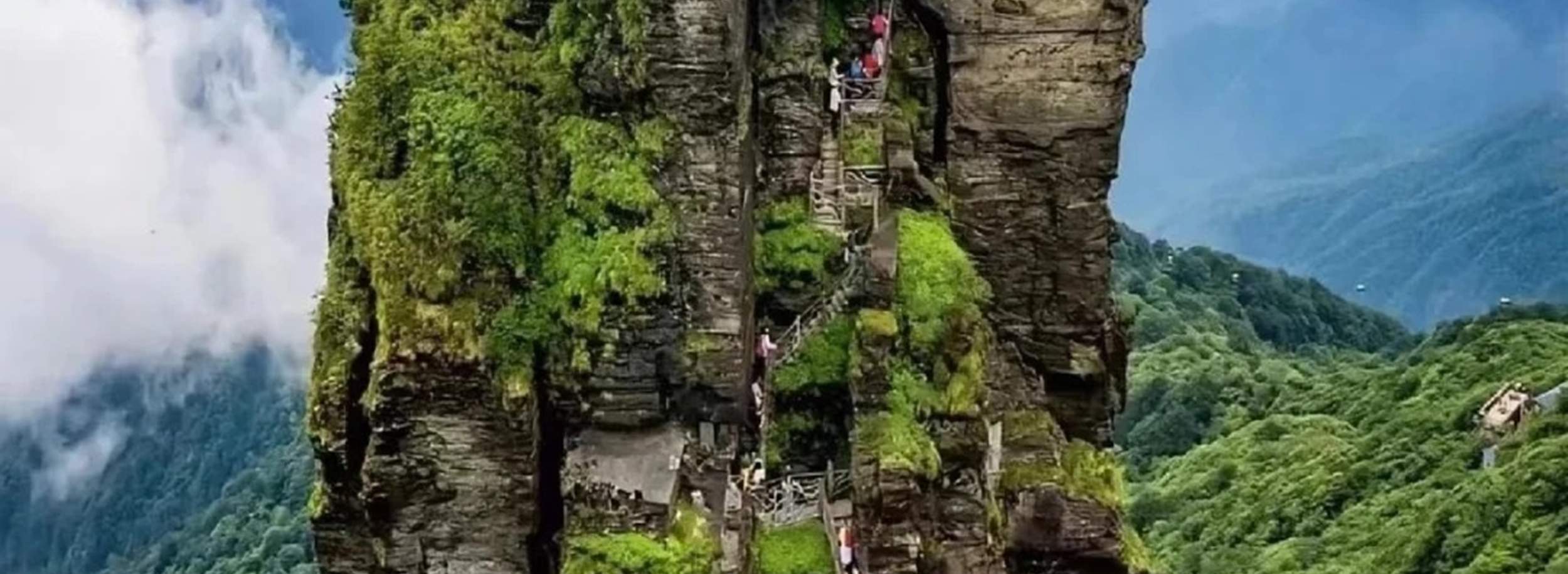
Fanjing Mountain: A Sustainable Ecotourism Success Story in Guizhou, China – Travel And Tour World

Fanjing Mountain Ecotourism Report: An Integrated Model for Achieving Sustainable Development Goals
Executive Summary
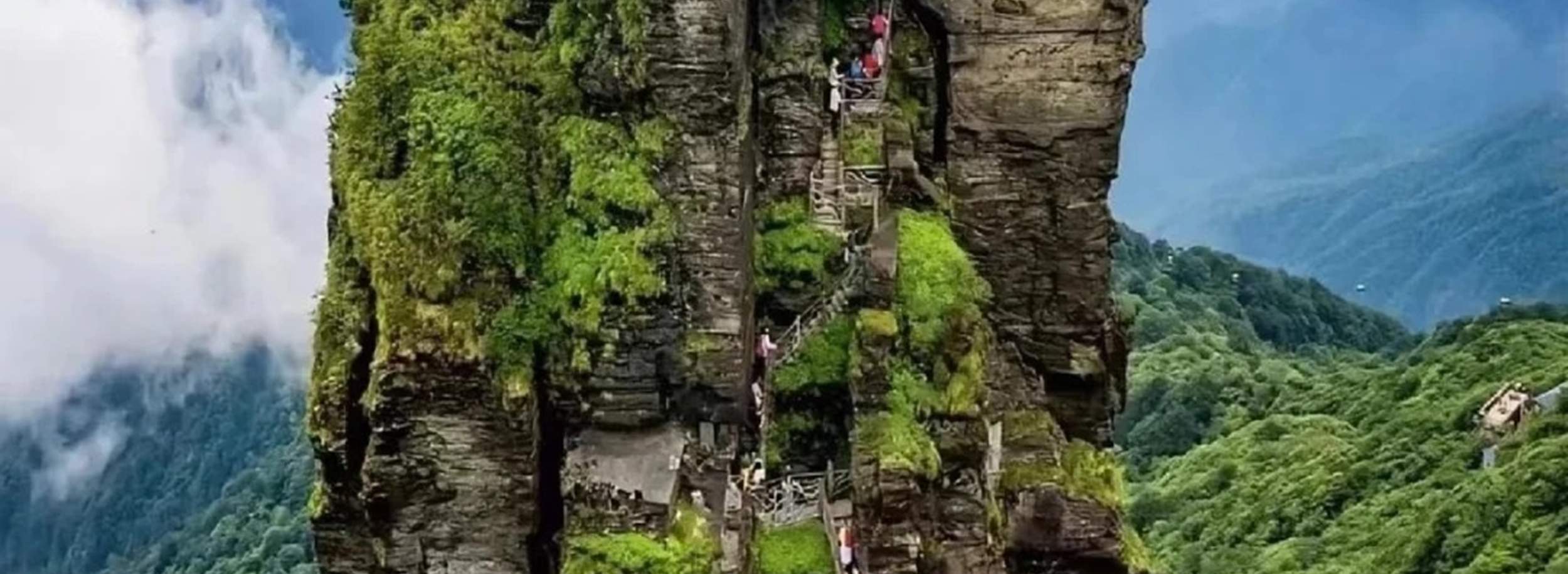
Fanjing Mountain (Fanjingshan) in Guizhou Province, China, has emerged as a paradigm of sustainable ecotourism since its designation as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2018. The site successfully integrates environmental conservation with socio-economic development, providing a replicable framework for achieving multiple Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). This report analyzes the strategies employed at Fanjing Mountain, focusing on its contributions to decent work (SDG 8), poverty alleviation (SDG 1), biodiversity protection (SDG 15), and responsible tourism (SDG 12).
Economic Advancement and Community Upliftment through Sustainable Tourism
Contribution to SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
The development of ecotourism at Fanjing Mountain has directly stimulated the local economy, creating stable employment and reducing the need for outward migration. The tourism boom has fostered a thriving local service industry, aligning with the principles of inclusive and sustainable economic growth.
- Visitor and Revenue Growth: Between 2019 and 2023, the scenic area attracted 6.25 million visitors.
- Economic Impact: This influx generated 1.22 billion yuan ($170 million) in direct tourism revenue.
- Employment Creation: A significant number of jobs in hospitality, transportation (drivers), and tour guiding have been created for residents of surrounding villages.
- Sector Growth: The local tourism sector is experiencing an estimated 50% increase in annual revenue.
Contribution to SDG 1: No Poverty
By transforming ecological assets into economic opportunities, the Fanjing Mountain model provides a direct pathway to poverty alleviation for local communities. The government’s guiding principle, “lucid waters and lush mountains are invaluable assets,” has been operationalized to ensure that economic benefits are distributed locally, improving livelihoods and community well-being.
Environmental Stewardship and Biodiversity Conservation
Commitment to SDG 15: Life on Land
The core of Fanjing Mountain’s success lies in its unwavering commitment to preserving its unique terrestrial ecosystems and biodiversity. Management practices prioritize the protection of its rich flora and fauna, including critically endangered species.
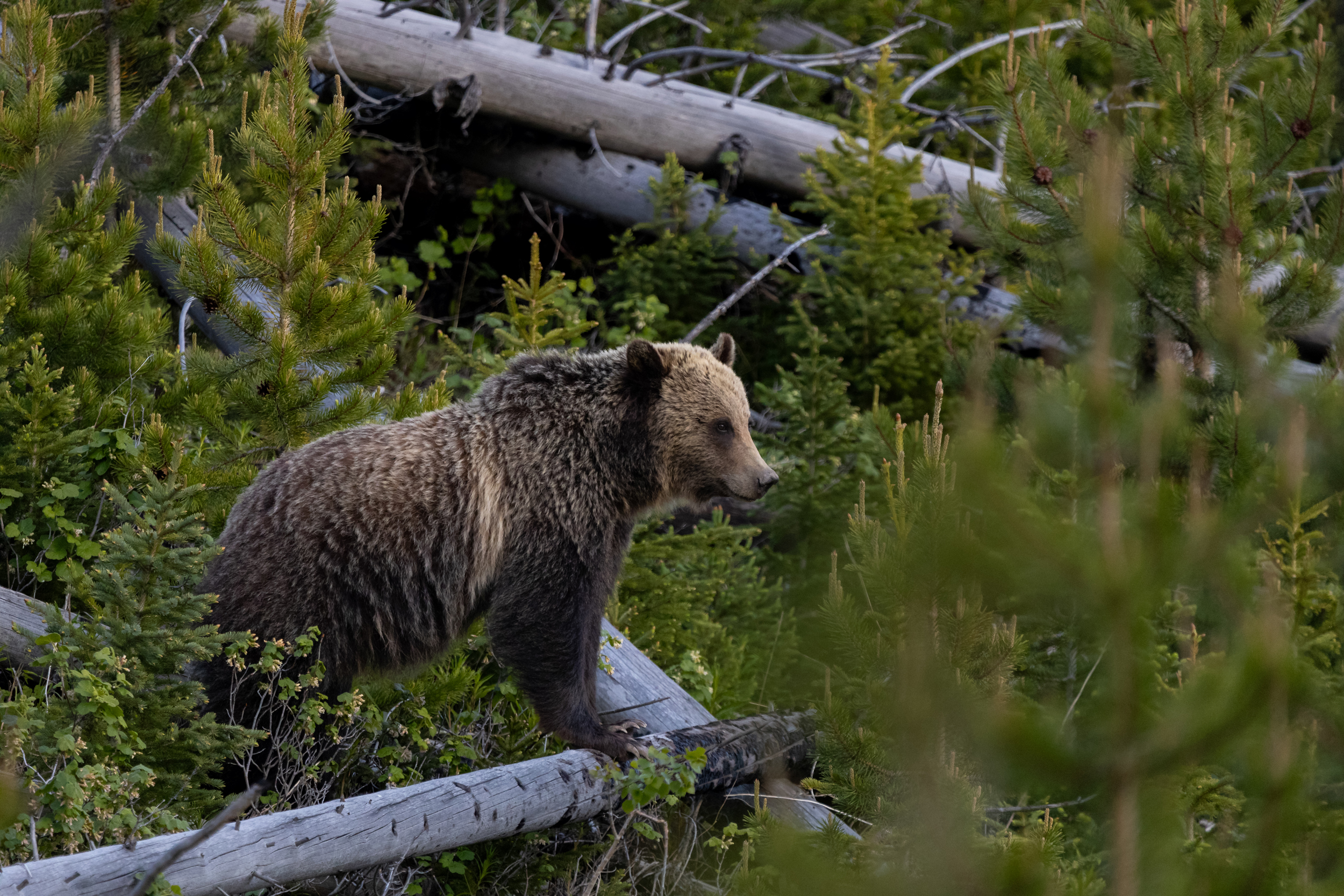
- Habitat Protection: The region is a vital habitat for the Guizhou golden snub-nosed monkey, one of the world’s rarest primates. Ecological corridors have been established to ensure wildlife mobility and protection.
- Biodiversity Gains: Since its designation as a nature reserve, conservation efforts have led to the discovery of 37 new species.
- Ecosystem Health: Environmental monitoring confirms the long-term health of the ecosystem, with all surface water in the core area meeting Grade I quality standards.
Implementation of SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
Fanjing Mountain’s management has implemented a robust framework for sustainable tourism, ensuring that visitor activities do not compromise the ecological integrity of the site. This approach balances tourism growth with environmental preservation.
- Visitor Management: A strict online booking system is enforced to cap daily visitor numbers, preventing over-tourism.
- Sustainable Infrastructure: The use of electric vehicles for tourist transport minimizes the carbon footprint and pollution within the scenic area.
- Low-Impact Tourism: Tourist routes are strategically designed to minimize human-wildlife interaction and reduce the overall environmental impact of visits.
- Environmental Safeguards: Comprehensive fire prevention measures and regular environmental monitoring are standard operational procedures.
Synergies with Ancillary Sustainable Industries
Fostering Sustainable Local Economies
The pristine environment preserved through conservation efforts has catalyzed growth in other sustainable industries, creating a diversified local economy. The high-quality natural resources have attracted businesses that align with ecological principles, such as the Gui Tea Group, which sources high-quality matcha from local farmers. This demonstrates a positive feedback loop where environmental protection underpins broader economic prosperity, with products reaching over 50 countries.
Conclusion: A Global Blueprint for Sustainable Development
The Fanjing Mountain case study provides a compelling blueprint for integrating environmental conservation (SDG 15) with economic growth (SDG 8) and community well-being (SDG 1, SDG 11). By adopting a holistic strategy grounded in sustainable practices (SDG 12), the region has transformed from an underdeveloped area into a globally recognized ecotourism destination. The lessons learned from Fanjing Mountain offer valuable insights for policymakers and tourism developers worldwide on how to harness natural heritage to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals.
Analysis of Sustainable Development Goals in the Article
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
-
SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
The article emphasizes the creation of a “thriving local economy” through ecotourism, providing a “steady stream of jobs for locals” in hospitality, tour guiding, and other services, which directly contributes to economic growth and decent work.
-
SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
The focus on protecting Fanjing Mountain, a designated “World Heritage Site,” aligns with the goal of safeguarding the world’s cultural and natural heritage. The development model integrates the local community, ensuring they benefit from tourism revenue and can sustain their livelihoods without migrating.
-
SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
The article describes a “sustainable tourism model” that balances visitor numbers with environmental preservation. Measures like a “strict online booking system,” “environmentally conscious infrastructure like electric vehicles,” and “careful planning of tourist routes” are examples of promoting sustainable practices.
-
SDG 15: Life on Land
This is a central theme, with the article highlighting the mountain’s “breathtaking biodiversity.” Specific conservation efforts mentioned include protecting the “endangered Guizhou golden snub-nosed monkey,” creating “ecological corridors,” and maintaining the pristine ecosystem, which has led to the discovery of “37 new species” since it became a nature reserve.
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
-
Under SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
- Target 8.9: “By 2030, devise and implement policies to promote sustainable tourism that creates jobs and promotes local culture and products.” The article is a case study of this target in action. It details how Fanjing Mountain’s development has created jobs for locals, leading to a “50% increase in annual revenue” for the local tourism sector and supporting local industries like tea production.
-
Under SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
- Target 11.4: “Strengthen efforts to protect and safeguard the world’s cultural and natural heritage.” The article explicitly states that Fanjing Mountain was “declared a World Heritage Site in 2018” and details the extensive measures taken to preserve its natural and ecological value for “future generations.”
-
Under SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
- Target 12.b: “Develop and implement tools to monitor sustainable development impacts for sustainable tourism…” The article describes the implementation of a sustainable tourism strategy through tools and policies such as limiting visitor numbers via an online booking system, using electric vehicles, and designing routes to “minimise impact on wildlife.”
-
Under SDG 15: Life on Land
- Target 15.1: “By 2020, ensure the conservation, restoration and sustainable use of terrestrial and inland freshwater ecosystems and their services, in particular forests… mountains…” The entire article focuses on the conservation and sustainable use of the Fanjing Mountain ecosystem, a key terrestrial and freshwater environment.
- Target 15.5: “Take urgent and significant action to reduce the degradation of natural habitats, halt the loss of biodiversity and… protect and prevent the extinction of threatened species.” The article directly addresses this by highlighting the protection of the “endangered Guizhou golden snub-nosed monkey” and the creation of “ecological corridors to facilitate the movement of wildlife.”
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
-
For Target 8.9 (Sustainable Tourism and Jobs):
- Economic Impact: The article provides specific financial data, stating that the scenic area generated “1.22 billion yuan ($170 million) in revenue” between 2019 and 2023 and that the local tourism sector is “witnessing a 50% increase in annual revenue.”
- Job Creation: It is mentioned that the tourism boom “has provided a steady stream of jobs for locals” and that “Tour guides, drivers, and other workers are predominantly from the surrounding villages,” indicating progress in local employment.
-
For Target 11.4 (Protecting Natural Heritage):
- Heritage Site Status: The designation of Fanjing Mountain as a “World Heritage Site” in 2018 is a key indicator of its recognized value and the commitment to its protection.
-
For Target 12.b (Monitoring Sustainable Tourism):
- Visitor Management: The implementation of a “strict online booking system that limits visitor numbers” to around “8,000 visitors per day during the summer months” serves as an indicator of a management tool for sustainable tourism.
-
For Target 15.1 and 15.5 (Biodiversity and Ecosystem Health):
- Water Quality: The article states that “all surface water in its core area meeting Grade I standards,” which is a direct indicator of ecosystem health.
- Species Conservation: The protection of the “endangered Guizhou golden snub-nosed monkey” is a clear indicator of efforts to prevent the extinction of threatened species.
- Biodiversity Growth: The fact that “37 new species have been discovered” since the area was designated a nature reserve implies that the conservation efforts are successfully preserving a rich and thriving ecosystem.
4. Table of SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth | 8.9: Promote sustainable tourism that creates jobs and promotes local culture and products. | Tourism revenue of 1.22 billion yuan ($170 million) from 2019-2023. |
| Creation of a “steady stream of jobs for locals” in hospitality and tour guiding. | ||
| SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities | 11.4: Strengthen efforts to protect and safeguard the world’s cultural and natural heritage. | Designation as a “World Heritage Site” in 2018. |
| SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production | 12.b: Develop and implement tools to monitor sustainable development impacts for sustainable tourism. | Implementation of a strict online booking system to limit daily visitors to ~8,000. |
| SDG 15: Life on Land | 15.1: Ensure the conservation, restoration and sustainable use of terrestrial and inland freshwater ecosystems. | All surface water in the core area meets Grade I standards. |
| 15.5: Halt the loss of biodiversity and protect threatened species. | Active protection of the endangered Guizhou golden snub-nosed monkey. | |
| Discovery of 37 new species since the area became a nature reserve. |
Source: travelandtourworld.com

What is Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0










/campaigns/16-days-of-activism-against-gender-based-violence/pr-web-banner.tmb-1200v.jpg?sfvrsn=8cc7b98e_1#)