MV joins agreement for future regional wastewater treatment plant – Telluride Daily Planet
Regional Collaboration for Sustainable Wastewater Management
Introduction
The Town of Mountain Village, in partnership with San Miguel County and the Town of Telluride, has taken a significant step forward by approving a memorandum of understanding (MOU) to establish a future sewer authority and develop a new regional wastewater treatment plant. This initiative aligns with several Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly SDG 6 (Clean Water and Sanitation), SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities), and SDG 15 (Life on Land).
Background and Need for a New Facility
- The current wastewater treatment facility is outdated and challenging to upgrade.
- A new facility will help the region comply with health and environmental regulations, supporting SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-being) and SDG 13 (Climate Action).
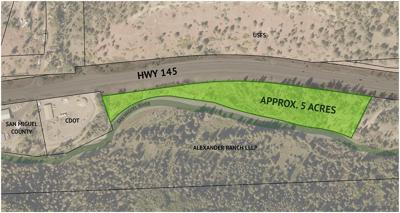
- The Town of Mountain Village has secured a five-acre lot for the potential development of the new plant, located near land acquired for future community housing, promoting SDG 1 (No Poverty) and SDG 10 (Reduced Inequalities).
Project Significance and Regional Impact
Mountain Village Assistant Town Manager Michelle Bulson emphasized the critical nature of this project for regional sustainability:
“If we have a wastewater treatment plant that’s not functioning, that creates a lot of problems. We’re trying to be proactive here.”
The project addresses the growing needs of the region, including managing waste from numerous local festivals, which currently poses challenges for waste disposal facilities.
Key Components of the Agreement
- Land acquisition and swaps to facilitate construction and infrastructure improvements.
- Intersection improvements by San Miguel County to enhance safety and support future housing development.
- Commitment to trail easements, supporting SDG 15 (Life on Land) and promoting sustainable community access.
Maintenance and Financial Sustainability
Council member Pete Duprey highlighted the importance of ongoing investment in the wastewater treatment plant to ensure long-term functionality and cost-effectiveness:
“We have to make sure that we are investing, reinvesting in the plant as time goes on. We want to keep rates low, but we need a high functioning plant so it’s less expensive in the long term.”
This approach supports SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production) by emphasizing efficient use of resources.
Timeline and Future Considerations
- The new regional wastewater treatment plant is expected to be operational within five to ten years.
- In the interim, careful management and capital improvements of the existing plant will continue.
- Balancing current expenditures with future investments is critical for sustainable development.
Water Resource Management and Infrastructure Development
In March, Mountain Village entered another MOU to drill a second well in Ilium and initiate legal water applications, sharing costs estimated between $30,000 and $35,000. This effort supports SDG 6 (Clean Water and Sanitation) and SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure).
Future phases include constructing a storage tank, estimated at $2 million, which will enhance fire response capabilities and community safety, aligning with SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities) and SDG 13 (Climate Action).
Conclusion
The collaborative efforts of Mountain Village, San Miguel County, and Telluride demonstrate a commitment to sustainable infrastructure development that addresses environmental, social, and economic dimensions. By focusing on modernizing wastewater treatment and securing water resources, the region advances multiple Sustainable Development Goals, ensuring a healthier and more resilient community for the future.
1. Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) Addressed in the Article
- SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation
- The article discusses the development of a new regional wastewater treatment plant to replace an outdated facility, aiming to meet health and environmental regulations.
- Ensuring a sustainable water supply for future housing development and fire response is also highlighted.
- SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
- The collaboration between local governments to improve infrastructure supports sustainable urban development.
- Plans for community housing and intersection improvements are mentioned.
- SDG 15: Life on Land
- Commitments to trail easements and land swaps indicate attention to land management and conservation.
- SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being
- Improving wastewater treatment helps protect public health by preventing pollution and contamination.
2. Specific Targets Under the Identified SDGs
- SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation
- Target 6.3: Improve water quality by reducing pollution, minimizing release of hazardous chemicals and materials, and substantially increasing recycling and safe reuse globally.
- Target 6.4: Substantially increase water-use efficiency across all sectors and ensure sustainable withdrawals to address water scarcity.
- Target 6.6: Protect and restore water-related ecosystems.
- SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
- Target 11.1: Ensure access for all to adequate, safe, and affordable housing and basic services.
- Target 11.2: Provide access to safe, affordable, accessible, and sustainable transport systems.
- Target 11.6: Reduce the adverse per capita environmental impact of cities, including air quality and waste management.
- SDG 15: Life on Land
- Target 15.1: Ensure the conservation, restoration, and sustainable use of terrestrial and inland freshwater ecosystems and their services.
- SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being
- Target 3.9: Reduce the number of deaths and illnesses from hazardous chemicals and air, water, and soil pollution and contamination.
3. Indicators Mentioned or Implied in the Article
- Indicators for SDG 6 (Clean Water and Sanitation)
- Proportion of wastewater safely treated (Indicator 6.3.1) – implied by the focus on updating the wastewater treatment plant to meet regulations.
- Proportion of bodies of water with good ambient water quality (Indicator 6.3.2) – implied through the goal of meeting environmental regulations.
- Water use efficiency (Indicator 6.4.1) – implied by the efforts to ensure sustainable water supply for future housing.
- Indicators for SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities)
- Proportion of urban population living in slums or inadequate housing (Indicator 11.1.1) – indirectly related through community housing development.
- Proportion of population with convenient access to public transport (Indicator 11.2.1) – related to intersection improvements for safety and accessibility.
- Municipal solid waste collected and managed in controlled facilities (Indicator 11.6.1) – linked to waste management from festivals and portable toilets.
- Indicators for SDG 15 (Life on Land)
- Forest area as a proportion of total land area (Indicator 15.1.1) – indirectly related through land swaps and trail easements.
- Proportion of important sites for terrestrial and freshwater biodiversity that are covered by protected areas (Indicator 15.1.2) – implied by conservation efforts.
- Indicators for SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-being)
- Mortality rate attributed to household and ambient air pollution (Indicator 3.9.1) – indirectly addressed by improving wastewater treatment to reduce pollution.
4. Table of SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation |
|
|
| SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities |
|
|
| SDG 15: Life on Land |
|
|
| SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being |
|
|
Source: telluridenews.com

What is Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0