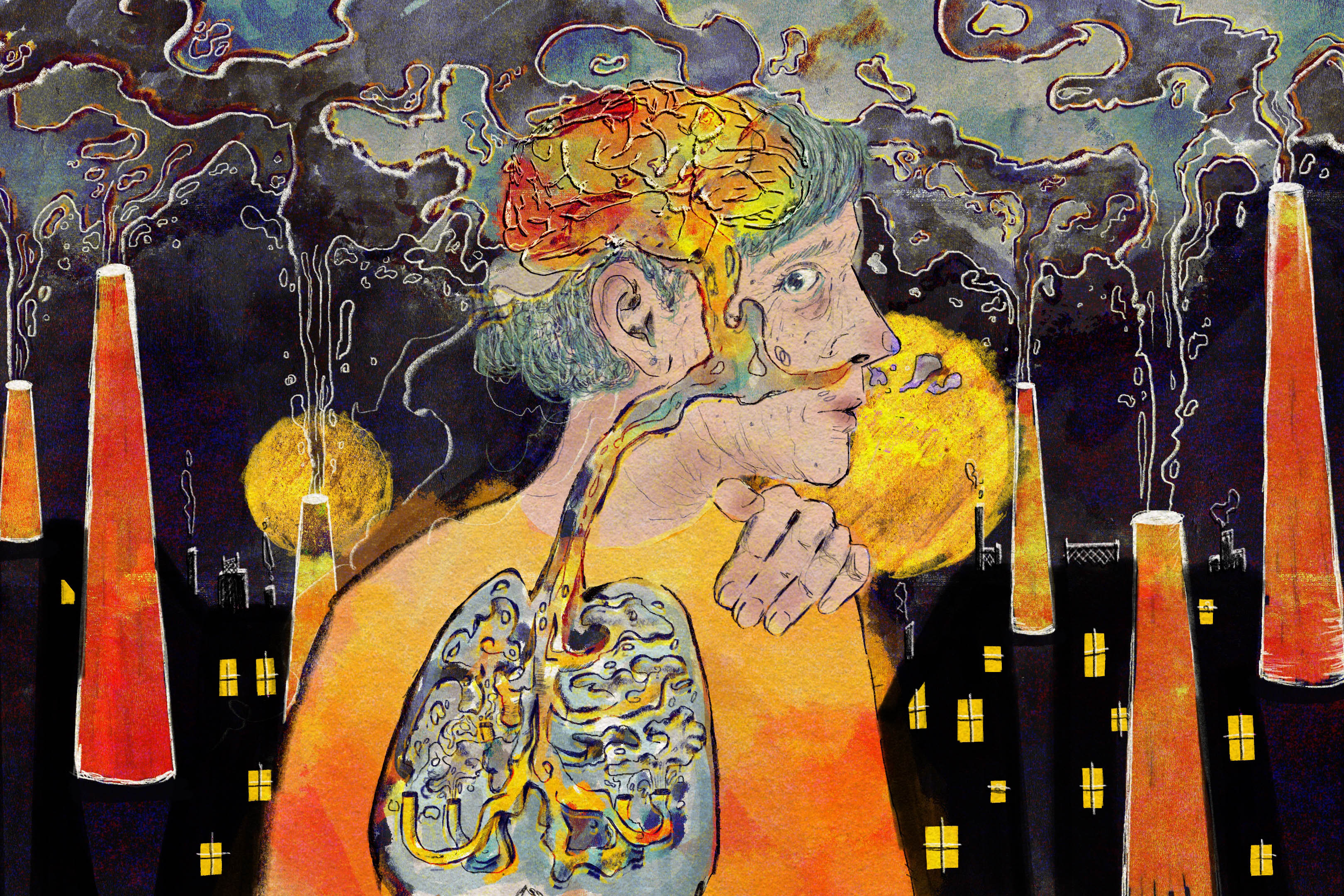
Heart Cancer Strikes Very Rarely. An Expert Reveals Why. – ScienceAlert
Report on the Infrequency of Primary Cardiac Malignancies and Implications for Sustainable Development Goals
This report examines the biological mechanisms contributing to the low incidence of primary heart cancer. The findings are contextualized within the framework of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-being) and SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure).
The Cellular Basis of Cancer and its Relation to Public Health (SDG 3)
Cancer is a non-communicable disease characterized by the uncontrolled division of cells, posing a significant global health challenge targeted by SDG 3. The process of cell division is normally regulated by molecular checkpoints. However, mutations in the genes that control this process, caused by random errors or exposure to carcinogens, can lead to cancer. The incidence of cancer varies significantly by tissue type. For instance, heart cancer affects approximately 3 in 10,000 people, whereas breast cancer is projected to affect 1 in 20 women. This disparity highlights the importance of understanding tissue-specific cancer resistance to advance the goals of SDG 3.
Protective Mechanisms of Cardiac Tissue
The heart possesses unique biological features that confer a high resistance to the development of primary tumors. These mechanisms are crucial for maintaining cardiovascular health, a key component of SDG 3.
- Limited Cell Division: The primary defense against cardiac cancer is the extremely low rate of cell division in the adult heart. Cell division declines dramatically after age 20, and less than 50% of heart cells are replaced over an average human lifespan. This limited proliferation reduces the opportunities for DNA replication errors and subsequent cancerous mutations.
- Anatomical Protection: The heart’s location within the thoracic cavity provides physical shielding from many environmental carcinogens, such as ultraviolet (UV) light and inhaled substances, which commonly affect organs like the skin and lungs. This protection aligns with the environmental health aspects of SDG 3.
The Nature and Treatment of Cardiac Cancers
Despite its resistance, the heart is not entirely immune to cancer. Understanding the nature of these rare tumors is essential for comprehensive cancer care as promoted by SDG 3.
- Metastatic Origin: Most cancers found in the heart are not primary tumors but are the result of metastasis, where cancer cells migrate from another part of the body.
- Aggressiveness and Treatment: When primary heart tumors do occur, they can be highly aggressive. Treatment protocols often involve surgery and chemotherapy. Successful patient outcomes depend on a holistic approach to care that includes palliative and integrative medicine, which focuses on relieving symptoms and addressing the overall well-being of the patient, in line with the principles of SDG 3.
Research, Innovation, and Future Health Outcomes (SDG 9 & SDG 3)
Scientific investigation into the heart’s cellular dynamics is a driver of medical progress, reflecting the aims of SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure) to foster innovation for societal benefit. This research has profound implications for treating cardiovascular diseases, a leading cause of mortality worldwide.
- Informing Regenerative Medicine: Studying the limited division of heart cells helps scientists understand why the heart has a poor capacity for self-repair after injury, such as a heart attack.
- Driving Technological Advancement: Research in this field leverages and promotes new technologies, such as the reprogramming of blood cells into heart cells. These innovations allow for the creation of advanced disease models to study cardiac conditions and develop novel therapies.
- Pursuing Heart Regeneration: The ultimate objective of this research is to achieve heart regeneration. Success in this area would represent a significant breakthrough in treating heart disease and would directly contribute to SDG 3’s target of reducing premature mortality from non-communicable diseases.
Analysis of SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
The article primarily addresses issues related to the following Sustainable Development Goals:
- SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being: The entire article focuses on cancer, a major non-communicable disease (NCD). It discusses the biological mechanisms of the disease, its prevalence, treatment options, and the importance of medical research in improving health outcomes.
- SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure: The article highlights the crucial role of scientific research and technological innovation in understanding and treating diseases. It mentions the work of biologists, new technologies for creating disease models, and the development of new treatments, which are all central to this goal’s emphasis on enhancing scientific research.
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being
-
Target 3.4: By 2030, reduce by one-third premature mortality from non-communicable diseases through prevention and treatment and promote mental health and well-being.
- Explanation: The article is centered on cancer, a primary NCD. It discusses the severity of the disease (“can make a person sick, sometimes very seriously”) and mentions treatments like “surgery and chemotherapy” that help patients “survive longer,” directly aligning with the target of reducing mortality through treatment.
-
Target 3.b: Support the research and development of vaccines and medicines for the communicable and non-communicable diseases.
- Explanation: The author identifies as a “biologist who specializes in the blood vessels of the cardiovascular system” and explains how research provides critical insights. The text states, “Understanding why cancer doesn’t happen is just as important for developing new and better treatments as knowing why it does.” This directly supports the call for R&D into NCDs.
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
-
Target 9.5: Enhance scientific research, upgrade the technological capabilities of industrial sectors in all countries… encouraging innovation.
- Explanation: The article showcases the output of scientific research and technological advancement. It points to “New technologies, such as the ability to reprogram blood cells into heart cells,” which have allowed researchers to develop “new heart disease models to study and one day achieve heart regeneration.” This exemplifies the enhancement of scientific research and innovation for solving complex problems.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being
-
For Target 3.4: The article provides statistics that can serve as indicators for disease incidence, which is related to the broader goal of reducing mortality (Indicator 3.4.1: Mortality rate attributed to… cancer).
- Incidence Rate of Heart Cancer: “Studies show 3 in 10,000 people develop heart cancer.”
- Incidence Rate of Breast Cancer: “1 in 20 women are expected to develop breast cancer.”
- Treatment Efficacy: The statement that patients who received “surgery and chemotherapy… survived longer” is a qualitative indicator of progress in reducing mortality through treatment.
-
For Target 3.b: The article implies progress through the description of ongoing research activities.
- Qualitative Indicator of R&D: The article itself, authored by an “Associate Professor of Cardiothoracic Surgery and Bioengineering,” and its discussion of how “research into how heart cells divide helps scientists better understand” disease, serves as an indicator of active medical research.
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
-
For Target 9.5: The article points to specific technological advancements as indicators of innovation.
- Indicator of Technological Advancement: The mention of “New technologies, such as the ability to reprogram blood cells into heart cells” and the development of “new heart disease models” are concrete examples of innovation resulting from scientific research.
4. Table of SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being | 3.4: Reduce by one-third premature mortality from non-communicable diseases through prevention and treatment. |
|
| SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being | 3.b: Support the research and development of vaccines and medicines for non-communicable diseases. |
|
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure | 9.5: Enhance scientific research and encourage innovation. |
|
Source: sciencealert.com

What is Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0




























.jpg?#)