Georgia Tech’s Record-Setting $5.8B Economic Impact Leads USG – Georgia Tech News Center

Georgia Institute of Technology’s Contribution to Sustainable Development Goals: Fiscal Year 2024 Report
SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
Georgia Tech’s activities in fiscal year 2024 significantly advanced SDG 8 by promoting sustained, inclusive, and sustainable economic growth, full and productive employment, and decent work for all.
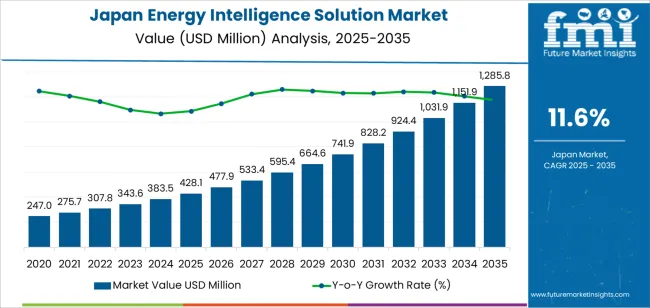
- Economic Impact: The Institute generated a record-setting economic impact of $5.8 billion, marking a 9.9% increase from the previous fiscal year. This represents 25% of the total $23.1 billion impact from all 26 University System of Georgia (USG) institutions.
- Job Creation: A total of 36,705 jobs were generated, directly contributing to state and local employment.
- On-campus employment accounted for 11,634 jobs.
- Institute-related spending created an additional 25,071 jobs in the community.
SDG 4: Quality Education
The Institute demonstrated its commitment to inclusive and equitable quality education and the promotion of lifelong learning opportunities for all.
- Educational Attainment: 12,202 degrees were conferred in fiscal year 2024, equipping a new generation of talent.
- Return on Educational Investment: Graduates from the Class of 2024 are projected to earn over $1.4 million more throughout their careers than they would without a college degree. The class is expected to accumulate more than $44.5 billion in lifetime earnings.
- Institutional Recognition: For the third consecutive year, The Princeton Review named Georgia Tech the best public value college, underscoring its role in providing high-return, quality education.
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure & SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
Georgia Tech’s focus on research and innovation directly supports the development of resilient infrastructure, sustainable industrialization, and the strengthening of communities.
- Fostering Innovation: As stated by President Ángel Cabrera, investment in Georgia Tech “fuels the development of our nation’s finest talent, research, and innovation,” which are foundational elements for achieving SDG 9.
- Strengthening Communities: The substantial economic output and job creation serve to strengthen communities across Georgia, making them more inclusive, safe, resilient, and sustainable in line with SDG 11.
Broader Impact on SDG 1 (No Poverty) & SDG 10 (Reduced Inequalities)
The long-term outcomes of a Georgia Tech education contribute directly to poverty reduction and the lessening of inequalities.
- By providing education that leads to significantly higher lifetime earnings, the Institute offers a clear pathway to economic security, directly addressing the targets of SDG 1.
- As a public university offering a high return on investment, Georgia Tech enhances social mobility and provides access to opportunities that help reduce income and social inequalities, aligning with the core principles of SDG 10.
Analysis of SDGs in the Article
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
The article highlights issues that are directly and indirectly connected to several Sustainable Development Goals. The primary focus on economic growth, job creation, and the value of higher education links the content to the following SDGs:
- SDG 4: Quality Education – The article is centered on a university, Georgia Tech, detailing the number of degrees conferred and the significant financial return on investment for its graduates. This directly relates to providing quality tertiary education.
- SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth – The article’s main theme is the university’s economic impact, including a $5.8 billion contribution to the state’s economy and the creation of over 36,000 jobs. This directly addresses the goal of promoting sustained, inclusive, and sustainable economic growth and productive employment.
- SDG 1: No Poverty – By providing education that leads to significantly higher lifetime earnings (“over $1.4 million more than they would without a college degree”), the university contributes to poverty reduction and enhances the financial security of its graduates.
- SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities – The article mentions that the university’s activities are “strengthening communities across our state.” Its substantial economic impact and job creation are fundamental to building resilient and economically strong local communities.
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
Based on the information provided, several specific SDG targets can be identified:
- Target 4.4: “By 2030, substantially increase the number of youth and adults who have relevant skills, including technical and vocational skills, for employment, decent jobs and entrepreneurship.”
- Explanation: The article states that Georgia Tech conferred 12,202 degrees in fiscal year 2024. The high expected earnings of these graduates ($44.5 billion throughout their careers) indicate that the skills they acquired are highly relevant and valued in the job market, directly aligning with this target.
- Target 8.2: “Achieve higher levels of economic productivity through diversification, technological upgrading and innovation…”
- Explanation: The article quotes President Cabrera stating, “Every dollar invested in Georgia Tech fuels the development of our nation’s finest talent, research, and innovation, driving economic growth.” This directly links the university’s focus on research and innovation to achieving higher economic productivity, as evidenced by the $5.8 billion economic impact.
- Target 8.5: “By 2030, achieve full and productive employment and decent work for all…”
- Explanation: The article explicitly mentions job creation as a key impact, stating that “Georgia Tech leads all USG institutions in job creation” and “generated a total of 36,705 jobs.” This is a direct contribution to the goal of achieving full and productive employment.
- Target 1.2: “By 2030, reduce at least by half the proportion of men, women and children of all ages living in poverty…”
- Explanation: The article quantifies the financial benefit of a degree, noting that graduates “can expect to earn over $1.4 million more than they would without a college degree.” This substantial increase in earning potential is a powerful tool for lifting individuals and their families out of poverty.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
Yes, the article provides several quantitative and qualitative indicators that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets:
- Indicator for Target 4.4: The number of degrees conferred annually (12,202 in FY 2024) serves as a direct measure of the number of adults with new, relevant skills. The projected increase in lifetime earnings for graduates ($1.4 million per graduate) serves as an indicator of the quality and relevance of the education provided.
- Indicator for Target 8.2: The total economic impact ($5.8 billion) and its year-over-year growth (a 9.9% increase from FY 2023) are direct indicators of the university’s contribution to economic productivity and growth.
- Indicator for Target 8.5: The total number of jobs generated (36,705) is a clear and direct indicator for measuring progress toward employment goals. This is further broken down into on-campus jobs (11,634) and jobs related to institute spending (25,071).
- Indicator for Target 1.2: The differential in lifetime earnings between a college graduate and a non-graduate ($1.4 million) is a powerful proxy indicator for poverty reduction, as it measures the direct financial uplift provided by the education.
4. Summary Table of SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 4: Quality Education | Target 4.4: Increase the number of youth and adults with relevant skills for employment. |
|
| SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth |
Target 8.2: Achieve higher levels of economic productivity through innovation.
Target 8.5: Achieve full and productive employment and decent work. |
|
| SDG 1: No Poverty | Target 1.2: Reduce the proportion of people living in poverty. |
|
| SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities | Target 11.a: Support positive economic links between areas by strengthening regional development. |
|
Source: news.gatech.edu

What is Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0










/campaigns/16-days-of-activism-against-gender-based-violence/pr-web-banner.tmb-1200v.jpg?sfvrsn=8cc7b98e_1#)