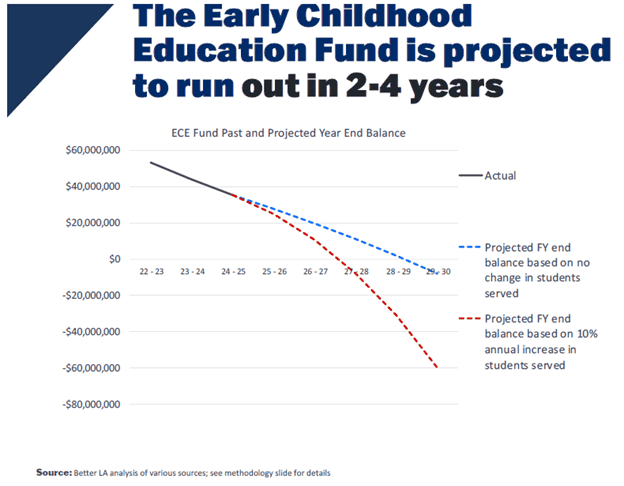
Lifelong Learning in 2025: How the World Became a Classroom (and Why That’s Good for Everyone) – Vocal

Lifelong Learning in 2025: A Report on Its Role in Sustainable Development

Introduction
Traditional education models have evolved significantly by 2025. Lifelong learning, defined as the continuous pursuit of knowledge and skills at all ages, has become essential. This shift aligns closely with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly SDG 4 (Quality Education), SDG 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth), and SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-being).
1. The Imperative of Lifelong Learning
- Changing Work Landscape: Automation, artificial intelligence, and the gig economy require rapid adaptation and reskilling, supporting SDG 8.
- Longer, Healthier Lives: Increased life expectancy creates opportunities for reinvention and personal growth, contributing to SDG 3.
- Mental Health and Well-being: Engaging in learning activities improves cognitive health and emotional well-being, reinforcing SDG 3.
- Community and Social Inclusion: Learning fosters social connections and inclusivity across generations and cultures, advancing SDG 10 (Reduced Inequalities).
2. Evolution of Learning Modalities
- Micro-credentials and digital badges have gained acceptance, enabling recognition of specific skills relevant to the workforce (SDG 4, SDG 8).
- Online bootcamps provide intensive, focused training for new careers within weeks or months.
- Self-paced platforms such as Coursera, Khan Academy, and Udemy democratize access to education globally.
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) classrooms offer immersive learning experiences, enhancing engagement and understanding.
3. Scientific Foundations of Lifelong Learning
- Neuroplasticity: The brain’s ability to form new neural pathways supports learning at any age.
- Interleaving Techniques: Mixing different learning types improves retention and application.
- Community Learning: Group learning increases motivation and accountability.
These findings emphasize that lifelong learning is accessible and effective for all ages, promoting SDG 4.
4. Lifelong Learning in the Workplace
- Employers encourage continuous upskilling through workshops and courses on emerging technologies like AI and coding (SDG 8).
- Learning is increasingly viewed as a benefit, with companies funding education and allowing personalized learning plans.
- Peer learning and mentorship foster intergenerational knowledge exchange and collaboration.
Case Study: A Singaporean logistics company improved productivity by implementing weekly “learning hours” with access to a digital course library.
5. Lifelong Learning Beyond Employment
- Creative pursuits such as music, photography, and language learning enhance personal fulfillment and social inclusion (SDG 3, SDG 11).
- Health and wellness education, including nutrition and mindfulness, supports healthier lifestyles.
- Civic engagement through learning empowers communities to address local challenges, contributing to SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities) and SDG 13 (Climate Action).
6. Overcoming Barriers to Lifelong Learning
- Cost: Availability of free or low-cost online courses and digital subscriptions via public libraries.
- Time Constraints: Microlearning formats enable learning in short, manageable segments.
- Access: Smartphones and public WiFi extend educational opportunities to underserved and rural populations (SDG 9 – Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure).
- Confidence: Peer support and mentorship programs help learners overcome self-doubt.
7. Lifelong Learning Across All Ages
- Children: Self-directed projects and coding clubs supplement formal education.
- Teenagers: Virtual exchanges and global competitions foster cross-cultural collaboration.
- Adults: Career changers and retirees engage in new hobbies and professional development.
- Seniors: Brain fitness apps and storytelling groups maintain cognitive health and social engagement.
8. Community-Driven Learning Initiatives
- Makerspaces and libraries host workshops on diverse topics, promoting inclusive education.
- Book clubs and learning circles provide peer support and accountability.
- Volunteering as a form of teaching reinforces knowledge and community service (SDG 17 – Partnerships for the Goals).
9. Technology as an Enabler of Lifelong Learning
- AI tutors and adaptive learning apps personalize education and provide real-time feedback.
- VR classrooms offer immersive experiences that transcend geographical barriers.
- Social platforms facilitate resource sharing and learner interaction worldwide.
10. Roadmap to Lifelong Learning
- Identify personal interests and curiosities.
- Set achievable micro-goals to maintain momentum.
- Incorporate diverse learning methods: videos, reading, practice, and discussion.
- Join learning communities for motivation and support.
- Track progress through journals, digital badges, or portfolios.
Stories of Lifelong Learning Impact
- Rosa, 46: Transitioned to freelance coding after attending a women’s bootcamp; now mentors youth.
- Samir, 70: Learning Japanese via an app, inspiring his grandchildren to learn as well.
- Jade, 29: Changed careers through an online UX design course, gaining new skills and community.
Conclusion
In 2025, investing in lifelong learning is crucial for personal and societal advancement. This approach supports multiple SDGs by promoting inclusive, equitable quality education (SDG 4), fostering decent work and economic growth (SDG 8), and enhancing health and well-being (SDG 3). Lifelong learning empowers individuals to adapt, innovate, and contribute meaningfully to their communities and the global sustainable development agenda.
Resources for Lifelong Learning
- Coursera, Khan Academy, Udemy – Online courses
- Duolingo, Babbel – Language learning
- Local libraries and community centers
- Meetup, Discord, Reddit – Learning groups and communities
- Books: Range by David Epstein; Mindset by Carol Dweck
1. Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) Addressed or Connected
- SDG 4: Quality Education
- The article emphasizes lifelong learning, upskilling, and access to education at all ages.
- It highlights digital learning platforms, micro-credentials, and inclusive education models.
- SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being
- Mental health benefits of learning and cognitive health in seniors are discussed.
- Health and wellness classes such as nutrition and mindfulness are mentioned.
- SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
- Continuous upskilling and adapting to changing work environments like AI and automation.
- Career transitions and workforce productivity improvements are highlighted.
- SDG 10: Reduced Inequalities
- Access to education for underserved groups via smartphones and public WiFi.
- Overcoming barriers such as cost, time, and confidence.
- SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
- Community-driven learning through libraries, makerspaces, and volunteering.
- Building social networks and civic engagement through education.
- SDG 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure
- Use of technology like AI tutors, VR classrooms, and adaptive learning platforms.
2. Specific Targets Under Identified SDGs
- SDG 4: Quality Education
- Target 4.3: Ensure equal access to affordable and quality technical, vocational and tertiary education, including university.
- Target 4.4: Increase the number of youth and adults with relevant skills for employment and entrepreneurship.
- Target 4.5: Eliminate gender and wealth disparities in education and ensure equal access for vulnerable populations.
- Target 4.7: Ensure that all learners acquire knowledge and skills needed to promote sustainable development.
- SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being
- Target 3.4: Promote mental health and well-being.
- SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
- Target 8.2: Achieve higher levels of economic productivity through diversification, technological upgrading and innovation.
- Target 8.6: Reduce the proportion of youth not in employment, education or training.
- SDG 10: Reduced Inequalities
- Target 10.2: Empower and promote social, economic and political inclusion of all.
- SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
- Target 11.7: Provide universal access to safe, inclusive and accessible green and public spaces.
- SDG 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure
- Target 9.5: Enhance scientific research and upgrade technological capabilities of industrial sectors.
3. Indicators Mentioned or Implied to Measure Progress
- SDG 4 Indicators
- Proportion of youth and adults with information and communications technology (ICT) skills.
- Participation rate in formal and non-formal education and training in the previous 12 months.
- Number of learners obtaining micro-credentials or digital badges.
- SDG 3 Indicators
- Prevalence of mental health conditions and cognitive decline among older adults.
- Participation in health and wellness educational programs.
- SDG 8 Indicators
- Employment rates of adults who have completed upskilling or reskilling programs.
- Productivity metrics linked to workplace learning initiatives (e.g., the Singapore logistics company case).
- SDG 10 Indicators
- Access to digital learning resources among underserved populations.
- Reduction in barriers such as cost and time for education participation.
- SDG 11 Indicators
- Number of community learning spaces and participation rates.
- Levels of civic engagement through educational activities.
- SDG 9 Indicators
- Adoption rates of AI and VR technologies in education.
- Effectiveness of adaptive learning platforms measured by learner outcomes.
4. Table: SDGs, Targets and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 4: Quality Education |
|
|
| SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being |
|
|
| SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth |
|
|
| SDG 10: Reduced Inequalities |
|
|
| SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities |
|
|
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure |
|
|
Source: vocal.media

What is Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0