IFC and Becamex IDC Boost Vietnam’s Green Growth with Eco-Industrial Parks Initiative – AInvest
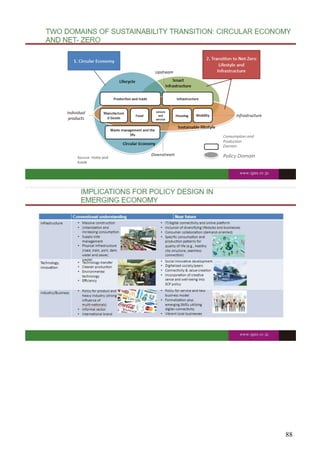
Report on the IFC-Becamex Partnership for Eco-Industrial Park Development in Vietnam
1.0 Strategic Partnership for Sustainable Industrialisation
The International Finance Corporation (IFC), in a strategic collaboration with Becamex IDC of Vietnam and VSIP of Singapore, has initiated a comprehensive assessment programme for eco-industrial parks (EIPs) across Vietnam. This partnership is a significant advancement in aligning the nation’s industrial development with global sustainability benchmarks and directly supports the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
This initiative exemplifies SDG 17 (Partnerships for the Goals) by leveraging international cooperation between a global financial institution, a leading domestic developer, and a regional partner to mobilise resources and technical expertise for sustainable development.
2.0 Programme Objectives and Direct Contributions to SDGs
The primary goal of the partnership is to establish a robust Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) framework for EIPs, thereby accelerating Vietnam’s transition to a green economy. The key objectives include:
- Developing Vietnam’s first Eco-Industrial Park model that complies with international standards.
- Strengthening ESG competencies to facilitate access to green financial resources.
- Enhancing Vietnam’s global competitiveness by attracting high-quality, sustainable investments.
- Reducing the environmental footprint of industrial zones through optimised resource management.
This programme makes direct contributions to several SDGs:
- SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure): By promoting sustainable industrialisation, upgrading infrastructure, and fostering innovation in resource efficiency, the EIP model is central to building resilient and sustainable industrial infrastructure.
- SDG 13 (Climate Action): A core focus is the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions within industrial parks, representing a tangible action to combat climate change.
- SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities): The integration of EIPs within urban and economic zones, such as Ho Chi Minh City, supports the development of inclusive, safe, and sustainable urban-industrial ecosystems.
- SDG 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth): The initiative is designed to attract high-value investments, which promotes sustained economic growth and the creation of higher-quality jobs.
3.0 Assessment and Implementation Framework
The IFC will utilise its Global Eco-Industrial Parks Assessment and Certification (GEIPAC) programme to guide the implementation. The process involves a structured approach to ensure alignment with international best practices.
3.1 Assessment Methodology
The GEIPAC framework will be applied as follows:
- Conduct preliminary assessments of up to five industrial parks.
- Evaluate park management and performance against international EIP standards.
- Identify specific strengths and gaps to provide actionable recommendations for improvement.
- Optimise park operations to enhance efficiency and reduce environmental impact, directly supporting SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production).
3.2 Scaling and National Impact
The collaboration aims to scale successful pilot models across key economic regions. This strategy aligns with national resolutions, including the establishment of Vietnam International Financial Centers, enhancing the capacity to mobilise resources for large-scale sustainable projects. The successful implementation will position Ho Chi Minh City as a model for sustainable urban-industrial development.
4.0 Financial Viability and Economic Competitiveness
The transition to EIP models presents a clear business case for sustainable investment.
- Investment and Savings: While the initial investment for an EIP is approximately 10% higher than for a traditional park, participating companies can expect annual savings of 2-3% on operational and business costs.
- Access to Green Finance: Strong ESG credentials, validated through the GEIPAC assessment, will improve access to green financing, a critical enabler for sustainable projects.
- Global Supply Chains: By reducing emissions and improving environmental performance, Vietnamese EIPs can enhance their position in global supply chains, attracting multinational corporations with strong sustainability mandates.
5.0 Advancing Sustainable Infrastructure
Eco-industrial parks serve as catalysts for broader sustainable infrastructure initiatives. As hubs for logistics and manufacturing, they are ideal environments for advancing green transportation. The development of EIPs will accelerate the transition to electric vehicles and other sustainable mobility solutions, further contributing to the objectives of SDG 9 and SDG 11 through integrated, sustainable transport systems.
6.0 Conclusion
The strategic alliance between the IFC and Becamex IDC marks a pivotal move towards embedding sustainability into Vietnam’s industrial core. By systematically implementing internationally recognised EIP standards, the programme directly advances multiple Sustainable Development Goals, including those related to industry, climate action, sustainable cities, and global partnerships. This initiative not only enhances Vietnam’s environmental responsibility but also strengthens its economic competitiveness, positioning the nation as a proactive participant in the global green transition.
Sustainable Development Goals Analysis
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
-
SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
The article connects to SDG 8 by focusing on enhancing Vietnam’s economic standing and job quality. The initiative aims to “attract high-quality investments and create better jobs,” promoting “inclusive growth” and reinforcing “Vietnam’s competitiveness on the global stage.” This aligns with the goal of achieving sustainable and inclusive economic growth.
-
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
This is a central theme. The article details a plan to “upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable” through the development of eco-industrial parks (EIPs). The collaboration focuses on “sustainable industrial development,” implementing “Vietnam’s first Eco-Industrial Park model,” and using “international standards” to facilitate access to green financing, directly addressing the goal of building resilient infrastructure and fostering sustainable industrialization.
-
SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
The project is set in “industrial and urban zones,” with a specific mention of making Ho Chi Minh City a “model for sustainable urban-industrial development.” The article also highlights the role of EIPs in accelerating “green transportation” and the “transition to electric vehicles,” which are key components of creating sustainable and inclusive cities.
-
SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
The EIP model promotes sustainable production patterns. The article states that these parks “optimize operations” and can “reduce operational expenses” by 2-3% annually. This implies more efficient use of resources and a reduction in waste, which are core principles of responsible production.
-
SDG 13: Climate Action
The article explicitly states that a critical role of eco-industrial parks is “reducing greenhouse gas emissions.” The entire initiative is framed within Vietnam’s pursuit of “green growth” and is designed to help the country become a “key player in the industrial green transition,” directly contributing to climate change mitigation efforts.
-
SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals
The article is a clear example of SDG 17 in action. It describes a multi-stakeholder partnership between an international organization (IFC), a Vietnamese developer (Becamex IDC), and a Singaporean developer (VSIP). This “strategic alliance” leverages “international collaboration and expert insights” to mobilize financial resources (“access to green financing”) and technical assistance for sustainable development.
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
-
Target 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable
The core of the article is the agreement to implement an “eco-industrial park (EIP) assessment programme” and establish “Vietnam’s first Eco-Industrial Park model.” This directly involves retrofitting industrial zones to be more sustainable, increasing resource efficiency, and adopting cleaner processes to meet “global standards.”
-
Target 13.2: Integrate climate change measures into national policies, strategies and planning
The partnership is described as being in “strategic alignment with national resolutions” and Vietnam’s overall pursuit of “green growth.” By implementing EIPs that focus on “reducing greenhouse gas emissions,” the initiative integrates climate action into regional and industrial planning.
-
Target 17.3: Mobilize additional financial resources for developing countries from multiple sources
A key aim of the initiative is to “facilitate broader access to green financing.” By establishing a robust ESG framework and meeting international standards, the project enhances the capacity of Vietnamese developers to “mobilize resources” and attract green investment for sustainable projects.
-
Target 8.2: Achieve higher levels of economic productivity through diversification, technological upgrading and innovation
The adoption of the EIP model, which is described as being about 10% more expensive upfront but yielding long-term savings, represents a technological and operational upgrade. This innovation is intended to “enhance ESG competencies” and “reinforce Vietnam’s competitiveness on the global stage.”
-
Target 11.6: Reduce the adverse per capita environmental impact of cities
By developing EIPs in “industrial and urban zones” like Ho Chi Minh City, the project aims to reduce negative environmental impacts, such as greenhouse gas emissions, and promote sustainable practices like “green transportation,” contributing to a lower environmental footprint for these urban areas.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
The article implies several quantitative and qualitative indicators that can be used to measure progress:
- Number of parks assessed: The article states that the IFC will conduct “preliminary assessments of up to five parks,” providing a clear, measurable output for the initial phase of the project.
- Reduction in operational costs: A specific financial indicator is mentioned: “annual savings of 2-3% on operations and business costs” for companies within the EIPs, which demonstrates financial viability and resource efficiency.
- Reduction in greenhouse gas emissions: While no specific percentage is given, the “reducing greenhouse gas emissions” is stated as a key role of the parks, making it a primary indicator of environmental performance.
- Establishment of an ESG framework: The creation of a “robust Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) framework” is a key deliverable that can be assessed for its comprehensiveness and implementation.
- Access to green financing: The success in mobilizing “green financial resources” can be measured by the amount of green investment attracted by the parks participating in the program.
- Job quality: Progress can be measured by tracking the “creation of better jobs,” which implies monitoring wages, working conditions, and skill development within the EIPs.
- Adoption of green transport: The “transition to electric vehicles and sustainable mobility solutions” within the parks serves as a tangible indicator of progress towards sustainable infrastructure.
4. Table of SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators Identified in the Article |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth | 8.2: Achieve higher levels of economic productivity through technological upgrading and innovation. |
|
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure | 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable. |
|
| SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities | 11.6: Reduce the adverse per capita environmental impact of cities. |
|
| SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production | 12.2: Achieve the sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources. |
|
| SDG 13: Climate Action | 13.2: Integrate climate change measures into national policies, strategies and planning. |
|
| SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals | 17.3: Mobilize additional financial resources for developing countries. |
|
Source: ainvest.com

What is Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0







































































_21.jpg?#)






