Mental health treatment and its impact on survival outcomes in patients with comorbid mental health and cardiovascular diseases: a retrospective cohort study – BMC Psychiatry
Study Report on Comorbid Mental Health and Cardiovascular Diseases in Northwest Ethiopia
Study Setting
The study was conducted at four major healthcare facilities in Northwest Ethiopia, namely:
- Debre Markos Comprehensive Specialized Hospital
- Tibebe Gihon Comprehensive Specialized Hospital
- University of Gondar Comprehensive Specialized Hospital
- Felege Hiwot Comprehensive Specialized Hospital
These institutions play a critical role in advancing Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 3: Good Health and Well-being, by providing specialized care for patients with complex health conditions.
Study Period and Design
The research was conducted from January 1, 2023, to May 31, 2023, employing a retrospective cohort design. This approach utilized a one-year dataset of existing medical records to evaluate patient outcomes, aligning with SDG 3’s focus on strengthening health systems through evidence-based research.
Source and Study Population
The study population comprised patients diagnosed with comorbid mental health and cardiovascular diseases receiving care at the participating hospitals. Identification was through hospital admission and discharge records, outpatient clinic logs, and electronic health records, supporting SDG 3’s aim to ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all ages.
Eligibility Criteria
Inclusion Criteria
- Confirmed diagnosis of comorbid mental health and cardiovascular disease documented in medical records.
- Age 18 years or older at diagnosis.
- Availability of medical records covering the study period.
Exclusion Criteria
- Incomplete medical records.
- History of prior cardiovascular surgeries.
- Terminal illnesses unrelated to the comorbid conditions.
These criteria ensured data quality and relevance, contributing to SDG 3’s target of reducing premature mortality from non-communicable diseases.
Study Variables
- Dependent Variables: Hospital readmission and emergency department visits.
- Independent Variables: Mental health treatment, age, sex, and residence.
Sample Size Determination
The study included all eligible patients during the study period without a priori sample size calculation, maximizing statistical power and generalizability. A total of 319 patients with comorbid mental health and cardiovascular diseases from January 2018 to December 2022 were identified across the four hospitals. This comprehensive inclusion supports SDG 10: Reduced Inequalities, by ensuring diverse patient representation.
Sampling Technique
A proportional simple random sampling technique was employed to ensure representativeness across hospitals. The sample allocation formula used was:
ni = (Ni / N) × n
Where:
- ni: Sample size from hospital i
- Ni: Number of eligible patients in hospital i
- N: Total eligible patients across all hospitals
- n: Total sample size (319)
Sample allocation was as follows:
- Debre Markos Comprehensive Specialized Hospital: ~104 patients
- University of Gondar Comprehensive Specialized Hospital: ~87 patients
- Felege Hiwot Comprehensive Specialized Hospital: ~70 patients
- Tibebe Gihon Comprehensive Specialized Hospital: ~58 patients
Random selection within each hospital was performed using computer-generated random numbers, ensuring unbiased sampling in line with SDG 16: Peace, Justice, and Strong Institutions.
Data Collection Procedure
Data were collected using a structured questionnaire developed from extensive literature review, capturing sociodemographic, clinical, and medication-related variables from patient medical records. Comorbid conditions such as diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia, and hypertension were identified based on clinician documentation.
Mental health treatment assessment included pharmacy refill records, therapist notes, treatment plans, and diagnosis codes. Clinical outcomes such as psychiatric symptoms and hospitalization rates were analyzed. Emergency department visits and hospital readmissions were reviewed for relevance to comorbid conditions.
Diagnosis dates were extracted from multiple sources, with special attention to the timing of psychiatric and cardiovascular diagnoses to accurately define comorbidity onset. This comprehensive data collection supports SDG 3 by improving understanding of complex health interactions and informing integrated care models.
Operational Definitions
- Comorbid Mental Health and Cardiovascular Diseases: Coexistence of cardiovascular and psychiatric disorders.
- Mental Health Treatment: Interventions aimed at symptom alleviation and well-being improvement.
- Hospital Readmission: Unplanned hospital admission related to comorbid conditions.
- Emergency Department Visit: Immediate medical attention encounters related to comorbid conditions.
- Event Occurred: Patients experiencing hospital readmission or emergency visits during the study.
- Censored: Patients without events during follow-up or lost to follow-up.
- Survival Time: Duration from study start to event occurrence.
Data Quality Assurance
Quality assurance measures included:
- Development and pre-testing of a structured questionnaire to ensure clarity and consistency.
- Training of clinical pharmacist data collectors on protocols and ethical considerations.
- Inter-rater reliability assessment through independent chart reviews and consensus discussions.
- Periodic supervisory audits by principal investigators and site coordinators.
- Verification of diagnoses using multiple documentation sources to minimize information bias.
- Exclusion of records with missing essential variables and triangulation to recover missing data where possible.
- Use of total population sampling to reduce selection bias.
These measures align with SDG 3’s emphasis on quality health data to inform policy and practice.
Data Processing and Analysis
Data were coded and entered into a secure electronic database. Descriptive statistics summarized demographic and clinical characteristics. Cox proportional hazards regression analyzed factors influencing time to hospital readmission and emergency department visits, with follow-up spanning one year.
Key analytical steps included:
- Assessment of model assumptions using Schoenfeld residuals.
- Bivariate analysis to select variables with P
- Inclusion of clinically relevant variables based on evidence and biological plausibility.
- Reporting of crude and adjusted hazard ratios with 95% confidence intervals; significance at P
- Multicollinearity assessment using variance inflation factor (mean VIF = 1.21).
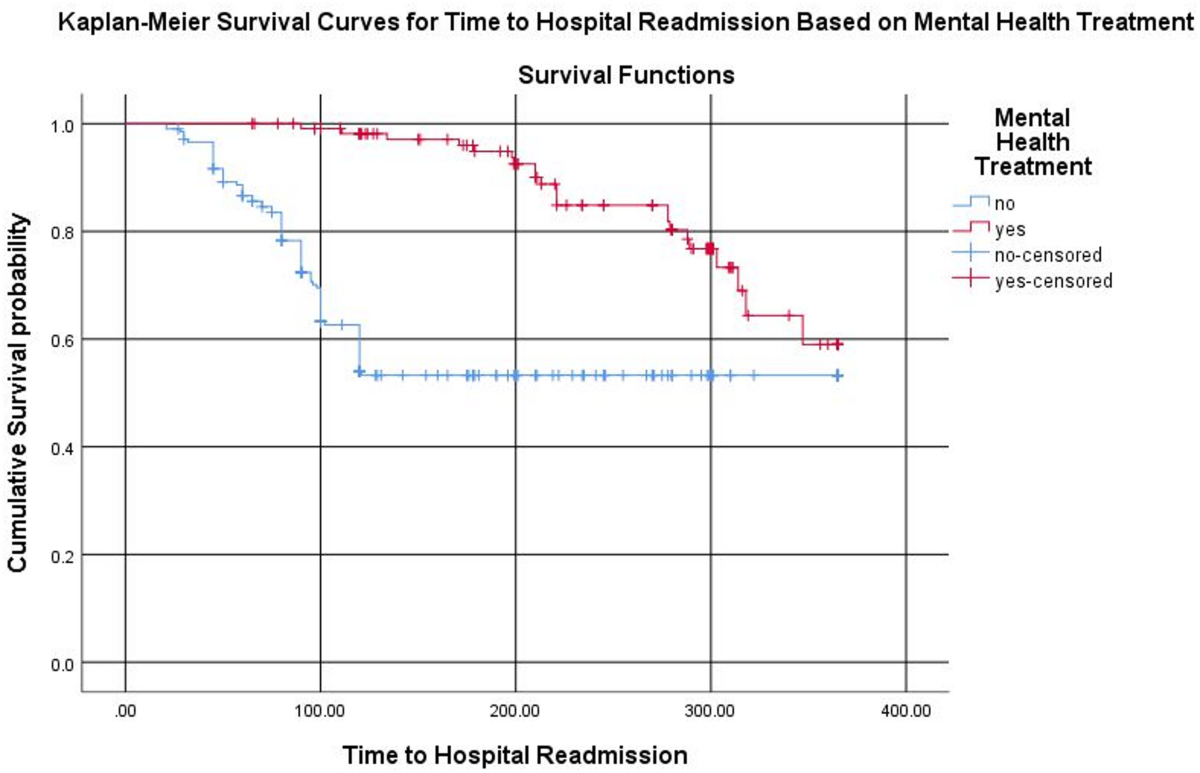
- Kaplan-Meier survival curves and log-rank tests to compare survival functions by mental health treatment status.
This rigorous analysis supports SDG 3 by identifying determinants of health outcomes, guiding interventions to reduce hospital readmissions and emergency visits among patients with complex comorbidities.
1. Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) Addressed or Connected
- SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being
- The article focuses on comorbid mental health and cardiovascular diseases, hospital readmissions, emergency department visits, and mental health treatment, all directly related to ensuring healthy lives and promoting well-being.
- SDG 10: Reduced Inequalities
- The study includes patients from multiple hospitals in Northwest Ethiopia, addressing health disparities and aiming for equitable healthcare access and outcomes.
- SDG 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure
- The use of electronic health records, structured questionnaires, and statistical software for data analysis reflects the promotion of research infrastructure and innovation in healthcare.
2. Specific Targets Under Those SDGs Identified
- SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being
- Target 3.4: By 2030, reduce by one third premature mortality from non-communicable diseases through prevention and treatment and promote mental health and well-being.
- Target 3.8: Achieve universal health coverage, including financial risk protection and access to quality essential healthcare services.
- Target 3.c: Substantially increase health financing and recruitment, development, training, and retention of the health workforce in developing countries.
- SDG 10: Reduced Inequalities
- Target 10.2: Empower and promote the social, economic and political inclusion of all, irrespective of age, sex, disability, race, ethnicity, origin, religion or economic or other status.
- SDG 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure
- Target 9.5: Enhance scientific research, upgrade the technological capabilities of industrial sectors, including health sector innovations.
3. Indicators Mentioned or Implied in the Article to Measure Progress
- Indicators related to SDG 3:
- Hospital readmission rates for patients with comorbid mental health and cardiovascular diseases.
- Emergency department visit rates related to comorbid conditions.
- Proportion of patients receiving mental health treatment (pharmacy refill records, treatment plans, therapist notes).
- Survival time (time to hospital readmission or emergency visit) measured in days.
- Psychiatric symptom changes, hospitalization rates for mental health crises.
- Indicators related to SDG 10:
- Distribution of patients by age, sex, and residence to assess equitable access and outcomes.
- Indicators related to SDG 9:
- Use of electronic health records and ICD-10 coding for diagnoses.
- Implementation of structured questionnaires and statistical software for data analysis.
4. Table of SDGs, Targets and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being |
|
|
| SDG 10: Reduced Inequalities |
|
|
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure |
|
|
Source: bmcpsychiatry.biomedcentral.com








