Housing infrastructure law expected to spur $2B in new development – WCAX
Report on Vermont’s Community Housing Infrastructure Program (CHIP) and its Alignment with Sustainable Development Goals
Program Overview
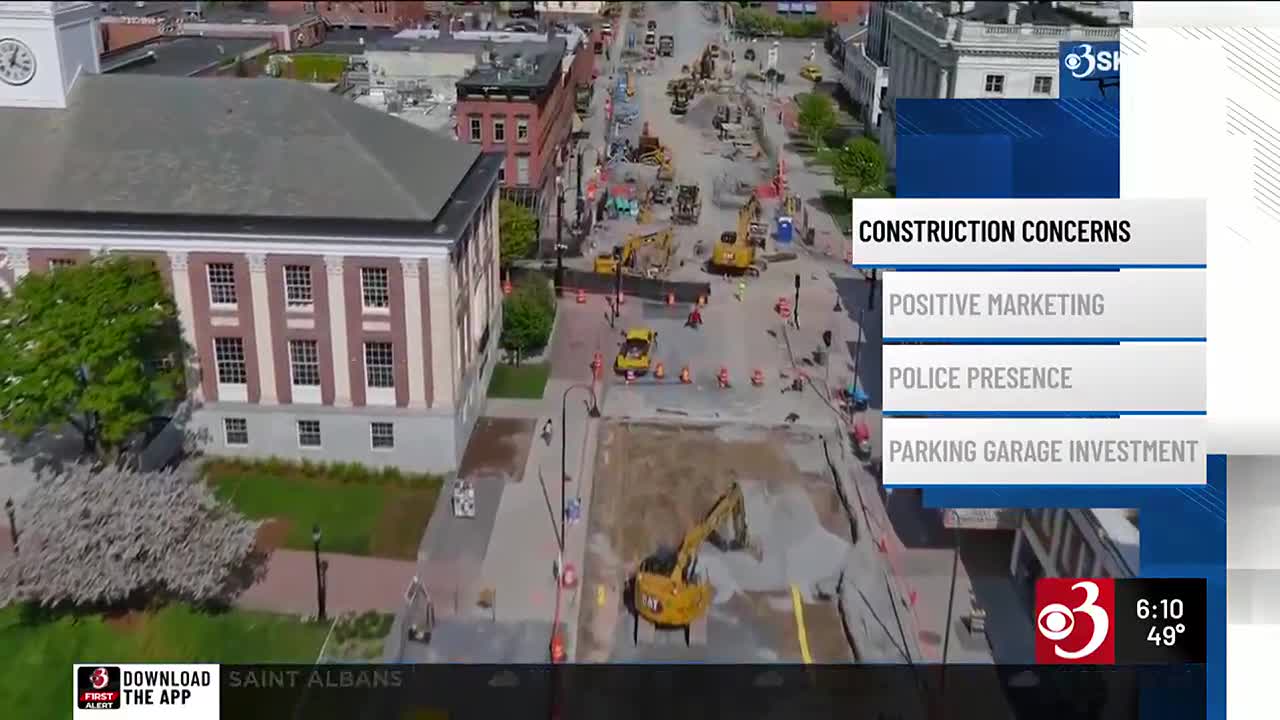
A new legislative initiative in Vermont, the Community Housing Infrastructure Program (CHIP), has been established to address the state’s housing shortage. The program is projected to stimulate approximately $2 billion in housing infrastructure development over the next decade.
- The core mechanism of CHIP involves providing tax incentives to developers for the construction of essential housing infrastructure.
- This strategy is designed to lower the overall cost of construction, thereby encouraging the development of new homes.
- A key feature of the program is its provision to empower smaller municipalities to participate in financing infrastructure projects.
Alignment with Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
The CHIP initiative directly supports the advancement of several United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) by tackling critical infrastructure and social equity challenges.
-
SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
- The program’s primary objective is to increase the availability of housing, directly contributing to Target 11.1, which aims to ensure access for all to adequate, safe, and affordable housing.
- By enabling infrastructure development, such as at the former Fairmont Speedway site, CHIP promotes the creation of inclusive and resilient human settlements.
-
SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
- Local business leaders have identified the housing deficit as a significant risk to the sustainability of Vermont’s economy.
- A lack of housing hinders the ability of companies to recruit essential personnel, thereby impeding productive employment and sustainable economic growth.
-
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
- CHIP represents a direct investment in developing quality, reliable, and sustainable infrastructure as outlined in Target 9.1.
- This infrastructure is foundational for supporting long-term economic development and enhancing the well-being of residents.
-
SDG 10: Reduced Inequalities
- The housing shortage disproportionately affects economic mobility and exacerbates inequality.
- By aiming to lower housing costs and increase supply, the program seeks to reduce the financial strain on families and promote greater economic inclusion.
Economic and Social Implications
The lack of sufficient housing infrastructure has been cited as a primary driver of several adverse socio-economic conditions within the state. These challenges, which the CHIP program aims to mitigate, include:
- Increased cost of living for residents.
- Significant financial strain on families.
- Limited economic mobility for the workforce.
- Difficulties for local industries in recruiting and retaining talent, including designers, engineers, and craftspeople.
Implementation and Future Outlook
State officials are moving forward with the program’s implementation, with the goal of opening the application process for developers by early next year. The initiative is poised to transform underutilized sites into productive residential areas, fostering community growth and sustainability in alignment with global development objectives.
SDGs Addressed or Connected to the Issues
-
SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
The article’s core subject is the “Community Housing Infrastructure Program” (CHIP), a new law designed to increase the housing supply in Vermont. This directly aligns with SDG 11, which aims to make cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient, and sustainable. The focus on building “new homes” and “housing infrastructure” is central to this goal.
-
SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
The article explicitly links the lack of housing to economic problems. A business leader is quoted saying the housing shortage “risks the sustainability of Vermont’s economy,” “limits economic mobility,” and “hinders our ability to recruit the next generation of designers, engineers, and craftspeople.” By addressing the housing crisis, the program supports sustained and inclusive economic growth.
-
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
The Vermont law is focused on spurring “$2-billion in housing infrastructure.” This directly relates to SDG 9, which calls for building resilient infrastructure to support economic development and human well-being. The program’s mechanism—giving tax breaks to developers to “build out housing infrastructure”—is a clear example of promoting infrastructure development.
Specific SDG Targets Identified
-
Target 11.1: Ensure access for all to adequate, safe and affordable housing and basic services.
The article highlights a “lack of housing” and a program designed to build “new homes.” The CHIP program aims to bring “down the cost of construction,” which is a step toward making housing more affordable and accessible for all, directly addressing the core of Target 11.1.
-
Target 9.1: Develop quality, reliable, sustainable and resilient infrastructure…to support economic development and human well-being.
The program is explicitly named the “Community Housing Infrastructure Program” and is intended to “spur $2-billion in housing infrastructure.” The article states this is necessary because the housing shortage “strains families” and risks the economy, linking the infrastructure development directly to supporting economic development and human well-being as outlined in Target 9.1.
-
Target 8.3: Promote development-oriented policies that support productive activities, decent job creation, entrepreneurship, creativity and innovation.
The article notes that the housing shortage hinders the ability of businesses to “recruit the next generation of designers, engineers, and craftspeople.” The new law is a development-oriented policy that, by easing the housing crisis, supports the productive activities of businesses like Hubbardton Forge and enables them to create and fill jobs.
-
Target 11.3: Enhance inclusive and sustainable urbanization and capacity for…sustainable human settlement planning.
The article mentions that the “CHIP program will also allow smaller towns to help finance infrastructure.” This provision enhances the capacity of smaller, potentially less-resourced communities to participate in sustainable planning and development, which is a key component of Target 11.3.
Indicators Mentioned or Implied
-
Financial Investment in Infrastructure
The article provides a clear, quantifiable indicator: the law is expected to “spur $2-billion in housing infrastructure over the next decade.” This serves as a direct indicator for measuring investment toward Target 9.1.
-
Number of New Housing Units
The primary goal of the program is to build “new homes.” While a specific number is not given, the number of housing units constructed as a result of the CHIP program is an implied primary indicator for measuring progress toward Target 11.1.
-
Cost of Construction and Cost of Living
The article states the program aims to bring “down the cost of construction” and that the current housing lack “drives up the cost of living.” Therefore, tracking changes in construction costs and the overall cost of living in Vermont would be implied indicators of the program’s success.
-
Workforce Recruitment and Economic Mobility
The article implies that success can be measured by economic outcomes. An improvement in the “ability to recruit the next generation of designers, engineers, and craftspeople” and an increase in “economic mobility” are qualitative and quantitative indicators linked to the success of the housing program, relevant to Target 8.3.
Summary Table of SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities | Target 11.1: Ensure access for all to adequate, safe and affordable housing and basic services. | Number of new homes built; Reduction in the cost of living. |
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure | Target 9.1: Develop quality, reliable, sustainable and resilient infrastructure to support economic development and human well-being. | $2-billion investment in housing infrastructure; Reduction in the cost of construction. |
| SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth | Target 8.3: Promote development-oriented policies that support productive activities and decent job creation. | Improved ability to recruit skilled workers; Increased economic mobility. |
| SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities | Target 11.3: Enhance inclusive and sustainable urbanization and capacity for sustainable human settlement planning. | Number of smaller towns participating in financing infrastructure. |
Source: wcax.com

What is Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0



































![Lancaster homeowner’s energy-efficient renovation sparks clash over historic preservation [Lancaster Watchdog] – LancasterOnline](https://bloximages.newyork1.vip.townnews.com/lancasteronline.com/content/tncms/assets/v3/editorial/9/ed/9ed03d32-c902-44d2-a461-78ad888eec38/69050b156baeb.image.png?resize=150,75#)











































