United States Municipal Drinking Water Market Outlook – openPR.com

Global Municipal Drinking Water Market: A Report on Contributions to Sustainable Development Goals
Market Overview and Alignment with SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation
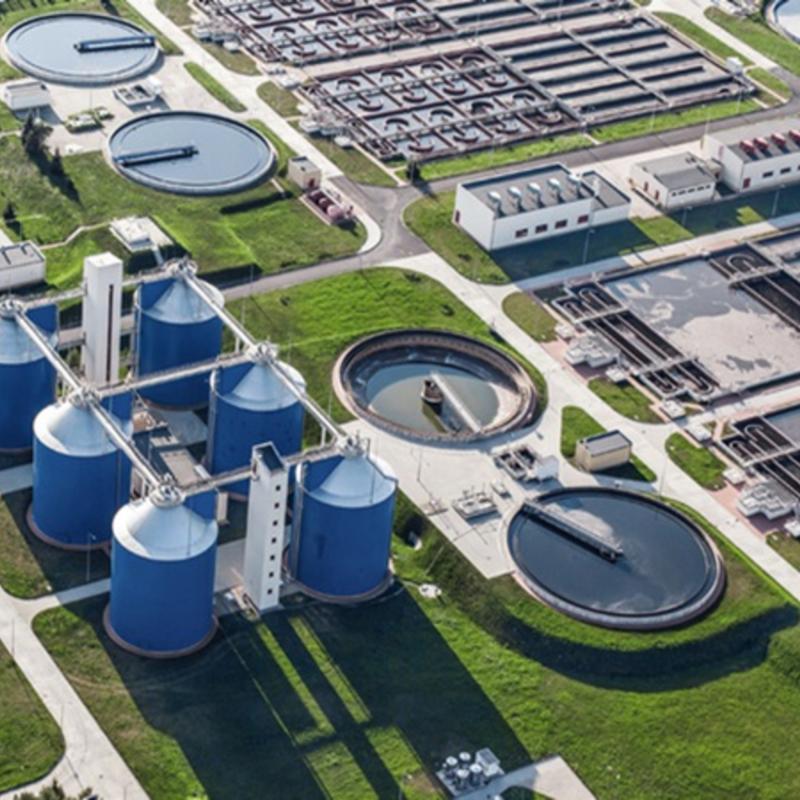
The Global Municipal Drinking Water Market is projected for significant growth, driven by its critical role in achieving Sustainable Development Goal 6 (SDG 6), which aims to ensure the availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all. The market encompasses the systems, infrastructure, and technologies required to provide safe, clean, and potable water to populations, directly supporting public health (SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being) and the development of resilient urban environments (SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities).
Key drivers for market expansion include:
- Increasing global urbanization and population growth, which place greater demand on water resources.
- Implementation of stringent water quality regulations by governments worldwide to protect public health.
- Growing investments in modernizing aging water infrastructure to improve efficiency and reduce water loss, aligning with SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure).
Technological Advancements and Innovation for Sustainable Water Management (SDG 9)
Technological innovation is central to advancing the municipal drinking water sector and meeting sustainability targets. Modern solutions enhance efficiency, safety, and resource management, contributing directly to SDG 9 by building resilient infrastructure and fostering innovation.
- Core Treatment Technologies: Established methods such as filtration, chlorination, UV treatment, and reverse osmosis remain fundamental to ensuring water potability.
- Smart Water Management: The adoption of smart technologies, including real-time monitoring systems and IoT-enabled distribution networks, improves operational efficiency, minimizes water loss, and ensures consistent quality.
- Energy-Efficient Systems: A focus on developing energy-efficient treatment systems helps reduce the environmental footprint of water management, supporting SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production).
Recent Industry Developments and Regional Contributions to SDGs
United States
Recent developments in the U.S. focus on integrating advanced technologies to enhance water safety and infrastructure resilience, contributing to SDG 3 and SDG 11.
- Xylem Inc. has expanded its municipal water treatment solutions by integrating advanced filtration and disinfection technologies.
- SUEZ Water Technologies USA launched smart water management systems to improve water quality and distribution efficiency.
- Pentair has partnered with municipalities to implement next-generation drinking water systems, enhancing public health and supply reliability.
Europe
European initiatives emphasize smart technology and IoT to create sustainable urban water supplies, aligning with SDG 9 and SDG 11.
- Veolia Europe introduced advanced municipal drinking water systems that incorporate IoT and real-time monitoring capabilities.
- SUEZ Europe expanded its water treatment solutions for urban centers to improve overall water quality for residents.
- Xylem Europe has partnered with municipalities to deploy next-generation water purification systems, supporting sustainable urban development.
Japan
In Japan, key players are launching integrated solutions that combine treatment with advanced monitoring to ensure water safety and sustainability, supporting SDG 6.
- Kurita Water Industries launched comprehensive municipal drinking water solutions integrating filtration, disinfection, and monitoring.
- Toshiba Water Solutions expanded its water treatment offerings for both urban and industrial applications.
- Hitachi Zosen Japan has partnered with cities to implement advanced water treatment systems, improving safety and long-term sustainability.
Market Segmentation
By Type
- Waste Water Treatment
- Potable Water Treatment
- Sea Water Treatment
By Treatment Systems
- Chemicals
- Membrane Systems
- Disinfection Equipment and Filters
- Others
By End-User
- Public Water Supply
- Private Water Supply
- Institute Water Supply
- Hotels and Restaurants
- Industrial Water Supply
- Others
Competitive Landscape
The market features several key international corporations dedicated to advancing water treatment technology and infrastructure. Leading companies include:
- Evoqua Water Technologies
- Pall Corporation
- Veolia Water Technologies
- Kurita Water Industries
- Aquatech
- MWH Global
- WesTech Engineering
- Degremont Industry
- Suez Environnement
- RWL Water Group
Analysis of Sustainable Development Goals in the Article
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
The article on the Municipal Drinking Water Market addresses several Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) due to its focus on providing clean water, developing infrastructure, promoting public health, and fostering sustainable urban environments. The primary SDGs connected are:
- SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation: This is the most directly relevant SDG, as the entire article revolves around the systems, technologies, and infrastructure required to provide “safe, clean, and potable water supply.”
- SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities: The market specifically targets “municipal” and “urban populations,” directly linking to the goal of making cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient, and sustainable. The provision of clean water is a fundamental service for sustainable cities.
- SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being: The article explicitly states that “public health initiatives are key drivers” and that new systems are implemented for “enhancing public health and reliability.” Access to safe drinking water is crucial for preventing waterborne diseases and ensuring well-being.
- SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure: The text heavily emphasizes technological advancements and infrastructure development. It discusses “investments in smart water management and infrastructure modernization,” “IoT-enabled distribution networks,” and “advanced filtration and disinfection technologies,” which are all central to this SDG.
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
Based on the article’s content, several specific SDG targets can be identified:
- Target 6.1: “By 2030, achieve universal and equitable access to safe and affordable drinking water for all.” The article’s core subject—the market for providing “safe, clean, and potable water supply” to populations—is a direct effort towards achieving this target.
- Target 6.3: “By 2030, improve water quality by reducing pollution…” The mention of “stringent water quality regulations” and the deployment of technologies like “filtration, UV treatment, reverse osmosis, and chlorination” are aimed at improving the quality of municipal water, aligning with this target.
- Target 11.1: “By 2030, ensure access for all to adequate, safe and affordable housing and basic services and upgrade slums.” Safe drinking water is a critical “basic service” for urban populations. The market’s focus on “municipal drinking water” systems directly supports the provision of this service in cities.
- Target 3.9: “By 2030, substantially reduce the number of deaths and illnesses from hazardous chemicals and air, water and soil pollution and contamination.” By focusing on improving water treatment and purification to enhance “public health,” the industry’s efforts contribute to reducing illnesses caused by contaminated water.
- Target 9.1: “Develop quality, reliable, sustainable and resilient infrastructure…to support economic development and human well-being.” The article highlights “infrastructure modernization” and the implementation of “next-generation drinking water systems” to enhance “reliability,” which directly corresponds to building resilient water infrastructure.
- Target 9.4: “By 2030, upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable, with increased resource-use efficiency and greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies…” The article points to trends like “smart water management systems,” “IoT-enabled distribution networks,” and “energy-efficient treatment systems” as key developments, reflecting a move towards more sustainable and efficient technologies.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
The article, being a market analysis, does not cite official SDG indicators but implies several metrics that can be used to measure progress:
- Adoption of Advanced Technologies: Progress can be measured by the rate of adoption of technologies mentioned in the article, such as “advanced filtration and disinfection technologies,” “smart water management systems,” and “IoT-enabled distribution networks.” This serves as an indicator for Targets 9.4 and 6.3.
- Investment in Infrastructure: The level of “investments in… infrastructure modernization” is a key implied indicator for measuring progress towards Target 9.1. The growth of the municipal drinking water market itself reflects increased investment.
- Implementation of Real-Time Monitoring: The deployment of “real-time monitoring” systems, as mentioned in the recent developments by Veolia and Kurita Water Industries, is a specific indicator for improved water quality management (Target 6.3) and efficient infrastructure (Target 9.4).
- Public-Private Partnerships: The article notes that companies like Pentair, Xylem, and Hitachi Zosen have “partnered with cities” and “municipalities.” The number and scale of such partnerships can be an indicator of accelerated implementation of improved water systems, contributing to Targets 6.1 and 11.1.
- Improved Distribution Efficiency: The launch of systems aimed at “improving quality and distribution efficiency” by SUEZ provides a direct, measurable outcome. This can be tracked through metrics like reduced water loss and consistent supply, indicating progress towards Targets 9.1 and 9.4.
4. Summary Table of SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators (Implied from the article) |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation | 6.1: Achieve universal and equitable access to safe and affordable drinking water. 6.3: Improve water quality. |
Growth of the municipal drinking water market; Implementation of advanced treatment systems (filtration, UV, reverse osmosis); Use of real-time monitoring for water quality. |
| SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities | 11.1: Ensure access for all to adequate, safe and affordable basic services. | Number of partnerships between technology companies and municipalities to deploy new water systems; Expansion of water treatment solutions for urban centers. |
| SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being | 3.9: Substantially reduce deaths and illnesses from water pollution and contamination. | Deployment of next-generation drinking water systems designed to enhance public health; Adherence to stringent water quality regulations. |
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure | 9.1: Develop quality, reliable, sustainable and resilient infrastructure. 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure with clean and environmentally sound technologies. |
Level of investment in water infrastructure modernization; Rate of adoption of smart water management, IoT-enabled networks, and energy-efficient treatment systems; Improved distribution efficiency. |
Source: openpr.com

What is Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0