Power Plant Boiler Market Size, Share | CAGR of 5.2% – Market.us
Global Power Plant Boiler Market: A Report on Sustainable Development Alignment
The Global Power Plant Boiler Market is projected to expand from USD 21.7 billion in 2024 to USD 36.0 billion by 2034, reflecting a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 5.2%. This growth is intrinsically linked to the global pursuit of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly SDG 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy) and SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure). The market’s trajectory is shaped by the dual pressures of increasing energy demand for economic development and the urgent need for climate action as outlined in SDG 13 (Climate Action). A power plant boiler, a critical component for thermal power generation, remains central to this dynamic, with its evolution reflecting the transition towards more efficient and sustainable energy systems.
Market expansion is driven by the imperative to provide universal access to electricity, a cornerstone of SDG 7. However, this is balanced by stringent environmental regulations compelling a shift away from traditional, high-emission technologies. The adoption of supercritical and ultra-supercritical boilers, which offer higher efficiency and lower emissions, directly supports the targets of SDG 7 and SDG 13. Furthermore, the integration of renewable energy sources like biomass and waste-to-energy systems aligns with SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production) by creating circular economy models within the power sector.
Key Findings in the Context of Sustainable Development
- Market Growth Projection: The market is forecast to reach USD 36.0 billion by 2034, driven by infrastructure development (SDG 9) and the need for reliable energy (SDG 7).
- Dominant Boiler Type: Pulverized coal towers hold a 54.8% share, highlighting the persistent challenge of transitioning from fossil fuels to meet SDG 13 climate targets.
- Prevalent Capacity: Boilers in the 400–800 MW range lead with a 49.1% share, indicating a focus on scalable infrastructure for stable power grids, essential for SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities).
- Leading Technology: Subcritical technology accounts for 48.2% of the market, signifying a large installed base of older, less efficient systems that present an opportunity for modernization in line with SDG 7 and SDG 13.
- Primary Fuel Source: Coal-based systems command a 69.3% market share, underscoring the significant gap that remains in achieving global clean energy and climate goals.
- Main Application: Power generation constitutes 61.3% of applications, directly addressing the core objective of SDG 7 to ensure energy access.
- Regional Leadership: The Asia Pacific region dominates with a 47.20% share, reflecting its rapid industrialization (SDG 9) and immense energy needs.
Market Segmentation Analysis and SDG Implications
By Type
Pulverized Coal Towers maintain a 54.8% market share, primarily due to their established role in providing base-load power in coal-reliant economies. While this technology has been instrumental in advancing economic growth (SDG 8) and energy access (SDG 7), its high emissions profile presents a significant obstacle to achieving SDG 13 (Climate Action). The market’s reliance on this type underscores the critical need for investment in cleaner alternatives and carbon capture technologies.
By Capacity
The 400–800 MW capacity segment holds a dominant 49.1% share. This range offers an optimal balance of efficiency and grid stability, making it a strategic choice for powering industrial zones and urban centers. This supports the development of resilient infrastructure (SDG 9) and sustainable communities (SDG 11) by ensuring a reliable energy supply.
By Technology
Subcritical technology leads with a 48.2% market share, largely due to its prevalence in legacy power plants. As a less efficient and more carbon-intensive technology compared to supercritical alternatives, its dominance highlights a major area for improvement. Upgrading or replacing these systems is a key opportunity to advance both SDG 7 (Clean Energy) and SDG 13 (Climate Action).
By Fuel Type
Coal-based boilers represent 69.3% of the market, reflecting the global energy sector’s ongoing dependence on fossil fuels. This segment’s size illustrates the scale of the challenge in transitioning to a low-carbon economy. A decisive shift towards gas, biomass, and other cleaner fuels is imperative to align the industry with the Paris Agreement and SDG 13.
By Application
Power Generation is the primary application, accounting for 61.3% of the market. This directly correlates with the global effort to achieve SDG 7. Other applications, such as waste-to-energy, are gaining traction and strongly support SDG 11 and SDG 12 by converting waste into a valuable energy resource and promoting circular economy principles.
Market Dynamics and Their Relation to SDGs
Driving Factors
The primary driver is rising global electricity demand, which is fundamental to achieving nearly all SDGs, including SDG 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth) and SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure). Expanding access to reliable energy in developing nations is a prerequisite for poverty reduction, education, and healthcare improvements, reinforcing the critical role of the power sector in sustainable development.
Restraining Factors
Stringent environmental regulations, enacted in response to global commitments under SDG 13 (Climate Action), serve as a major restraint on the expansion of conventional, fossil-fuel-based boiler systems. These policies increase operational costs for high-emission plants and incentivize investment in cleaner technologies, thereby shaping the market’s evolution towards sustainability.
Growth Opportunity
The modernization of aging power plants presents a significant growth opportunity. Replacing outdated, inefficient subcritical boilers with advanced supercritical or ultra-supercritical technologies allows for a simultaneous advancement of multiple goals: improving energy efficiency (SDG 7), reducing emissions (SDG 13), and upgrading critical national infrastructure (SDG 9).
Latest Trends
The accelerating shift toward supercritical and ultra-supercritical boilers is a key market trend. These advanced technologies require less fuel per megawatt-hour, directly contributing to resource efficiency (SDG 12) and reducing the carbon intensity of power generation (SDG 13). This trend reflects a market-driven alignment with global sustainability objectives.
Regional Analysis from a Sustainability Perspective
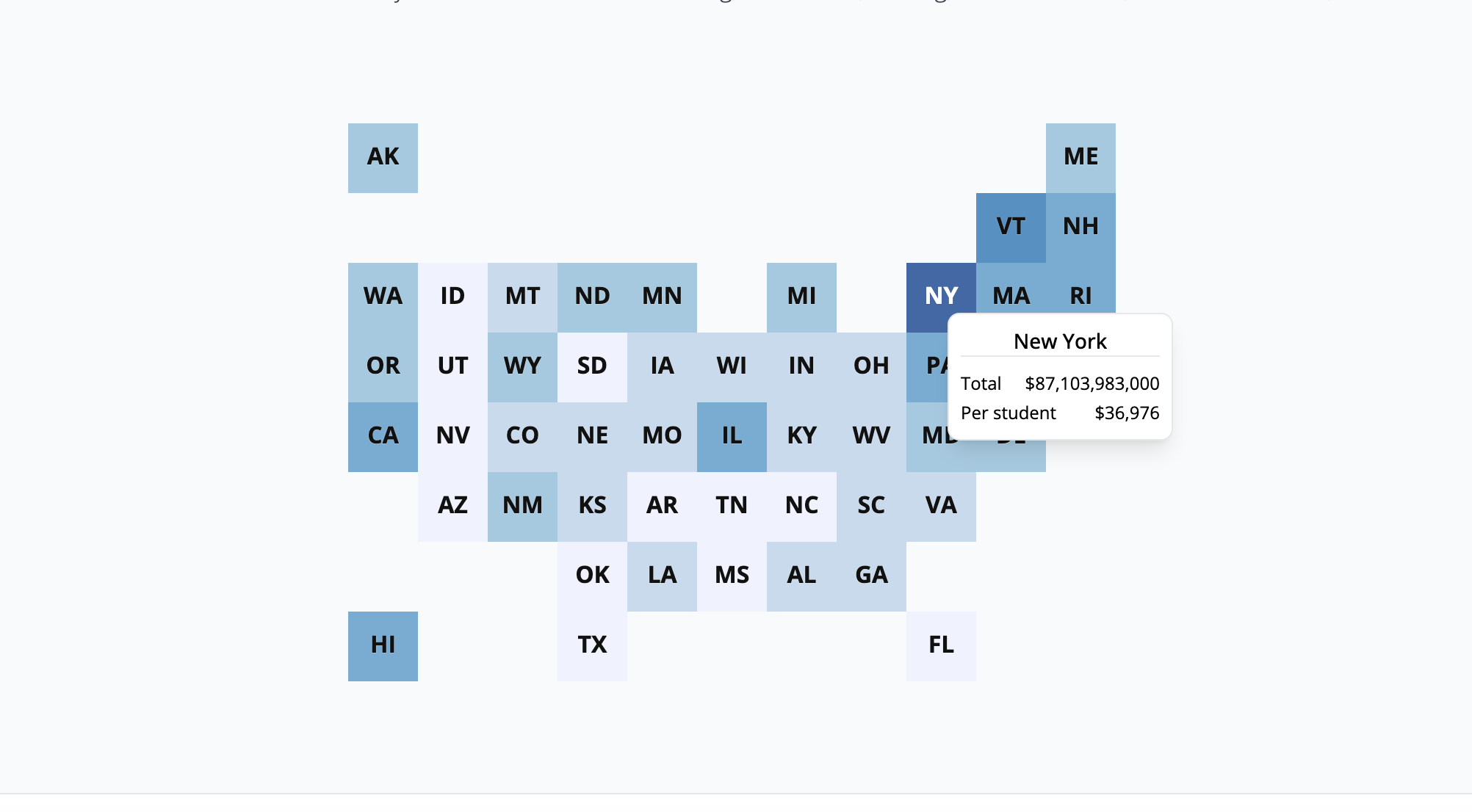
The Asia Pacific region, with a market value of USD 10.2 billion and a 47.20% share, is the epicenter of market activity. This is driven by rapid industrialization (SDG 9) and the need to provide electricity to vast populations (SDG 7). However, the region’s heavy reliance on coal poses a profound challenge to SDG 13. In contrast, North America and Europe are focused on retrofitting existing plants with emission control technologies and transitioning towards renewables, reflecting a more mature stage of alignment with climate goals. The Middle East & Africa and Latin America are expanding their energy infrastructure, presenting an opportunity to leapfrog older technologies and invest directly in more sustainable boiler systems.
Key Regions and Countries
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Player Analysis and Corporate Responsibility
Market leaders are increasingly being evaluated on their contributions to the sustainable energy transition.
- General Electric leverages its innovation in high-efficiency turbines and boiler systems to support utilities in reducing their carbon footprint, aligning with SDG 9 and SDG 13.
- Babcock & Wilcox Enterprise focuses on advanced emission control technologies and boilers capable of firing biomass and other waste fuels, contributing to SDG 7 and SDG 12.
- Dongfang Electric Corporation and Harbin Electric are central to Asia’s infrastructure build-out (SDG 9) but face pressure to pivot their portfolios towards cleaner technologies to address climate concerns.
- Doosan Heavy Industries & Construction is diversifying its offerings to include advanced, lower-emission boiler technologies and is exploring next-generation power systems, including hydrogen, in line with future energy needs.
Top Key Players in the Market
- Babcock & Wilcox Enterprise
- Dongfang Electric Corporation
- Doosan Heavy Industries & Construction
- General Electric
- Mitsubishi Hitachi Power Systems
- Siemens
- IHI Corporation
- John wood Group
- Bharat Heavy Electrical Limited
- Thermax
- Andritz Group
- Sumitomo Heavy Industries
- Valmet
- Harbin Electric
Recent Developments in the Sector
- March 2025: Dongfang Boiler’s investment in a hydrogen electrolyzer production line signals a strategic pivot towards green hydrogen, a key pillar for achieving a net-zero energy system and advancing SDG 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy).
- March 2024: B&W’s contracts for industrial boilers in the Middle East and Central Asia support industrial development (SDG 9) in these regions, providing critical steam and power for petrochemical facilities.
Analysis of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in the Power Plant Boiler Market
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
- SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy – The article’s core focus is on power generation, energy demand, efficiency, and the integration of cleaner technologies.
- SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure – The text discusses industrial growth, investment in power generation infrastructure, and the modernization of aging facilities with innovative technologies.
- SDG 13: Climate Action – The article highlights the conflict between the reliance on fossil fuels like coal and the increasing pressure from environmental regulations to reduce emissions.
- SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth – The report details significant market growth, value, and industrial expansion, particularly in the Asia Pacific region.
- SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production – The trend towards more efficient boiler technologies that use less fuel per unit of energy produced relates to sustainable resource management.
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
- Target 7.1: Ensure universal access to affordable, reliable and modern energy services. This is supported by the article’s statement that “the need for stable and large-scale power generation is increasing rapidly” due to growing urban populations and industrial activities, especially in “fast-growing economies” where there is “pressure to expand electricity access.”
- Target 7.2: Increase substantially the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix. The article points to this target by mentioning “the rising integration of renewable energy sources is creating new opportunities for hybrid systems, where conventional boilers operate alongside solar thermal or biomass inputs.”
- Target 7.a: Enhance international cooperation to facilitate access to clean energy research and technology… and promote investment in energy infrastructure and clean energy technology. This is reflected in the trend of “modernizing old plants” and the “shift toward Supercritical and ultra-supercritical boiler technologies,” which are described as “cleaner and more cost-effective power generation” solutions.
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
- Target 9.1: Develop quality, reliable, sustainable and resilient infrastructure… to support economic development and human well-being. The article directly addresses this by discussing the market for “crucial component[s] in thermal power plants,” investments in “power infrastructure,” and the need for “grid stability.”
- Target 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable, with increased resource-use efficiency and greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies. This is a central theme, highlighted by the “growing emphasis on improving efficiency and reducing emissions,” the “adoption of supercritical and ultra-supercritical boilers,” and the “growth opportunity” in “modernizing aging thermal power plants.”
SDG 13: Climate Action
- Target 13.2: Integrate climate change measures into national policies, strategies and planning. The article provides evidence of this through its “Restraining Factors” section, which states, “Governments are pushing for cleaner energy solutions to reduce air pollution and carbon emissions,” and these “strict environmental rules” are limiting the expansion of traditional boiler systems.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
Implied Indicators for SDG 7
- Indicator 7.1.1 (Proportion of population with access to electricity): Progress is implied by the article’s focus on meeting “rising electricity demand” and the “pressure to expand electricity access” in developing regions.
- Indicator 7.2.1 (Renewable energy share in the total final energy consumption): The article implies this indicator by mentioning the use of “biomass inputs” and the development of “hybrid systems” that integrate “solar thermal” energy. The market share of boilers using “Others” as a fuel type (which includes biomass) could be a proxy measure.
- Indicator 7.a.1 (International financial flows to developing countries in support of clean energy research and technology): This is implied by the market value data, such as the “USD 10.2 billion” market in Asia Pacific, and investments in “modernizing” plants with “advanced boiler technologies” like supercritical systems.
Implied Indicators for SDG 9
- Indicator 9.4.1 (CO2 emission per unit of value added): This is strongly implied by the trend towards technologies that “release fewer emissions per unit of energy generated.” The market share shift from “Subcritical” (48.2%) to more efficient “Supercritical” and “Ultra-supercritical” technologies serves as a direct measure of progress.
Implied Indicators for SDG 13
- Indicator 13.2.2 (Total greenhouse gas emissions per year): The article provides a proxy for this through its fuel type analysis. The overwhelming market share of “Coal Based” systems at “69.3%” indicates high potential emissions, while any shift towards “Gas Based” or “Others” (including biomass) would indicate a reduction.
4. Table of SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators (Mentioned or Implied in the Article) |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy | 7.1: Ensure universal access to affordable, reliable and modern energy services. 7.2: Increase the share of renewable energy. 7.a: Promote investment in clean energy technology. |
– Growth in electricity generation capacity to meet rising demand. – Market share of boilers using renewable fuels (biomass). – Investment value (e.g., USD 21.7 billion market) in new and modernized boiler technologies. |
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure | 9.1: Develop quality, reliable, and sustainable infrastructure. 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries for sustainability and efficiency. |
– Investment in power generation infrastructure (e.g., Asia Pacific’s USD 10.2 billion market). – Market share of high-efficiency technologies (Supercritical, Ultra-supercritical) versus less efficient ones (Subcritical). |
| SDG 13: Climate Action | 13.2: Integrate climate change measures into national policies. | – Market share of fuel types (e.g., Coal at 69.3% vs. Gas and Others) as a proxy for emissions intensity. – Mention of “strict environmental rules” and regulations impacting market growth. |
| SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth | 8.2: Achieve higher levels of economic productivity through technological upgrading and innovation. | – Projected market growth (CAGR of 5.2%). – Adoption of innovative technologies like pulverized coal towers and supercritical boilers. |
| SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production | 12.2: Achieve the sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources. | – Shift towards boilers that “produce more electricity using less fuel,” indicating improved resource efficiency. |
Source: market.us

What is Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0