|
Source: market.us








