Transparent Solar Cells Market Size, Share | CAGR of 20.1% – Market.us
Global Transparent Solar Cells Market: A Report on Contributions to Sustainable Development Goals
The Global Transparent Solar Cells (TSCs) Market is undergoing significant expansion, driven by a global commitment to renewable energy and sustainable development. This report analyzes the market’s trajectory, key segments, and regional dynamics, with a specific focus on its alignment with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
Market Overview and Growth Projections
The market for Transparent Solar Cells is projected to expand from USD 17.1 Million in 2024 to USD 106.8 Million by 2034, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 20.1%. This growth is a direct contributor to SDG 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy) by introducing novel ways to harness solar power, particularly in urban environments.
TSCs, which capture energy from non-visible light, are pivotal for advancing SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities). Their integration into windows, facades, and electronic devices allows infrastructure to generate clean energy without compromising aesthetics or land use. Technological advancements, such as perovskite-based cells achieving 12.3% efficiency, underscore the innovation driving this sector, aligning with SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure).
Key Market Highlights
- Market Growth: Expected to reach USD 106.8 Million by 2034, supporting SDG 7.
- Dominant Technology: Thin-Film Photovoltaics (TPV) held a 52.8% market share, indicating a scalable technology for clean energy deployment.
- Primary Application: Building Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV) accounted for 47.3% of the market, directly advancing SDG 11.
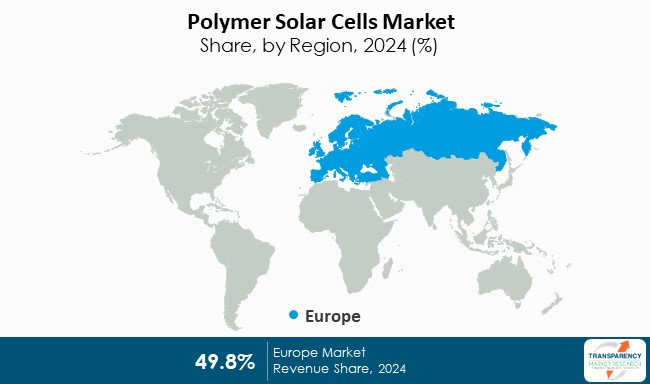
- Regional Leadership: Europe leads with a 34.80% share, driven by strong policy alignment with SDG 13 (Climate Action).
Market Segmentation Analysis
Analysis by Cell Type
Thin-Film Photovoltaics (TPV) dominated the market with a 52.8% share in 2024. The flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and scalability of TPV technology are crucial for the mass production of TSCs. This supports SDG 9 by fostering industrial innovation and makes clean energy solutions more accessible, thereby contributing to SDG 7.
Analysis by Transparency Type
Partially transparent cells accounted for over 83.5% of the market. This segment strikes a critical balance between energy generation and light transmission, making it an ideal solution for architectural applications. This innovation is fundamental to creating energy-efficient buildings and supports the objectives of SDG 11 by enabling urban infrastructure to become self-sustaining.
Analysis by Application
Building Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV) is the leading application, with a 47.3% market share. BIPV transforms buildings from energy consumers into energy producers, a core tenet of sustainable urban development. This application is a direct enabler of SDG 7 and SDG 11, reducing the carbon footprint of cities and promoting resource efficiency.
Key Market Segments
-
By Cell Type
- Thin-Film Photovoltaics (TPV)
- Polymer Solar Cell
- Others
-
By Transparency Type
- Partial
- Full
-
By Application
- Building Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV)
- Automobile
- Consumer Electronics
- Others
Emerging Trends and Innovations
Continuous improvements in TSC efficiency, particularly with perovskite-based cells, represent a significant trend. These advancements in materials science are a clear manifestation of SDG 9, driving the industry towards more effective and commercially viable clean energy solutions. Furthermore, government policies promoting domestic manufacturing, such as in India, align with SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production) by fostering localized, sustainable supply chains and contributing to national energy security under SDG 7.
Market Drivers: Government Initiatives and Policy Support
Government policies are a primary driver for the TSC market, creating a supportive ecosystem for technologies that advance climate and sustainability goals.
- Japan: A USD 1.5 billion investment in perovskite solar cells aims to enhance energy security and promote next-generation infrastructure, directly supporting SDG 7 and SDG 9.
- India: The Pradhan Mantri Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana and local content requirements are designed to accelerate rooftop solar adoption and build domestic manufacturing capacity, contributing to SDG 7, SDG 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth), and SDG 12.
- United States: The Inflation Reduction Act and Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act provide substantial incentives for clean energy technologies, including BIPV, accelerating progress towards SDG 7 and SDG 13.
These initiatives are instrumental in de-risking investment and scaling the deployment of TSCs, paving the way for a sustainable energy future.
Market Restraints: Addressing Cost Barriers
The high manufacturing cost of TSCs, with prices ranging from $300 to $600 per square meter, remains a significant barrier to widespread adoption. This challenge directly impacts the accessibility aspect of SDG 7. Overcoming this restraint through innovation in materials and fabrication processes is a key objective for the industry, aligning with the goals of SDG 9 to develop more efficient and affordable technologies.
Regional Insights and SDG Alignment
Europe
Europe’s market leadership, with a 34.80% share, is a result of its robust policy framework, including the European Green Deal. The region’s commitment to achieving a 40% renewable energy share by 2030 and its focus on energy-efficient buildings firmly align its market growth with SDG 7, SDG 11, and SDG 13.
North America
North America’s market position is bolstered by significant public and private investment in R&D, such as initiatives by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL). This focus on innovation is critical for advancing SDG 9 and developing the next generation of clean energy technologies.
Asia Pacific
Countries like Japan and India are leveraging TSC technology to meet ambitious non-fossil fuel targets and enhance energy independence. These national strategies contribute significantly to global efforts under SDG 7 and SDG 13 while promoting sustainable industrialization in line with SDG 9.
Key Player Analysis and Contributions to SDGs
Leading companies in the TSC market are actively contributing to sustainable development through their specialized technologies.
- Brite Solar: Specializes in transparent solar glass for greenhouses (agrivoltaics), a technology that supports both SDG 7 (Clean Energy) and SDG 2 (Zero Hunger) by enabling sustainable food production.
- Onyx Solar Group LLC: A leader in BIPV, Onyx Solar’s projects directly contribute to building sustainable cities and infrastructure, embodying the principles of SDG 11.
- InQs: Develops quantum dot-based TSCs for smart buildings and electronics, fostering innovation in urban infrastructure and contributing to SDG 9 and SDG 11.
- Energy Advance: Focuses on integrating PV modules into windows and facades, promoting energy-positive buildings in line with SDG 7.
Recent Industry Developments
Recent developments demonstrate the market’s transition from research to commercial-scale impact.
- In 2024, Brite-Solar commissioned Europe’s first dedicated manufacturing line for agri-PV panels. This development is a milestone for integrating renewable energy into agriculture, supporting SDG 2 and SDG 7.
- In 2024, Onyx Solar Group LLC continued its global expansion of BIPV projects. Its work on iconic structures showcases the successful integration of renewable energy technology into modern architecture, providing tangible examples of progress toward SDG 11.
Analysis of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in the Article
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
-
SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
- The entire article revolves around transparent solar cells, a form of renewable energy technology. It discusses advancements, market growth, and government initiatives aimed at increasing the adoption of solar power, which directly contributes to providing affordable and clean energy.
-
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
- The article highlights significant innovation in solar technology, such as perovskite-based cells and thin-film photovoltaics. It also covers the development of new infrastructure (Building Integrated Photovoltaics – BIPV) and the growth of the domestic manufacturing industry for solar components, supported by government policies and investments in R&D.
-
SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
- The text emphasizes the use of transparent solar cells in urban environments, particularly through BIPV. This technology helps create energy-efficient buildings, optimizes space in dense urban areas, and allows cities to reduce their carbon footprint, making them more sustainable.
-
SDG 13: Climate Action
- By promoting a shift from fossil fuels to renewable solar energy, the technologies and policies discussed in the article are direct measures to combat climate change. The article explicitly mentions that transparent solar cells offer an “opportunity for urban markets to reduce their carbon footprint.”
-
SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals
- The article mentions multiple instances of partnerships and collaborations. These include government initiatives providing financial incentives (subsidies, tax credits), international cooperation in R&D (like the U.S. NREL’s PV Fleet Initiative), and global recommendations from bodies like the International Energy Agency (IEA) to strengthen supply chains.
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
-
Under SDG 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy):
- Target 7.2: “By 2030, increase substantially the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix.” The article supports this with examples like India’s goal of 500 GW of non-fossil fuel capacity by 2030, the EU’s target of a 40% renewable energy share by 2030, and the IEA’s projection that solar PV will account for 80% of new renewable capacity additions by 2030.
- Target 7.3: “By 2030, double the global rate of improvement in energy efficiency.” This is addressed through the focus on “energy-efficient buildings” and the development of BIPV, which integrates energy generation into building materials to improve overall efficiency.
- Target 7.a: “By 2030, enhance international cooperation to facilitate access to clean energy research and technology…and promote investment in energy infrastructure and clean energy technology.” The article mentions cooperative R&D initiatives by the U.S. National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) and substantial government investments from the US, Japan, and India to advance solar technology.
-
Under SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure):
- Target 9.4: “By 2030, upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable, with increased resource-use efficiency and greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies…” The development and application of transparent solar cells in buildings (BIPV) is a direct example of upgrading infrastructure with clean technology.
- Target 9.5: “Enhance scientific research, upgrade the technological capabilities of industrial sectors…” The article details advancements in cell efficiency (perovskite cells reaching 12.3% efficiency), R&D investments (Japan’s $1.5 billion), and the creation of dedicated manufacturing facilities (Brite-Solar’s 150 MWp line in Europe).
-
Under SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities):
- Target 11.6: “By 2030, reduce the adverse per capita environmental impact of cities…” The article states that transparent solar cells integrated into buildings provide an “opportunity for urban markets to reduce their carbon footprint” and support the construction of “energy-efficient buildings.”
-
Under SDG 13 (Climate Action):
- Target 13.2: “Integrate climate change measures into national policies, strategies and planning.” The article provides numerous examples of governments doing this, such as India’s non-fossil fuel targets, Japan’s renewable energy goals, the US Inflation Reduction Act, and the EU’s REPowerEU initiatives.
-
Under SDG 17 (Partnerships for the Goals):
- Target 17.7: “Promote the development, transfer, dissemination and diffusion of environmentally sound technologies…” Government incentives, subsidies, and mandates discussed for the US, Japan, India, and the EU are all mechanisms to promote the diffusion of transparent solar technology.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
-
For SDG 7:
- Renewable energy capacity (Indicator 7.2.1): The article provides specific quantitative goals, such as India’s target of 500 GW non-fossil fuel capacity by 2030 and Japan’s goal to generate energy equivalent to 20 nuclear power plants by 2040.
- Share of renewable energy (Indicator 7.2.1): The EU’s target of a 40% share of renewables by 2030 and Japan’s target of up to 50% renewable energy in its electricity mix are mentioned.
- Financial flows for clean energy (Indicator 7.a.1): Specific investment figures are cited, including Japan’s $1.5 billion commitment, the US DOE’s $62 billion investment, and India’s investment of over ₹75,000 crore.
- Technology efficiency: The article mentions power conversion efficiencies (PCE) of up to 12.3% for perovskite designs, which serves as a direct measure of technological progress.
-
For SDG 9:
- Investment in R&D (Indicator 9.5.1): The $1.5 billion committed by Japan for perovskite solar cell commercialization is a direct indicator of R&D spending.
- Manufacturing capacity: The commissioning of a 150 MWp manufacturing line by Brite-Solar is a concrete indicator of industrial capacity growth.
- Market Growth Rate: The projected market growth from USD 17.1 Million in 2024 to USD 106.8 Million by 2034 at a CAGR of 20.1% indicates the rate of adoption of this new technology.
-
For SDG 11:
- Adoption of BIPV: The market share of BIPV, noted as over 47.3%, serves as an indicator of the integration of sustainable technology into urban infrastructure.
- Number of projects: The mention of Onyx Solar delivering solutions for over 400 projects is an indicator of the real-world application in making buildings more sustainable.
4. Table of SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy | 7.2: Increase substantially the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix. |
|
| 7.3: Double the global rate of improvement in energy efficiency. |
|
|
| 7.a: Enhance international cooperation and promote investment in clean energy technology. |
|
|
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure | 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable. |
|
| 9.5: Enhance scientific research and upgrade technological capabilities. |
|
|
| SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities | 11.6: Reduce the adverse per capita environmental impact of cities. |
|
| SDG 13: Climate Action | 13.2: Integrate climate change measures into national policies. |
|
| SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals | 17.7: Promote the development and diffusion of environmentally sound technologies. |
|
Source: market.us

What is Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0










































































