Water Treatment Systems Market Size to Hit USD 91.39 Billion by 2034 – Precedence Research
Water Treatment Systems Market Size and Forecast (2025 to 2034)
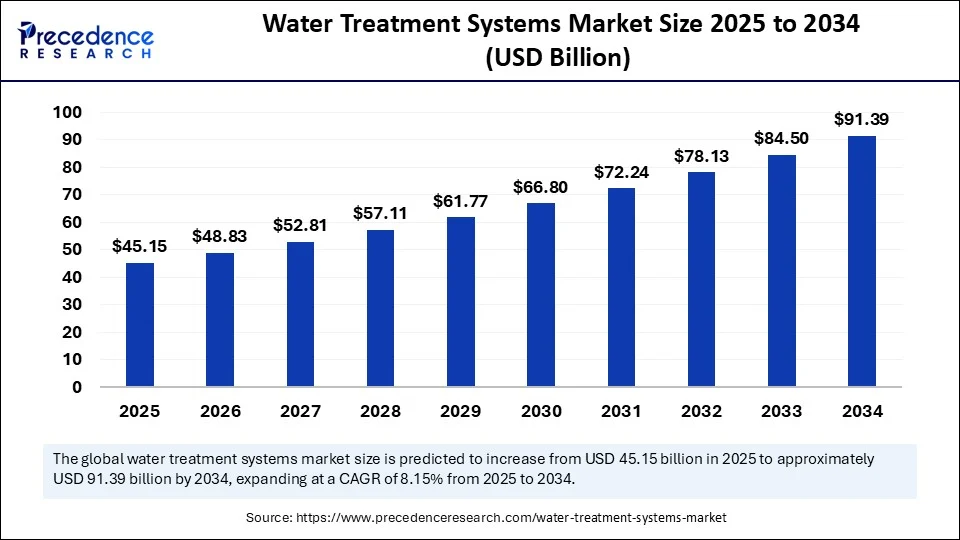
The global water treatment systems market was valued at USD 41.75 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow to USD 91.39 billion by 2034, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.15% from 2025 to 2034. This growth is driven by increasing water scarcity, stringent environmental regulations, and heightened municipal focus on wastewater management and clean water demand. These factors align closely with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 6: Clean Water and Sanitation, emphasizing universal access to safe and affordable drinking water.
Key Market Takeaways
- Market valuation stood at USD 41.75 billion in 2024.
- Expected market size of USD 91.39 billion by 2034.
- Projected CAGR of 8.15% between 2025 and 2034.
- Asia Pacific led the market with a 36% share in 2024.
- North America anticipated to register the fastest CAGR during the forecast period.
- Reverse osmosis systems held the largest technology segment share at 29% in 2024.
- Distillation systems expected to experience significant growth.
- Point-of-use (PoU) installations dominated with 75% market share in 2024.
- Point-of-entry (PoE) installations projected to grow at the highest CAGR.
- Residential applications accounted for the largest market share in 2024.
- Commercial applications forecasted to grow at the fastest rate.
Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Water Treatment Systems
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming water treatment by enabling smarter, more efficient, and predictive systems. AI integration with sensors, SCADA, and cloud platforms facilitates real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and optimized filtration cycles. These advancements support SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure by promoting sustainable industrialization and fostering innovation in water management technologies.
- AI-driven analytics detect contaminants, leaks, and equipment anomalies precisely.
- Machine learning optimizes chemical dosing and reduces energy consumption.
- Remote operations enhance accessibility, especially in decentralized and rural systems, supporting SDG 10: Reduced Inequalities.
- Smart wastewater treatment plants utilize AI for efficient sludge processing and nutrient removal.
Asia Pacific Market Size and Growth (2025 to 2034)
The Asia Pacific water treatment systems market was valued at USD 16.25 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 33.36 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 8.30%. The region’s dominance is attributed to high population density, rapid urbanization, industrialization, and critical water scarcity challenges, all of which underscore the importance of SDG 6.
Factors Driving Asia Pacific Market Leadership
- Government initiatives such as India’s Jal Jeevan Mission and Namami Gange program enhance water treatment infrastructure.
- Strict environmental regulations in countries like China mandate effluent treatment.
- Growing middle-class health awareness increases residential water purifier adoption.
- Technological innovations include solar-powered and mobile water treatment systems, promoting SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy.
North America Market Opportunities
North America is projected to experience the fastest market growth due to aging infrastructure, strict environmental regulations, and rising awareness of emerging contaminants such as PFAS and microplastics. Investments under policies like the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law support modernization efforts, aligning with SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities.
- Integration of AI and IoT for real-time water quality monitoring.
- Adoption of decentralized water treatment systems for underserved communities.
- Increased consumer demand for wellness-oriented water purification products.
- Industrial adoption of zero-liquid discharge and water recycling technologies supports SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production.
Market Overview
Water treatment systems are critical for ensuring public health and sustainable water resource management across residential, industrial, and municipal sectors. The market growth is propelled by urbanization, industrial expansion, and regulatory enforcement, all contributing to the achievement of SDG 6.
- High adoption of point-of-use and point-of-entry filtration systems in residential sectors.
- Industrial demand for closed-loop water recycling systems to reduce freshwater dependency.
- Government regulations enforcing wastewater discharge and effluent treatment standards.
- Technological advancements such as membrane filtration, UV disinfection, and AI-driven monitoring enhance efficiency and scalability.
- Decentralized systems improve water access in rural and remote areas, supporting SDG 10.
Water Treatment Systems Market Trends
- Smart Water Systems: AI, IoT, and automation improve monitoring, fault detection, and energy efficiency.
- Sustainability-Driven Innovation: Eco-friendly filtration materials, zero-liquid discharge systems, and water reuse models gain traction.
- Decentralized Treatment: Mobile, modular, and off-grid systems expand access in underserved regions.
- Stricter Regulations: Global tightening of water quality and discharge standards drives mandatory adoption.
Market Scope
| Report Coverage | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 91.39 Billion |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 45.15 Billion |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 41.75 Billion |
| Growth Rate (2025-2034) | CAGR of 8.15% |
| Dominant Region | Asia Pacific |
| Fastest Growing Region | North America |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered | Installation, Technology, Application, Region |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
Market Dynamics
Drivers
Rising Water Scarcity and Need for Clean Water
Global water scarcity, driven by population growth, urbanization, industrialization, and climate change, is the primary market growth driver. Governments enforce environmental regulations on wastewater discharge and industrial effluents, aligning with SDG 6. Public awareness of contaminants such as lead, PFAS, nitrates, and microplastics fuels demand for advanced purification systems in residential, commercial, and industrial sectors.
Restraints
High Costs and Environmental Concerns
High capital and maintenance costs of advanced water treatment technologies limit adoption, especially in low-income and rural areas. Lack of awareness and infrastructure further restrain market growth. Disposal of treatment waste such as brine and sludge poses environmental challenges. Technological complexity deters some consumers preferring simpler methods.
Opportunities
Emerging Markets and Technological Advancements
Emerging economies and rural areas present significant growth opportunities through decentralized, solar-powered, and mobile water treatment solutions. Integration of AI, IoT, and automation transforms water treatment into a smart, sustainable infrastructure, supporting SDG 9 and SDG 11. Health-conscious consumers drive demand for advanced residential systems. Corporate ESG commitments promote investment in water neutrality and recycling technologies.
Technology Insights
Reverse Osmosis Segment Leadership
Reverse osmosis (RO) systems held the largest market share (29%) in 2024 due to their high filtration efficiency, versatility, and consumer trust. RO removes up to 99% of contaminants including bacteria, viruses, heavy metals, and microplastics. Technological improvements such as energy recovery and smart sensors enhance efficiency and reduce environmental impact. RO is widely used in residential, pharmaceutical, food & beverage, and power generation sectors, supporting SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being.
Growth of Distillation Systems
Distillation systems are expected to grow significantly due to demand for ultra-pure, chemical-free water. This technology removes inorganic minerals, heavy metals, and biological contaminants by mimicking natural hydrological cycles. Modern distillers are compact, energy-efficient, and user-friendly, appealing to health-conscious consumers and specialized industrial applications. This supports SDG 12 by reducing reliance on chemical treatments.
Installation Insights
Point-of-Use Segment Dominance
The point-of-use (PoU) segment dominated with a 75% revenue share in 2024 due to affordability, convenience, and immediate water quality improvement. PoU systems are installed at water dispensing points in residential and commercial settings, offering easy installation and maintenance. They address contaminants such as lead, chlorine, and microplastics, contributing to SDG 6.
Growth of Point-of-Entry Segment
Point-of-entry (PoE) systems, treating all incoming water at the building level, are expected to grow at the fastest CAGR. PoE systems provide comprehensive protection for drinking, bathing, laundry, and appliances. These systems appeal to health-conscious consumers and luxury residential markets, enhancing water quality and property value.
Application Insights
Residential Segment Leadership
The residential segment held the largest market share in 2024, driven by increased awareness of waterborne diseases and distrust in municipal water supplies. Urbanization and aging infrastructure increase demand for point-of-use and point-of-entry purification systems. Wellness trends encourage adoption of alkaline and mineral-enhancing filters, supporting SDG 3 and SDG 6.
Commercial Segment Growth
The commercial segment is the fastest-growing application, driven by regulatory compliance and customer expectations. Hospitality, healthcare, education, and corporate sectors invest in advanced water treatment to ensure hygiene, safety, and sustainability. Integration with smart building management and IoT platforms supports SDG 9 and SDG 12 by optimizing resource use and reducing environmental impact.
Leading Companies in the Water Treatment Systems Market
- 3M
- Honeywell International Inc.
- DuPont
- Panasonic
- Pentair plc
- BWT Aktiengesellschaft
- Culligan
- Watts Water Technologies Inc.
- Aquasana, Inc.
- Calgon Carbon Corp.
- Pure Aqua, Inc.
- EcoWater Systems LLC
- Aquaphor
- FilterSmart
- WCC (Water Control Corp.)
Recent Developments
- June 2025: Kerala Water Authority awarded SUEZ a contract for upgrading Kochi City’s water supply system under the Kerala Urban Water Services Improvement Program, co-financed by the Asian Development Bank and Government of Kerala. This project supports SDG 6 by improving water distribution and management. (Source)
- April 2024: Thermax inaugurated a state-of-the-art manufacturing facility in Pune for water and wastewater treatment solutions, advancing resource conservation and sustainable development goals. (Source)
Segments Covered in the Report
By Installation
- Point-of-Use (PoU)
- Point-of-Entry (PoE)
By Technology
- Reverse Osmosis Systems
- Distillation Systems
- Disinfection Methods
- Filtration Methods
- Water Softeners
- Others
By Application
- Residential
- Commercial
- Industrial
By Region
- North America
- Asia Pacific
- Europe
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa
1. Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) Addressed in the Article
- SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation
- The article emphasizes the growing scarcity of clean water, the need for wastewater management, and the demand for clean and safe water access globally.
- It highlights investments in water purification, wastewater treatment, and water recycling technologies.
- References to government programs like India’s Jal Jeevan Mission and Namami Gange align with SDG 6 objectives.
- SDG 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure
- Technological advancements such as AI, IoT, automation, and smart sensors in water treatment systems are discussed.
- The article mentions infrastructure upgrades, especially in North America, and innovation in decentralized and modular treatment systems.
- SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
- Urbanization pressures and the need for sustainable water infrastructure in cities are highlighted.
- Smart water systems and decentralized treatment solutions contribute to sustainable urban living.
- SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
- Water recycling, zero-liquid discharge technologies, and sustainable water sourcing in industries are discussed.
- ESG goals and corporate water neutrality efforts are mentioned.
- SDG 13: Climate Action
- The article notes climate change impacts on water availability and quality, driving the need for resilient water treatment solutions.
2. Specific Targets Under the Identified SDGs
- SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation
- Target 6.1: Achieve universal and equitable access to safe and affordable drinking water for all.
- Target 6.3: Improve water quality by reducing pollution, minimizing release of hazardous chemicals and materials, and increasing recycling and safe reuse globally.
- Target 6.4: Increase water-use efficiency across all sectors and ensure sustainable withdrawals to address water scarcity.
- Target 6.a: Expand international cooperation and capacity-building support to developing countries in water and sanitation management.
- SDG 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure
- Target 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable, with increased resource-use efficiency and greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies.
- Target 9.5: Enhance scientific research, upgrade technological capabilities of industrial sectors, including water treatment technologies.
- SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
- Target 11.6: Reduce the adverse per capita environmental impact of cities, including air quality and waste management, which relates to water pollution control.
- SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
- Target 12.4: Achieve environmentally sound management of chemicals and wastes throughout their life cycle, including water treatment waste.
- Target 12.5: Substantially reduce waste generation through prevention, reduction, recycling, and reuse.
- SDG 13: Climate Action
- Target 13.1: Strengthen resilience and adaptive capacity to climate-related hazards and natural disasters, including water scarcity and pollution.
3. Indicators Mentioned or Implied to Measure Progress
- Indicators for SDG 6
- Proportion of population using safely managed drinking water services (implied by increased adoption of point-of-use and point-of-entry water treatment systems).
- Proportion of wastewater safely treated (implied by investments in wastewater treatment plants and technologies).
- Water use efficiency measured across sectors (implied by water recycling and zero-liquid discharge systems adoption).
- Compliance with water quality standards and reduction in contaminants such as lead, PFAS, microplastics, nitrates (mentioned as contaminants monitored and treated).
- Indicators for SDG 9
- Research and development expenditure in water treatment technologies (implied by AI, IoT, and automation integration).
- Number of industries adopting sustainable water treatment technologies (implied by industrial sector adoption of closed-loop and advanced filtration systems).
- Indicators for SDG 11
- Extent of urban water infrastructure coverage and modernization (implied by infrastructure upgrades in North America and Asia Pacific).
- Indicators for SDG 12
- Volume of water recycled and reused in industries (implied by zero-liquid discharge and water recycling units).
- Reduction in hazardous waste from water treatment processes (implied by eco-friendly filtration materials and waste management concerns).
- Indicators for SDG 13
- Resilience measures in water infrastructure to climate impacts (implied by adoption of decentralized and smart water treatment systems).
4. Table: SDGs, Targets and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation |
|
|
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure |
|
|
| SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities |
|
|
| SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production |
|
|
| SDG 13: Climate Action |
|
|
Source: precedenceresearch.com








