Drinking water access and quality in the Gaza Strip prior to 7 October 2023 and implications for reconstruction – BioMed Central
Report on Water Security and Health Challenges in the Gaza Strip: Emphasizing Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
Introduction
This report addresses the critical issues related to water security, quality, and public health in the Gaza Strip, with a focus on the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-being), SDG 6 (Clean Water and Sanitation), and SDG 13 (Climate Action). The analysis is based on extensive research and data from various authoritative sources.
Water Security and Supply Challenges
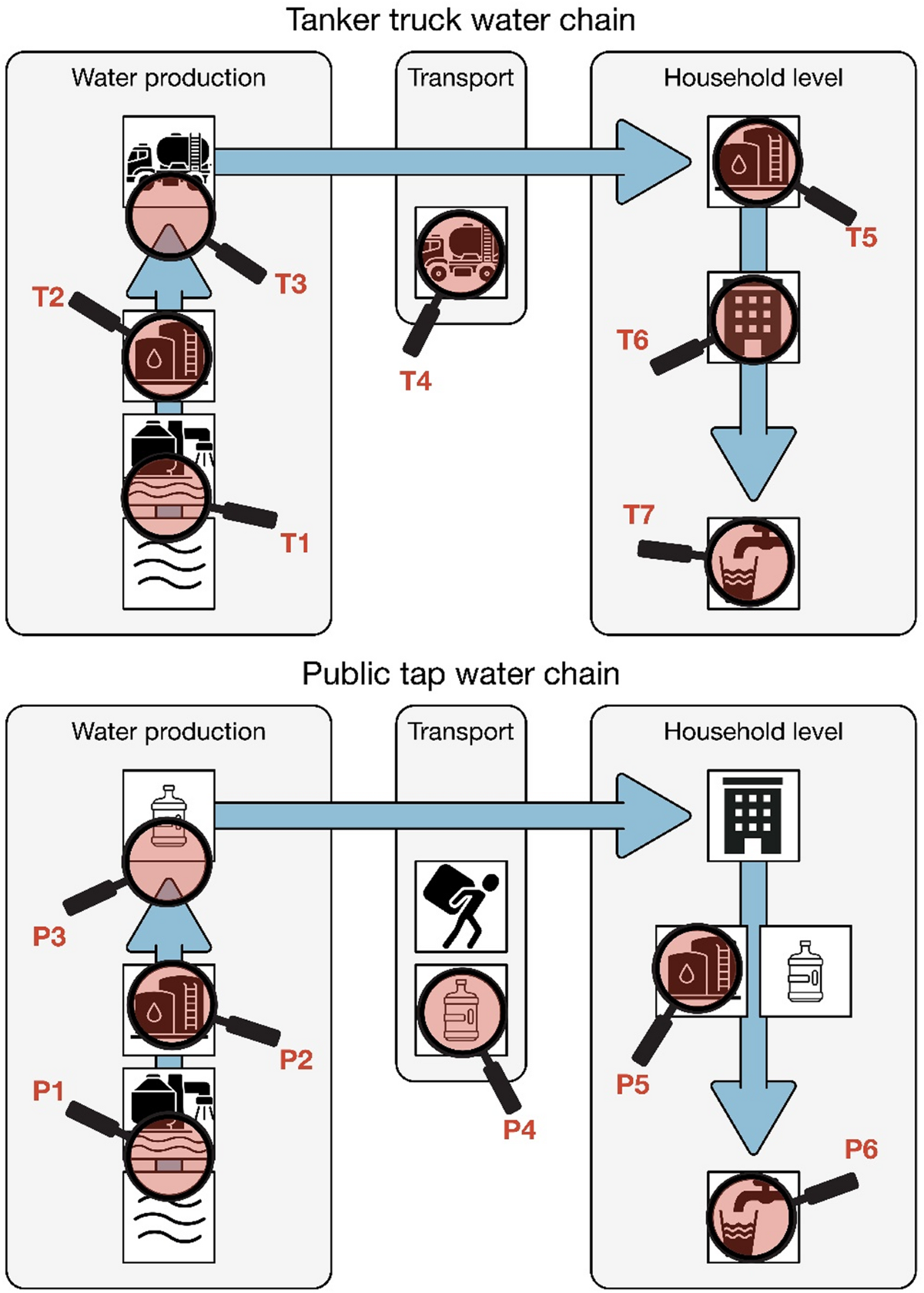
The Gaza Strip faces severe water supply, sanitation, and hygiene challenges, as highlighted by the World Bank’s 2018 diagnostic report. The scarcity of clean water and inadequate sanitation infrastructure threaten public health and sustainable development.
- SDG 6: Ensuring availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all is hindered by limited water resources and infrastructure deficits.
- Desalinated water is a primary source, but its quality and health impacts require continuous monitoring and improvement.
- Community water supply systems face operational and financial challenges affecting service delivery.
Water Quality and Public Health Implications
Studies by the Palestinian Water Authority and other organizations reveal contamination issues and microbial risks in drinking water, contributing to waterborne diseases and antimicrobial resistance.
- Waterborne Diseases: Characterization of potential diseases in Wadi Gaza indicates significant health risks linked to water quality.
- Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR): The presence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria in water supplies and healthcare settings exacerbates health challenges, aligning with SDG 3 targets on combating communicable diseases.
- Health Outcomes: Research shows associations between water mineral content and cardiovascular, bone, and dental health, emphasizing the need for water quality standards.
Environmental and Conflict-Related Impacts
The ongoing conflict and climate crisis in Gaza have profound effects on water resources and management, complicating efforts to achieve SDG 13 and SDG 16 (Peace, Justice, and Strong Institutions).
- Armed conflict disrupts water governance and damages infrastructure, leading to deteriorated water quality and availability.
- Climate change exacerbates water scarcity and vulnerability, requiring adaptive and resilient water management strategies.
- Soil and groundwater contamination further threaten sustainable water use and public health.
Community Perception and Water Use Behavior
Public perception of water quality influences water source choices, with many households resorting to unimproved sources due to undesirable water characteristics.
- Community satisfaction and trust in water services are critical for sustainable water management (SDG 6).
- Water insecurity is linked to mental health issues, highlighting the intersection of SDG 3 and SDG 6.
- Effective community-based management and demand-oriented policies can enhance water service delivery and sustainability.
Policy and Monitoring Recommendations
To align with the SDGs, the following actions are recommended:
- Implement comprehensive water quality monitoring systems to ensure safe drinking water (SDG 6.1).
- Strengthen healthcare capacity to address waterborne diseases and antimicrobial resistance (SDG 3.3 and 3.d).
- Promote integrated water resource management considering conflict and climate impacts (SDG 6.5 and SDG 13).
- Enhance community engagement and education on water use and hygiene practices (SDG 6.b).
- Develop policies for sustainable financing and cost recovery in water supply systems (SDG 6.a).
Conclusion
The water security and health challenges in the Gaza Strip are complex and multifaceted, directly impacting the achievement of multiple Sustainable Development Goals. Addressing these issues requires coordinated efforts across sectors, integrating health, environmental management, and community participation to ensure sustainable and equitable access to safe water and improved health outcomes.
References
Key references include reports and studies from the World Bank, Palestinian Water Authority, WHO, UNICEF, and various academic research articles addressing water quality, health impacts, antimicrobial resistance, and conflict-related water governance challenges.
1. Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) Addressed or Connected
- SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being
- The article discusses water quality, microbial contamination, antimicrobial resistance, and their impacts on human health, including diseases and non-communicable diseases.
- SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation
- Issues of water supply, sanitation, hygiene, water security, water quality, and water management in Gaza Strip are central themes.
- SDG 13: Climate Action
- The article references climate crisis impacts on water resources in Gaza.
- SDG 16: Peace, Justice and Strong Institutions
- Impacts of armed conflict on water governance and water resources management are discussed.
- SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals
- Collaborations between various organizations and authorities for water quality monitoring and health assessments are mentioned.
2. Specific Targets Under Identified SDGs
- SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being
- Target 3.3: End epidemics of water-borne diseases and combat communicable diseases.
- Target 3.4: Reduce premature mortality from non-communicable diseases through prevention and treatment.
- Target 3.d: Strengthen capacity for early warning, risk reduction, and management of health risks.
- SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation
- Target 6.1: Achieve universal and equitable access to safe and affordable drinking water.
- Target 6.3: Improve water quality by reducing pollution and minimizing release of hazardous chemicals.
- Target 6.4: Increase water-use efficiency and ensure sustainable withdrawals.
- Target 6.b: Support local engagement in water and sanitation management.
- SDG 13: Climate Action
- Target 13.1: Strengthen resilience and adaptive capacity to climate-related hazards.
- SDG 16: Peace, Justice and Strong Institutions
- Target 16.6: Develop effective, accountable, and transparent institutions at all levels (related to water governance in conflict zones).
- SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals
- Target 17.17: Encourage effective partnerships and multi-stakeholder collaboration.
3. Indicators Mentioned or Implied to Measure Progress
- Water Quality Indicators
- Microbial contamination levels in drinking water distribution systems (e.g., presence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Enterobacteriaceae).
- Concentration of chemical contaminants such as nitrates and minerals (calcium, magnesium, hardness) in water.
- Compliance with drinking water standards and guidelines (e.g., WHO Guidelines for Drinking-water Quality, Palestinian Drinking Water Standards).
- Health Indicators
- Incidence and prevalence of water-borne diseases and non-communicable diseases linked to water quality (e.g., hypertension, cardiovascular diseases, cancer mortality rates).
- Antimicrobial resistance rates in bacterial isolates from clinical and environmental sources.
- Population exposure to unsafe water and related health outcomes (e.g., infant methemoglobinemia, osteoporosis occurrence).
- Water Security and Access Indicators
- Access to safely managed drinking water services at household level.
- Water supply reliability and customer satisfaction with water services.
- Water consumption patterns and use of alternative unimproved water sources.
- Governance and Conflict Impact Indicators
- Assessment of water governance effectiveness in conflict-affected areas.
- Impact of armed conflict on water infrastructure and resource management.
4. Table of SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being |
|
|
| SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation |
|
|
| SDG 13: Climate Action |
|
|
| SDG 16: Peace, Justice and Strong Institutions |
|
|
| SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals |
|
|
Source: ehjournal.biomedcentral.com








