Teen tobacco use linked to higher rates of depression and anxiety – News-Medical

Adolescent Tobacco Use and Mental Health: A Report on a Study’s Implications for Sustainable Development Goal 3
Introduction
A recent study utilizing data from the National Youth Tobacco Survey (2021-2023) establishes a significant association between tobacco use and adverse mental health outcomes among adolescents. The findings present critical challenges to the achievement of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly SDG 3, which aims to ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages. This report analyzes the study’s findings through the lens of the SDG framework.
Key Findings of the Study
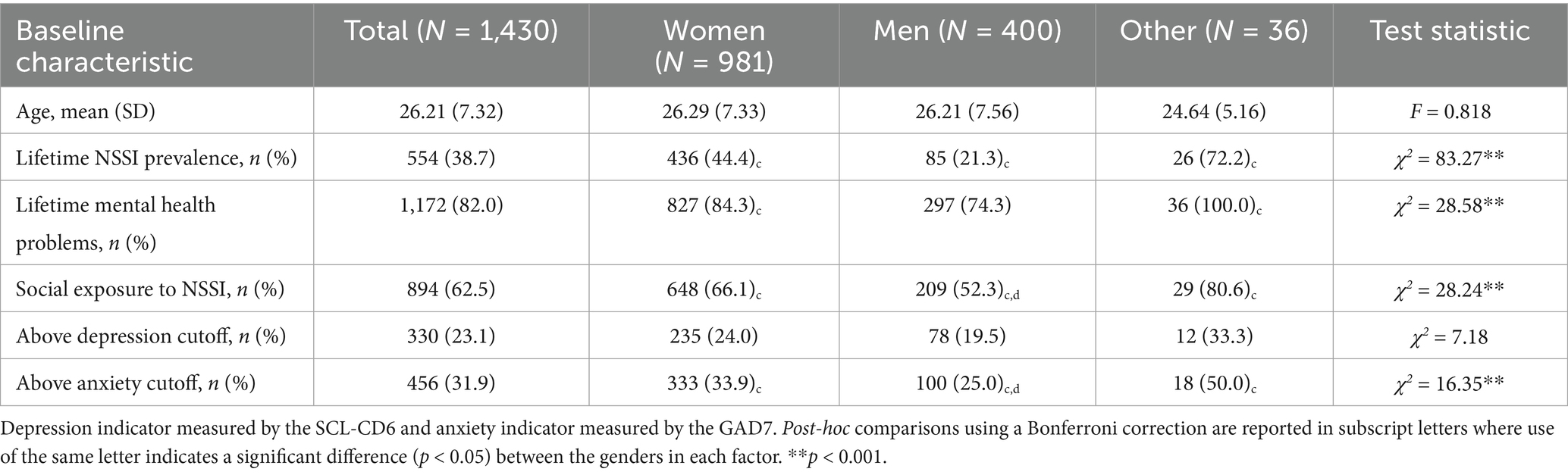
The research, based on a sample of 60,072 middle and high school students, revealed a strong correlation between the use of tobacco products and symptoms of depression and anxiety.
- Prevalence of Tobacco Use: 21.37% of adolescent respondents reported using tobacco products.
- 9.94% used only e-cigarettes.
- 3.61% used only conventional tobacco products (CTPs) such as cigarettes and cigars.
- 7.80% were dual users of both e-cigarettes and CTPs.
- Prevalence of Mental Health Symptoms:
- 25.21% of all respondents reported symptoms associated with depression.
- 29.55% reported symptoms of anxiety.
- Correlation: Compared to non-users, adolescents using any form of tobacco product showed a significantly higher likelihood of reporting depression and anxiety. The highest odds of mental health struggles were observed among dual users of both e-cigarettes and CTPs.
Direct Implications for Sustainable Development Goal 3: Good Health and Well-being
The study’s conclusions directly impact several targets within SDG 3, highlighting the interconnectedness of substance use, mental health, and non-communicable diseases (NCDs).
- Target 3.4: Promote Mental Health and Well-being: The demonstrated link between tobacco use and poor mental health underscores a significant barrier to promoting adolescent well-being. Addressing tobacco use is integral to reducing the burden of mental health conditions like depression and anxiety among youth.
- Target 3.5: Strengthen Prevention of Substance Abuse: The high prevalence of e-cigarette and tobacco use among adolescents signals a critical need to strengthen prevention strategies. The findings affirm that nicotine use is a key public health issue that must be addressed to fulfill this target.
- Target 3.a: Implement the WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control: The data provides compelling evidence for the necessity of robust implementation of tobacco control policies. This includes measures specifically tailored to new and emerging products like e-cigarettes that are popular among adolescents.
Broader Implications for Sustainable Development
- SDG 4 (Quality Education): Poor mental health and substance use can severely impede educational attainment. The findings call for integrating comprehensive health education into school curricula, focusing on the risks of tobacco and the importance of mental wellness to foster sustainable lifestyles.
- SDG 17 (Partnerships for the Goals): The complex, bidirectional relationship between tobacco use and mental health necessitates a multi-sectoral approach. Effective intervention requires collaboration between public health agencies, educational institutions, mental health service providers, and policymakers to create a supportive ecosystem for adolescent health.
Conclusion and Recommendations
The research confirms that all forms of adolescent tobacco use are significantly associated with adverse mental health outcomes, posing a direct threat to the progress of SDG 3. While causality was not determined, the strong association calls for immediate and integrated action.
- Continue to promote and expand access to mental health support systems for all adolescents.
- Design and implement tailored public health interventions to prevent and reduce all forms of tobacco use among youth, with a particular focus on e-cigarettes and dual use.
- Integrate tobacco control and mental health promotion into broader national strategies aimed at achieving the Sustainable Development Goals.
Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
-
SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being
This goal is central to the article, which focuses on the significant association between tobacco use (both conventional and e-cigarettes) and negative mental health outcomes, specifically depression and anxiety, among adolescents. The article directly addresses health-related risk-taking behaviors and the increasing rates of mental health challenges in this demographic, which are key concerns of SDG 3.
What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
-
Target 3.4: By 2030, reduce by one third premature mortality from non-communicable diseases through prevention and treatment and promote mental health and well-being.
The article directly supports this target by highlighting the need to “promote mental health support.” It establishes a clear link between a major risk factor (tobacco use) and poor mental health outcomes (“symptoms associated with depression” and “anxiety symptoms”). The study’s conclusion that tobacco use is “significantly associated with mental health issues” underscores the importance of addressing these interconnected problems to improve adolescent well-being.
-
Target 3.5: Strengthen the prevention and treatment of substance abuse, including narcotic drug abuse and harmful use of alcohol.
Tobacco, in both conventional and electronic forms, is a substance whose use the article investigates. The study focuses on the prevalence of tobacco use among adolescents, identifying that 21.37% of surveyed students had used tobacco products. The call to “implement tailored interventions to combat all forms of tobacco use among adolescents” is a direct call to action that aligns with strengthening the prevention of substance abuse in this age group.
-
Target 3.a: Strengthen the implementation of the World Health Organization Framework Convention on Tobacco Control in all countries, as appropriate.
While the article does not explicitly mention the WHO FCTC, its entire focus is on the problem of tobacco use and the need for interventions. The data presented on the high prevalence of e-cigarette and conventional tobacco product use among youth highlights the ongoing challenges in tobacco control. The conclusion calling for interventions to “combat all forms of tobacco use” directly relates to the objectives of the FCTC, which aims to protect present and future generations from the health consequences of tobacco consumption.
Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
-
Prevalence of mental health symptoms
The article provides specific data points that can serve as indicators. It states that “25.21% of respondents reported symptoms associated with depression and 29.55% reported anxiety symptoms.” These percentages are direct measures of the prevalence of mental health issues in the adolescent population studied and can be used to track progress towards Target 3.4.
-
Prevalence of current tobacco use among adolescents
The study offers precise indicators for substance use, relevant to both Target 3.5 and Target 3.a. It reports that among the students surveyed, “21.37% had used tobacco products, with 9.94% using only e-cigarettes, 3.61% using only CTPs, and 7.80% using both.” These statistics on the prevalence and type of tobacco use are crucial for measuring the effectiveness of prevention programs and tobacco control policies.
SDGs, Targets, and Indicators Analysis
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being | Target 3.4: Promote mental health and well-being. | Prevalence of mental health symptoms among adolescents.
|
| SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being | Target 3.5: Strengthen the prevention and treatment of substance abuse. | Prevalence of tobacco use among adolescents.
|
| SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being | Target 3.a: Strengthen the implementation of the WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control. | Prevalence of tobacco use among adolescents (as a measure of the effectiveness of control policies).
|
Source: news-medical.net

What is Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0























































.jpg?#)
















