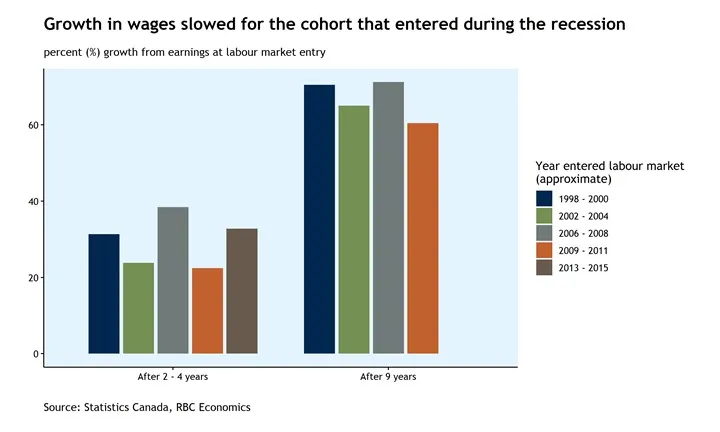
Canada Labour Market – rbc.com
Report on Institutional Governance and Sustainable Development Goal Alignment
Institutional Accountability and Transparency (SDG 16)
This report outlines the framework for institutional accountability and transparency, which is fundamental to achieving Sustainable Development Goal 16 (Peace, Justice and Strong Institutions). The following principles guide the dissemination of information:
- The information provided is intended for general purposes only and does not constitute professional legal, financial, or other advice, thereby establishing clear boundaries of institutional responsibility.
- Liability for the use of the information rests solely with the reader, which promotes individual accountability within a transparent legal framework.
- The institution and its affiliates shall not be held responsible for damages arising from the use of this document, reinforcing established governance and legal structures.
- A strong recommendation is made to consult with professional advisors for specific situations, fostering a culture of diligence and informed decision-making.
Responsible Information and Economic Integrity (SDG 8)
In alignment with Sustainable Development Goal 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth), the institution is committed to responsible communication practices that support economic integrity. The approach to information management is as follows:
- Accuracy and Timeliness: Information is presented based on the belief that it is factual and up-to-date; however, its absolute accuracy and completeness are not guaranteed. This reflects a commitment to good-faith communication while acknowledging the dynamic nature of data.
- Evolving Perspectives: All expressions of opinion reflect judgments at the date of publication and are subject to change, recognizing the fluid nature of economic analysis and market conditions.
- Forward-Looking Statements: The document may contain forward-looking statements, which are subject to specific cautionary protocols. This practice aligns with responsible corporate forecasting and risk management essential for sustainable economic growth.
Commitment to Climate Action and Data Integrity (SDG 13)
This report underscores a commitment to transparent reporting on climate-related matters, directly supporting Sustainable Development Goal 13 (Climate Action). Key considerations for sustainability data include:
- The acknowledgment that Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG), including climate-related metrics and data, may be founded on assumptions, estimates, and professional judgments.
- Stakeholders are directed to comprehensive climate and sustainability reports for detailed methodologies and cautionary statements, ensuring full transparency in climate action reporting.
- The institution clarifies its legal obligations regarding the updating of information, defining the scope and frequency of its reporting commitments to stakeholders.
Framework for Partnerships and Stakeholder Engagement (SDG 17)
To foster effective collaboration as outlined in Sustainable Development Goal 17 (Partnerships for the Goals), a clear framework for engagement with third parties and stakeholders is maintained.
- The institution explicitly states that no endorsement of third parties or their advice, products, or services is given or implied, ensuring independence and clarity in all communications.
- By directing stakeholders to official corporate sustainability reports, the institution utilizes a primary mechanism for transparent engagement and partnership with investors, regulators, and the public.
Analysis of Sustainable Development Goals in the Article
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
The provided text, being a legal disclaimer, does not directly discuss actions or initiatives related to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). However, it makes references that connect it to the broader framework of sustainability reporting, which is relevant to the following SDGs:
- SDG 13: Climate Action: The article explicitly mentions the company’s “latest climate report” and refers to “climate metrics, data and other information.” This indicates a corporate focus on measuring and reporting climate-related issues, which is a fundamental aspect of taking action on climate change.
- SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals: The entire premise of the article is corporate disclosure and reporting on sustainability. Publishing a “sustainability report” and being transparent about “ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) metrics” are key components of corporate responsibility. This aligns with the goal of enhancing partnerships through accountability and transparency to various stakeholders (investors, public, regulators).
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
The article’s content is too general to be mapped to specific SDG targets. It functions as a disclaimer about the nature of the company’s sustainability information rather than detailing the information itself.
- The text refers to external documents like a “climate report or sustainability report” where information relevant to specific targets would be located.
- Because the article does not describe any policies, actions, or outcomes, no specific targets—such as integrating climate change measures into policies (Target 13.2) or promoting mechanisms for climate change planning (Target 13.b)—can be identified from the text provided.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
Yes, the article explicitly mentions the categories of indicators that the company uses, although it does not provide the specific metrics.
- The text states that “ESG (including climate) metrics, data and other information” are used. This directly points to the existence of a set of indicators for measuring performance.
- The implied indicators are, therefore, the broad categories of:
- Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) metrics: A wide-ranging set of indicators used to assess a company’s performance in these three areas.
- Climate metrics: A subset of ESG metrics focused specifically on climate-related data, such as greenhouse gas emissions, energy consumption, or climate risk exposure.
4. Table of SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 13: Climate Action (Implied through reference to climate reporting) |
No specific targets are mentioned in the article. The text only refers to the existence of a “climate report.” | The article mentions the existence of “climate metrics, data and other information.” |
| SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals (Implied through the practice of corporate sustainability reporting) |
No specific targets are mentioned in the article. The text is an example of corporate disclosure, which relates to accountability within partnerships. | The article mentions the use of “ESG metrics, data and other information” for reporting purposes. |
Source: rbc.com

What is Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0


















-1920w.png?#)





















;Resize=805#)