Fossil Records Unlock Secrets of Climate Change Extinction Risks
Fossil Records Unlock Secrets of Climate Change Extinction Risks SciTechDaily


Sustainable Development Goals and Extinction Risk Due to Climate Change
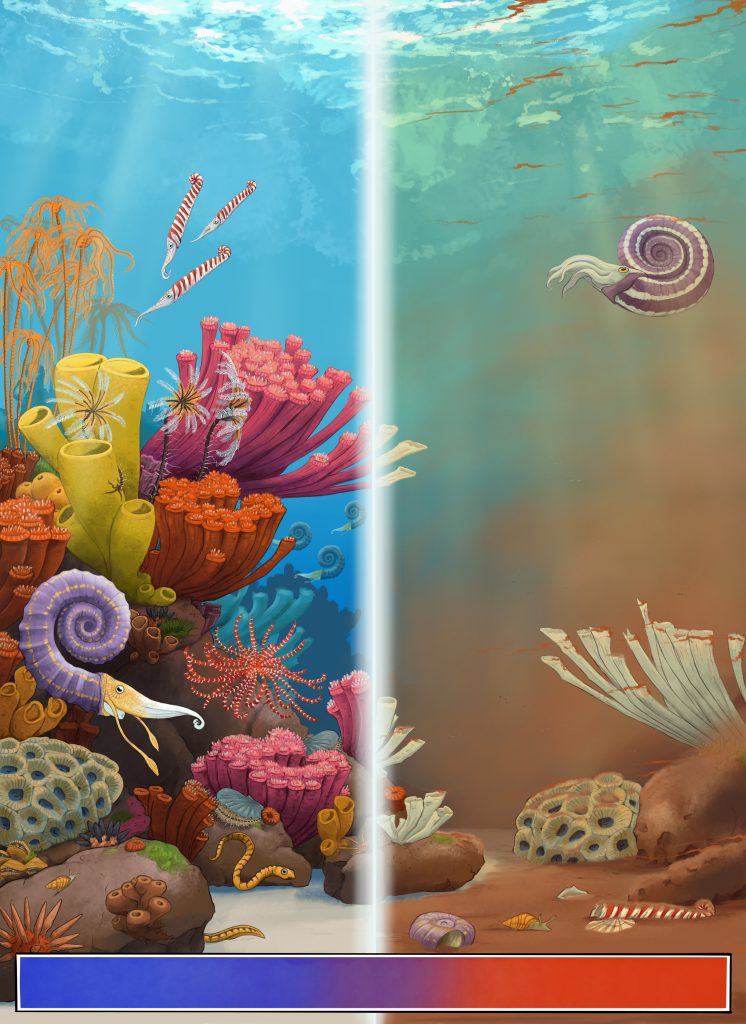

Artistic reconstruction of a late Triassic undersea scene before (left) and after (right) a climate change-related extinction event. Credit: Maija Karala
A recent study published in the journal Science has utilized the fossil record to investigate the characteristics that make certain species more vulnerable to extinction due to climate change. This research aims to identify the species that are currently most endangered by anthropogenic climate change, aligning with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) set by the United Nations.
Past climate change, often caused by natural variations in greenhouse gases resulting from volcanic activity, has led to numerous extinctions throughout Earth’s history. However, until now, it has remained unclear which factors contribute to a species’ resilience or vulnerability to such changes, as well as how the magnitude of climate change impacts extinction risk.
Research Methodology and Key Findings
Led by researchers at the University of Oxford, this study focused on analyzing the fossil record of marine invertebrates, such as sea urchins, snails, and shellfish, over the past 485 million years. Marine invertebrates have a well-documented fossil record, allowing for the identification of extinct species and potential reasons for their extinction.
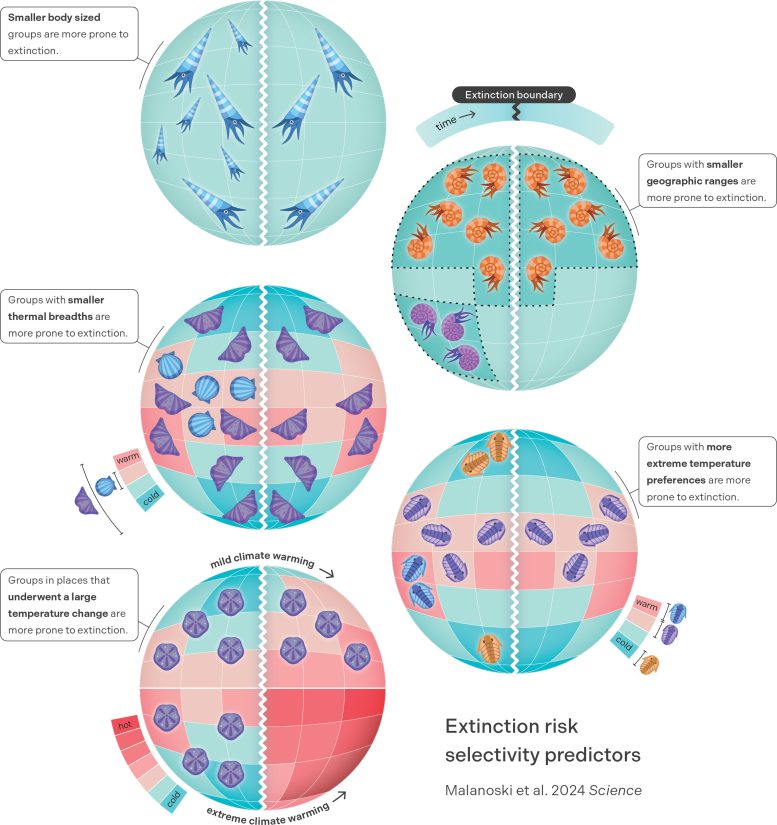
Infographic summarising the key traits and factors identified by the study that determine species risk to climate change-related extinction. Credit: Miranta Kouvari (Science Graphic Design).
By analyzing over 290,000 fossil records representing more than 9,200 genera, the researchers compiled a dataset of key traits that may influence a species’ resilience to extinction. This dataset included previously understudied traits like preferred temperature. The researchers then integrated this trait information with climate simulation data to develop a model that could determine the most significant factors in predicting extinction risk during climate change.
Key Findings:
- Species exposed to greater climate change, particularly those experiencing temperature changes of 7°C or more across geological stages, were significantly more likely to become extinct.
- Species inhabiting climatic extremes, such as polar regions, were disproportionately vulnerable to extinction. Additionally, species with narrow thermal ranges, especially those less than 15°C, were significantly more prone to extinction.
- Geographic range size was the strongest predictor of extinction risk. Species with larger geographic ranges were significantly less likely to go extinct. Body size also played a role, with smaller-bodied species facing a higher risk of extinction.
- All the studied traits had a cumulative impact on extinction risk. Species with both small geographic ranges and narrow thermal ranges were even more susceptible to extinction than those with only one of these traits.
Cooper Malanoski, the first author of the study from the University of Oxford, stated, “Our study revealed that geographic range was the strongest predictor of extinction risk for marine invertebrates. However, the magnitude of climate change is also an important predictor, which has implications for biodiversity today in the face of climate change.”
Implications and Future Research
With current human-driven climate change pushing many species to the brink of extinction, these findings can
SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
- SDG 13: Climate Action
- SDG 15: Life on Land
The article discusses the impact of climate change on species extinction, which is directly related to SDG 13, which aims to take urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts. It also addresses the issue of biodiversity loss, which is connected to SDG 15, which focuses on protecting, restoring, and promoting sustainable use of terrestrial ecosystems.
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
- SDG 13.1: Strengthen resilience and adaptive capacity to climate-related hazards and natural disasters
- SDG 15.5: Take urgent and significant action to reduce the degradation of natural habitats, halt the loss of biodiversity, and prevent the extinction of threatened species
The article highlights the need to strengthen resilience to climate change and its impacts, which aligns with SDG 13.1. It also emphasizes the importance of preventing species extinction and protecting biodiversity, which relates to SDG 15.5.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
- Indicator for SDG 13.1: Number of countries implementing national adaptation plans
- Indicator for SDG 15.5: Extent of species extinction and decline in biodiversity
The article does not explicitly mention specific indicators, but the identified targets can be measured using indicators such as the number of countries implementing national adaptation plans (SDG 13.1) and the extent of species extinction and decline in biodiversity (SDG 15.5).
Table: SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 13: Climate Action | 13.1: Strengthen resilience and adaptive capacity to climate-related hazards and natural disasters | Number of countries implementing national adaptation plans |
| SDG 15: Life on Land | 15.5: Take urgent and significant action to reduce the degradation of natural habitats, halt the loss of biodiversity, and prevent the extinction of threatened species | Extent of species extinction and decline in biodiversity |
Based on the analysis of the article, the relevant SDGs, targets, and indicators are as follows:
- SDGs:
- SDG 13: Climate Action
- SDG 15: Life on Land
- Targets:
- SDG 13.1: Strengthen resilience and adaptive capacity to climate-related hazards and natural disasters
- SDG 15.5: Take urgent and significant action to reduce the degradation of natural habitats, halt the loss of biodiversity, and prevent the extinction of threatened species
- Indicators:
- Indicator for SDG 13.1: Number of countries implementing national adaptation plans
- Indicator for SDG 15.5: Extent of species extinction and decline in biodiversity
Behold! This splendid article springs forth from the wellspring of knowledge, shaped by a wondrous proprietary AI technology that delved into a vast ocean of data, illuminating the path towards the Sustainable Development Goals. Remember that all rights are reserved by SDG Investors LLC, empowering us to champion progress together.
Source: scitechdaily.com

Join us, as fellow seekers of change, on a transformative journey at https://sdgtalks.ai/welcome, where you can become a member and actively contribute to shaping a brighter future.







