Demand for Energy Intelligence Solution in Japan | Global Market Analysis Report – 2035 – Future Market Insights
Report on the Demand for Energy Intelligence Solutions in Japan: 2025-2035 Outlook
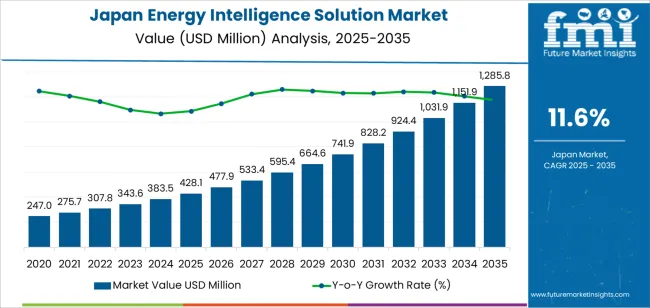
The demand for energy intelligence solutions in Japan is forecast to experience substantial growth, increasing from USD 428.1 million in 2025 to USD 1,285.8 million by 2035, at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 11.6%. This expansion is intrinsically linked to Japan’s national commitment to achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly in the areas of energy, climate action, and sustainable infrastructure.
Alignment with Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
The growth of this market is a direct enabler of several key SDGs. The adoption of these solutions is critical for Japan’s progress towards a sustainable and carbon-neutral future.
- SDG 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy): Energy intelligence solutions are fundamental for managing the integration of renewable energy sources into the national grid, optimizing energy distribution, and improving overall energy efficiency, thereby supporting the transition to cleaner energy systems.
- SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure): The market’s reliance on innovations like AI, IoT, and data analytics fosters the development of resilient, smart, and sustainable infrastructure. These technologies are upgrading industrial facilities and energy grids across Japan.
- SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities): The emphasis on smart buildings, particularly in the commercial sector, and smart city initiatives directly contributes to making urban areas more energy-efficient, resilient, and sustainable.
- SDG 13 (Climate Action): A primary driver for the market is Japan’s goal of achieving net-zero carbon emissions. Energy intelligence solutions provide the necessary tools for monitoring, managing, and reducing greenhouse gas emissions across all sectors.
Market Forecast and Key Metrics
Projected Growth Trajectory
- Phase 1 (2025-2030): The market is projected to grow from USD 428.1 million to USD 664.6 million. This initial phase will be driven by widespread adoption as industries and consumers invest in energy efficiency to align with national sustainability policies and reduce operational costs.
- Phase 2 (2030-2035): The market value is expected to nearly double, reaching USD 1,285.8 million. Growth in this period will be fueled by advanced technological integration, including AI and predictive analytics, and the maturation of smart city and distributed energy resource (DER) frameworks.
Quick Statistics
- 2025 Market Value: USD 428.1 million
- 2035 Forecast Value: USD 1,285.8 million
- Forecast CAGR (2025-2035): 11.6%
- Leading Solution Segment: Energy Management Systems
- Leading End-Use Segment: Commercial Buildings
Market Drivers and Challenges
Primary Growth Drivers
- National Sustainability Policies: Japan’s “Green Transformation (GX)” policy is a significant catalyst, pushing for digitalization and carbon-neutral growth in line with SDG 13.
- Technological Innovation: Advancements in AI, machine learning, and IoT are enhancing the capabilities of energy intelligence solutions, making them more effective for predictive maintenance and optimization, supporting SDG 9.
- Economic and Regulatory Pressures: Rising electricity costs and stringent regulations on emissions compel commercial and industrial sectors to adopt advanced energy management tools to ensure responsible consumption (SDG 12).
- Infrastructure Modernization: The expansion of data centers, smart manufacturing, and EV charging infrastructure necessitates sophisticated tools to manage increased electricity demand efficiently.
Key Market Restraints
- High Upfront Investment: The initial cost of deploying integrated intelligence platforms can be a barrier for some organizations.
- Legacy System Integration: Retrofitting older, fragmented energy systems with modern digital solutions presents significant technical challenges.
- Cybersecurity Concerns: The increasing connectivity of energy systems raises concerns about data governance and security.
Segment-Wise Analysis
Analysis by End-Use
Commercial buildings are the dominant end-use segment, accounting for 35% of the market demand. This leadership is driven by the corporate sector’s focus on reducing operational costs and achieving sustainability certifications. Implementing energy intelligence solutions in commercial buildings is a critical step towards creating sustainable cities (SDG 11) and promoting corporate responsibility.
Analysis by Solution
Energy Management Systems (EMS) represent the largest solution segment, with a 32.5% market share. EMS are crucial for organizations to monitor and control energy consumption in real-time, enabling them to reduce their carbon footprint and achieve efficiency targets aligned with SDG 9 and SDG 13.
Regional Demand Outlook
Growth in demand for energy intelligence solutions is evident across all regions of Japan, driven by specific local initiatives that support national SDG commitments.
- Kyushu & Okinawa (14.5% CAGR): This region leads in growth due to its aggressive adoption of renewable energy sources, which requires advanced systems for grid management and optimization, directly supporting SDG 7.
- Kanto (13.4% CAGR): High energy demand from the densely populated Tokyo metropolitan area and a focus on smart city projects drive the need for efficient energy management, contributing to SDG 11.
- Kinki (11.7% CAGR): The strong industrial base in cities like Osaka is adopting these solutions to enhance manufacturing efficiency and meet sustainability goals, aligning with SDG 9.
- Chubu (10.3% CAGR): The manufacturing sector is the primary driver, seeking to optimize energy consumption and reduce operational costs.
- Tohoku (9.1% CAGR) and Rest of Japan (8.6% CAGR): These regions show steady growth as sustainability efforts and the integration of renewable energy become more widespread.
Competitive Landscape
The market is led by established global technology firms that provide solutions integral to Japan’s decarbonization and digital transformation efforts. These companies are key partners in helping Japanese industries achieve their sustainability targets.
Key Market Players
- Schneider Electric: Holds an estimated market share of 29.0%, providing leading energy management and smart building platforms.
- Siemens
- ABB Ltd.
- Emerson
- General Electric
- Honeywell International Inc.
Analysis of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in the Article
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
- SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy: The article directly addresses this goal by focusing on energy efficiency, the integration of renewable energy sources like solar and wind, and the modernization of energy infrastructure through smart grid technologies. The entire premise of “energy intelligence solutions” is to manage energy more cleanly and efficiently.
- SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure: This goal is central to the article’s discussion of technological advancements such as AI, IoT, and data analytics being applied to energy systems. It also covers the upgrading of infrastructure (smart buildings, smart grids) and retrofitting industries to become more sustainable and resource-efficient.
- SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities: The article connects to this SDG through its emphasis on “smart city initiatives,” “green building certifications,” and the adoption of energy management systems in commercial and residential buildings to reduce the environmental impact of urban areas.
- SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production: The core function of energy intelligence solutions—to monitor, analyze, and optimize energy usage—directly supports the efficient use of natural resources. The article highlights how these solutions help businesses reduce energy costs and enhance operational efficiency, which aligns with sustainable consumption and production patterns.
- SDG 13: Climate Action: This goal is explicitly addressed through Japan’s stated commitments to “achieving net-zero carbon emissions,” “decarbonization,” and “carbon neutrality by 2050.” The article positions energy intelligence solutions as a key tool for reducing carbon footprints and greenhouse gas emissions.
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
-
SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
- Target 7.2: Increase substantially the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix. The article mentions Japan’s efforts to integrate renewable sources like “solar and wind” and the role of energy intelligence in managing these sources.
- Target 7.3: Double the global rate of improvement in energy efficiency. The article is fundamentally about improving energy efficiency across industrial, commercial, and residential sectors through “energy management systems” and “energy-efficient solutions.”
-
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
- Target 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable, with increased resource-use efficiency and greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies. The text discusses “retrofitting legacy energy systems,” “smart manufacturing,” and the adoption of “digital-transformation initiatives” in industrial facilities.
-
SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
- Target 11.6: Reduce the adverse per capita environmental impact of cities. This is addressed through the focus on improving energy efficiency in “commercial buildings” and “residential buildings,” which helps reduce overall energy consumption and emissions in urban areas.
- Target 11.b: Increase the number of cities implementing integrated policies for climate change mitigation. The article’s reference to Japan’s “smart city initiatives” and “green building certifications” reflects the implementation of such policies.
-
SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
- Target 12.2: Achieve the sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources. The deployment of energy intelligence solutions to “monitor, analyze, and optimize energy usage” is a direct measure to ensure the efficient use of energy resources.
-
SDG 13: Climate Action
- Target 13.2: Integrate climate change measures into national policies, strategies and planning. The article cites Japan’s “Green Transformation (GX)” policy and its national goal of achieving “carbon neutrality by 2050” as key drivers for the adoption of these technologies.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
-
SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
- Indicator for Target 7.2: The article implies progress through the “integration of renewable energy sources” and “clean energy initiatives” in regions like Kyushu & Okinawa, suggesting an increase in renewable energy capacity and adoption.
- Indicator for Target 7.3: The projected market growth for energy intelligence solutions (from USD 428.1 million in 2025 to USD 1,285.8 million by 2035) serves as a direct financial indicator of investment in energy efficiency. The market share of Energy Management Systems (32.5%) is another specific indicator of adoption.
-
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
- Indicator for Target 9.4: The adoption of energy intelligence solutions by “industrial facilities” and the implementation of “smart manufacturing/facility automation” are key indicators. The article also points to investment in “IoT,” “AI-driven insights,” and “digital-transformation initiatives” as measures of progress.
-
SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
- Indicator for Target 11.6: The market share of energy intelligence solutions in “commercial buildings” (35%) is a quantifiable indicator of efforts to reduce the environmental impact of urban infrastructure. The mention of “green building certifications” also serves as a qualitative indicator.
-
SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
- Indicator for Target 12.2: The rate of adoption of “energy management systems” and “energy analytics platforms” by commercial and industrial entities indicates progress towards more efficient resource management.
-
SDG 13: Climate Action
- Indicator for Target 13.2: The existence of national strategies like the “Green Transformation (GX)” policy is a clear indicator. Furthermore, the availability and adoption of “Carbon Footprint and Sustainability Tracking Platform” solutions, mentioned as a market segment, provide a direct tool for measuring and managing emissions reductions.
4. Summary Table of SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy | 7.2: Increase substantially the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix. | Increased integration of renewable energy sources like solar and wind, particularly in regions like Kyushu & Okinawa. |
| SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy | 7.3: Double the global rate of improvement in energy efficiency. | Market value growth of energy intelligence solutions (CAGR of 11.6%); Market share of Energy Management Systems (32.5%). |
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure | 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable. | Adoption of energy intelligence solutions in “industrial facilities”; Implementation of “smart manufacturing” and “digital-transformation initiatives.” |
| SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities | 11.6: Reduce the adverse per capita environmental impact of cities. | Market share of energy intelligence solutions in “commercial buildings” (35%); Pursuit of “green building certifications.” |
| SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities | 11.b: Increase the number of cities implementing integrated policies for climate change mitigation. | Implementation of “smart city initiatives” across Japan. |
| SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production | 12.2: Achieve the sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources. | Deployment of solutions to “monitor, analyze, and optimize energy usage,” enhancing operational efficiency. |
| SDG 13: Climate Action | 13.2: Integrate climate change measures into national policies, strategies and planning. | Implementation of Japan’s “Green Transformation (GX)” policy; Adoption of “Carbon Footprint and Sustainability Tracking Platform” solutions. |
Source: futuremarketinsights.com
What is Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0












































































