Manufacturing Value Added Flat – Econbrowser
Manufacturing Sector Analysis Post-“Liberation Day”
Overview
The anticipated manufacturing renaissance following “Liberation Day” has not materialized as expected. Recent data indicates stagnation and decline in key manufacturing metrics, raising concerns about the sector’s contribution to sustainable economic growth.
Manufacturing Performance Indicators
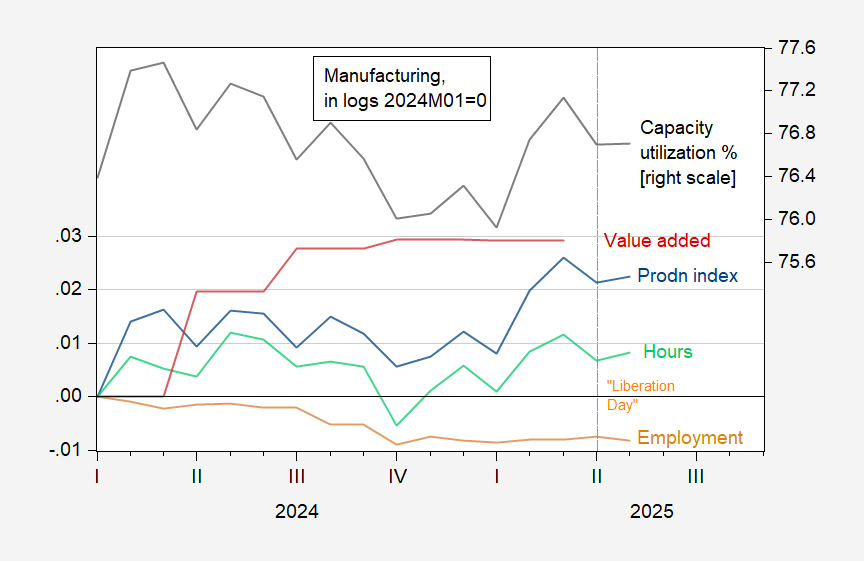
- Production Levels: Manufacturing production, measured in logarithmic scale, shows no significant growth since April 2024.
- Value Added: The value added by manufacturing, adjusted to 2017 dollars, remains flat, indicating limited economic contribution.
- Employment and Hours: Employment and aggregate hours worked by production workers have not increased, suggesting a lack of job creation within the sector.
- Capacity Utilization: The percentage of capacity utilization, based on NAICS data, remains steady without improvement, reflecting underused manufacturing capabilities.
Data Sources and Methodology
- Data on manufacturing production, employment, and hours were sourced from the Federal Reserve, Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA), and Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS).
- Aggregate hours of production workers were calculated by multiplying average weekly hours by the number of employees.
- All metrics are presented in logarithmic form with April 2024 as the baseline (2024M04=0).
Implications for Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
The stagnation in manufacturing employment and production undermines efforts to promote sustained, inclusive economic growth and productive employment, key targets under SDG 8. The lack of job creation in manufacturing limits opportunities for decent work.
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
The underutilization of manufacturing capacity and stagnant value addition highlight challenges in building resilient infrastructure and fostering innovation. Strengthening the manufacturing sector is critical to achieving SDG 9, which aims to promote sustainable industrialization.
SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
Efficient use of manufacturing capacity aligns with SDG 12, emphasizing sustainable consumption and production patterns. Current trends suggest inefficiencies that could be addressed to reduce waste and improve resource utilization.
Recommendations for Policy and Practice
- Implement targeted investments to modernize manufacturing infrastructure and adopt innovative technologies.
- Promote workforce development programs to enhance skills and increase employment opportunities in manufacturing.
- Encourage sustainable production practices to optimize resource use and reduce environmental impact.
- Monitor manufacturing sector performance regularly to align with SDG targets and adjust policies accordingly.
1. Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) Addressed or Connected
- SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
- The article discusses manufacturing production, employment, and capacity utilization, which are directly related to economic growth and employment quality.
- SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
- The focus on manufacturing production and value added relates to industrial development and infrastructure improvement.
2. Specific Targets Under Those SDGs
- SDG 8 Targets
- Target 8.2: Achieve higher levels of economic productivity through diversification, technological upgrading, and innovation, including through a focus on high-value added and labor-intensive sectors.
- Target 8.5: Achieve full and productive employment and decent work for all women and men, including young people and persons with disabilities, and equal pay for work of equal value.
- SDG 9 Targets
- Target 9.2: Promote inclusive and sustainable industrialization and, by 2030, significantly raise industry’s share of employment and gross domestic product.
- Target 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable, with increased resource-use efficiency and greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies.
3. Indicators Mentioned or Implied in the Article
- For SDG 8
- Employment levels in manufacturing (implied by employment and aggregate hours data).
- Productivity measures such as manufacturing production and value added in constant dollars.
- For SDG 9
- Capacity utilization rate in manufacturing (percentage of potential output being used).
- Value added in manufacturing as a share of GDP (implied by value added data).
4. Table: SDGs, Targets and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth |
|
|
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure |
|
|
Source: econbrowser.com








