EV Charging Smart Grids Market Sees Rapid Growth To 2031 | ABB – openPR.com

Report on the Global Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging Smart Grids Market and its Alignment with Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
Executive Summary
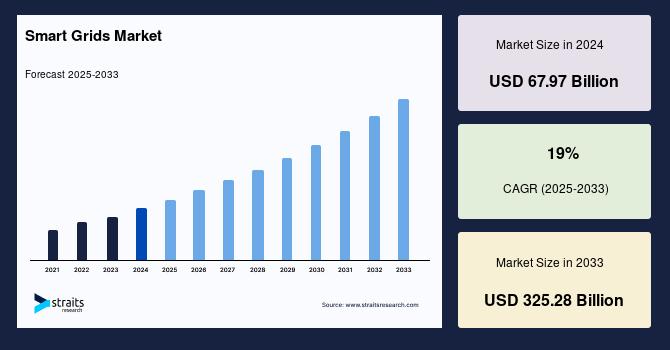
The Global EV Charging Smart Grids Market is experiencing substantial growth, with a valuation of US$ 1.2 billion in 2022 projected to reach US$ 10.1 billion by 2030, expanding at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 30.0% from 2024 to 2031. This expansion is intrinsically linked to the global pursuit of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). EV charging smart grids, which integrate electric vehicle charging with advanced grid technology, are pivotal in advancing goals related to clean energy, sustainable infrastructure, and climate action. These systems enable efficient load balancing, real-time energy management, and bi-directional power flow, thereby supporting the transition to a low-carbon economy.
Contribution to Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
The development and adoption of EV charging smart grids directly support the achievement of several key SDGs:
- SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy: Smart grids optimize the use of renewable energy sources for EV charging, enhancing grid stability and efficiency. By managing energy demand in real-time, they help make clean energy more reliable and accessible, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
- SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure: This market represents a significant advancement in building resilient and sustainable infrastructure. The technology fosters innovation in energy management and supports the modernization of the electricity grid to accommodate future demands.
- SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities: As urban areas face rising electricity demand from EVs, smart grids provide a critical solution for managing this load, improving grid resilience, and preventing blackouts. This contributes to the creation of safer, more resilient, and sustainable cities.
- SDG 13: Climate Action: By facilitating the widespread adoption of electric vehicles and maximizing the use of renewable energy, smart grids are a cornerstone of strategies to decarbonize the transportation and energy sectors, which is essential for mitigating climate change.
Market Analysis and Projections
Market Growth
The market is forecast to grow significantly, driven by increasing EV adoption, declining battery costs, and government initiatives promoting sustainable transportation.
- 2022 Market Value: US$ 1.2 billion
- 2030 Projected Market Value: US$ 10.1 billion
- Forecast CAGR (2024-2031): 30.0%
Market Segmentation
The market is segmented to provide a detailed analysis of its core components:
- By Charging Station Type:
- Public Charging Stations
- Private Charging Stations
- By Technology:
- Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Technology
- Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) Technology
Global Initiatives and Regional Outlook
Recent Industry Developments
Global initiatives reflect a strong commitment to the SDGs through the promotion of e-mobility and smart grid infrastructure.
- On May 31, 2023, the Government of India announced a target of 30% electric vehicle penetration by 2030, a policy that directly supports SDG 11 and SDG 13 by promoting sustainable urban transport and reducing emissions.
- On June 8, 2023, Delta announced its participation in Europe’s Smarter EV Charging initiative, showcasing innovative energy solutions that align with SDG 7 and SDG 9 by advancing the development of a low-carbon electricity grid.
Regional Analysis
The market is analyzed across key global regions, each contributing to the sustainable transition:
- North America (U.S., Canada, Mexico)
- Europe (U.K., Italy, Germany, Russia, France, Spain, The Netherlands)
- Asia-Pacific (India, Japan, China, South Korea, Australia, Indonesia)
- South America (Colombia, Brazil, Argentina)
- Middle East & Africa (Saudi Arabia, U.A.E., South Africa)
Key Industry Stakeholders
Leading corporations are at the forefront of developing the technology and infrastructure necessary to achieve these sustainable goals. Key market players include:
- ABB Ltd.
- ChargePoint Inc.
- EVgo Services LLC
- Schneider Electric
- Blink Charging Co.
- Toshiba Corporation
- Mojo Mobility Inc.
- General Electric
- Robert Bosch GmbH
- Chargemaster plc
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
- SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy – The article focuses on smart grids that manage electricity demand from electric vehicles (EVs), optimize the use of renewable energy, and support a low-carbon electricity grid.
- SDG 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure – The text discusses the development of EV charging infrastructure, smart grid technology, and innovations that make energy systems more resilient and sustainable.
- SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities – The article highlights how smart grids help cities manage the increasing demand for EV charging, contributing to more sustainable urban transport systems.
- SDG 13: Climate Action – By facilitating the adoption of EVs and supporting a low-carbon electricity grid, the technologies discussed are crucial for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and combating climate change.
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
-
SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
- Target 7.2: By 2030, increase substantially the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix. The article states that smart grids help “optimizing renewable energy use,” which is essential for integrating intermittent sources like solar and wind into the grid.
- Target 7.3: By 2030, double the global rate of improvement in energy efficiency. The article describes how EV charging smart grids enable “efficient load balancing” and “real-time energy management,” which are direct measures to improve energy efficiency and reduce peak demand pressure.
-
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure
- Target 9.1: Develop quality, reliable, sustainable and resilient infrastructure. The article is centered on “electric vehicle charging infrastructure” and “smart grid technology” that improves “grid resilience.”
- Target 9.4: By 2030, upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable, with increased resource-use efficiency and greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies. The entire concept of EV charging smart grids, including Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology, represents an upgrade to infrastructure using clean technology.
-
SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
- Target 11.2: By 2030, provide access to safe, affordable, accessible and sustainable transport systems for all. The article mentions the Indian government’s goal to have “30% electric vehicles on the road by 2030,” which is a move towards a sustainable transport system, enabled by the charging infrastructure discussed.
-
SDG 13: Climate Action
- Target 13.2: Integrate climate change measures into national policies, strategies and planning. The article cites the “Smarter EV Charging initiative in Europe” and the Indian government’s policy to increase EV adoption as examples of national and regional strategies to develop a “low-carbon electricity grid.”
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
-
Market Growth in Sustainable Infrastructure
The article provides a direct financial metric for the growth of the smart grid market: “The Global EV Charging Smart Grids Market reached US$ 1.2 billion in 2022 and is expected to reach US$ 10.1 billion by 2030.” This financial growth serves as an indicator for investment in and development of sustainable infrastructure (Target 9.1).
-
Adoption Rate of Clean Technology
A specific national target is mentioned: “the Government of India aims to have 30% electric vehicles on the road by 2030.” This percentage is a clear indicator for measuring the adoption of sustainable transport (Target 11.2) and clean technologies (Target 9.4).
-
Development of Low-Carbon Solutions
The participation of companies like Delta in the “Smarter EV Charging initiative in Europe” to support a “low-carbon electricity grid” is an indicator of progress. While not a quantitative metric, tracking the number and scale of such initiatives indicates progress towards integrating climate change measures (Target 13.2) and increasing the share of renewable energy (Target 7.2).
4. Table of SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy | 7.2: Increase the share of renewable energy. 7.3: Double the rate of improvement in energy efficiency. |
– Implementation of systems for “optimizing renewable energy use.” – Adoption of smart grids for “efficient load balancing” and “real-time energy management.” |
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure | 9.1: Develop sustainable and resilient infrastructure. 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure with clean and environmentally sound technologies. |
– Market size and growth of the EV Charging Smart Grids Market (from US$ 1.2 billion in 2022 to US$ 10.1 billion by 2030). – Investment in “electric vehicle charging infrastructure” and “smart grid technology.” |
| SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities | 11.2: Provide access to sustainable transport systems. | – Percentage of electric vehicles on the road (e.g., India’s goal of 30% by 2030). |
| SDG 13: Climate Action | 13.2: Integrate climate change measures into national policies. | – National policies and targets for EV adoption (e.g., Government of India). – Regional initiatives like the “Smarter EV Charging initiative in Europe” to support a “low-carbon electricity grid.” |
Source: openpr.com

What is Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0