Industry 4.0 Market to Hit USD 309.45 Billion by 2032, Growing – openPR.com

Industry 4.0 Market Report: A Catalyst for Sustainable Development
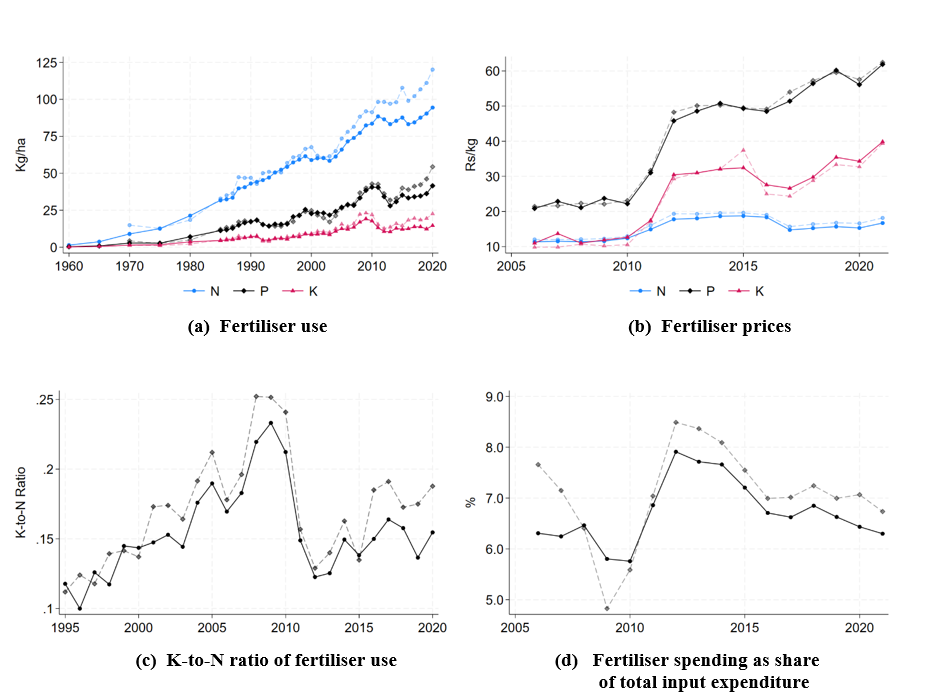
The global Industry 4.0 market, valued at USD 86.45 billion in 2023, is projected to reach USD 309.45 billion by 2032, demonstrating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.80% from 2024 to 2032. This expansion is driven by the integration of advanced digital technologies into industrial processes, which not only enhances efficiency but also significantly contributes to achieving the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
Key Drivers for Sustainable Industrial Transformation
The adoption of Industry 4.0 is propelled by several factors that align closely with global sustainability objectives.
- Rise of Smart Manufacturing: The shift towards data-driven production systems directly supports SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure) by building resilient and innovative industrial frameworks. It also advances SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production) by optimizing resource use and minimizing waste.
- Growing Adoption of Industrial IoT (IIoT): IIoT, which constituted nearly 48% of the revenue share in 2021, enables predictive maintenance and remote monitoring. This enhances industrial resilience (SDG 9) and promotes energy efficiency in systems like smart grids, contributing to SDG 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy).
- Need for Operational Efficiency: By reducing downtime and optimizing asset utilization, Industry 4.0 technologies enhance productivity, fostering economic growth and creating higher-value employment opportunities in line with SDG 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth).
- Advancements in Robotics and AI: Collaborative robots and AI-driven quality control are transforming factories into self-optimizing ecosystems. This technological leap fosters innovation (SDG 9) and can be leveraged to improve safety and working conditions for employees (SDG 8).
- Government Initiatives & Policies: Global policies such as “Industrie 4.0” and “Smart Factory EU” are accelerating digital transformation. These frameworks often include sustainability targets, creating partnerships that advance multiple SDGs, as envisioned by SDG 17 (Partnerships for the Goals).
Market Segmentation and Contribution to SDGs
By Technology
The technological pillars of Industry 4.0 offer distinct pathways to sustainable development.
- Industrial IoT (IIoT): Drives real-time data analytics for smart connectivity, crucial for resource management (SDG 12).
- AI & Machine Learning: Enables predictive insights, reducing energy consumption and material waste (SDG 7, SDG 12).
- Blockchain: Improves supply chain transparency and traceability, ensuring ethical sourcing and combating illicit trade, which supports SDG 12 and SDG 16 (Peace, Justice and Strong Institutions).
- AR/VR: Enhances remote training and maintenance, reducing the need for travel and its associated carbon footprint (SDG 13: Climate Action).
- Additive Manufacturing: Facilitates on-demand production, minimizing waste and enabling localized manufacturing (SDG 9, SDG 12).
- Digital Twin: Allows for virtual simulation to optimize processes and infrastructure for sustainability before physical implementation (SDG 9, SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities).
By Industry Vertical
The adoption of Industry 4.0 across various sectors directly addresses specific SDGs.
- Manufacturing: The dominant sector, where smart supply chains and robotics directly advance SDG 9 and SDG 12.
- Automotive: Integration of advanced sensors and 3D printing promotes cleaner and more efficient transportation solutions (SDG 11).
- Energy & Utilities: The use of smart grids and predictive maintenance is fundamental to achieving SDG 7.
- Healthcare: Digital twins and remote diagnostics improve access to and quality of care, supporting SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-being).
- Aerospace & Defense: Simulation models and smart logistics enhance efficiency and reduce the environmental impact of operations.
- Others (including Agriculture): Smart technologies in agriculture can optimize crop yields and water usage, contributing to SDG 2 (Zero Hunger).
Regional Analysis: A Global Push for Sustainable Industry
- North America: A leading region driven by innovation in AI and IoT, developing solutions that can be scaled globally to address various SDGs.
- Europe: Strong focus on sustainability and automation, with initiatives like Horizon Europe explicitly linking industrial modernization with goals for climate action and responsible production (SDG 13, SDG 12).
- Asia-Pacific: Expected to witness the fastest growth, where industrial expansion offers a critical opportunity to build new infrastructure that is inherently sustainable and inclusive (SDG 9, SDG 8).
- Middle East & Africa: Emerging adoption in the oil & gas sector provides a pathway to transition towards more efficient and cleaner energy operations (SDG 7).
- Latin America: Increasing investment in smart manufacturing is helping to build more resilient economies and industries (SDG 9).
Market Opportunities for a Sustainable Future
The future growth of Industry 4.0 presents significant opportunities to accelerate progress on the SDGs.
- Sustainable Manufacturing Initiatives: A primary opportunity lies in using Industry 4.0 to create energy-efficient processes and green automation, helping businesses achieve net-zero goals and advance SDG 13 (Climate Action).
- AI-Powered Predictive Maintenance: Reduces equipment failures and resource waste, directly supporting the principles of a circular economy and SDG 12.
- 5G and Edge Computing: Unlocks real-time data processing needed for complex systems like autonomous vehicles and smart grids, which are crucial for sustainable cities and clean energy (SDG 11, SDG 7).
Competitive Landscape
The market is led by major corporations actively developing solutions that align with sustainability objectives. Key players include:
- Siemens AG
- ABB Ltd.
- General Electric
- Honeywell International Inc.
- Cisco Systems Inc.
- Rockwell Automation Inc.
- Schneider Electric
- IBM Corporation
- Bosch Rexroth AG
- Intel Corporation
These industry leaders are pioneering smart factory solutions and intelligent platforms that are instrumental in driving the global transition towards a more sustainable and equitable industrial future.
Analysis of Sustainable Development Goals in the Article
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
- SDG 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure: The article is centered on “Industry 4.0,” which involves the digital transformation of manufacturing and industrial sectors. It directly discusses building “next-gen industrial infrastructure,” fostering innovation through technologies like AI and IIoT, and promoting “sustainable industrialization” through efficiency and new processes.
- SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth: The article highlights significant economic growth, with the Industry 4.0 market projected to grow from “USD 86.45 billion in 2023 to USD 309.45 billion by 2032.” It also focuses on achieving higher levels of economic productivity by enhancing “workforce productivity” and “operational efficiency” through technological upgrades.
- SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production: The article points to a shift towards more sustainable production patterns. It identifies “Sustainable Manufacturing Initiatives” as a key market opportunity, emphasizing “energy-efficient processes” and “green automation.” The goal of optimizing “asset utilization” and reducing “downtime” also contributes to more responsible use of resources.
- SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy: The article mentions the application of Industry 4.0 in the “Energy & Utilities” sector for “energy optimization” and the use of “smart grids.” Furthermore, the broader push for “energy-efficient processes” in manufacturing aligns with the goal of improving energy efficiency.
- SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals: The article explicitly mentions the role of partnerships in driving the adoption of Industry 4.0. It cites “Government Initiatives & Policies” such as “‘Make in India,’ ‘Smart Factory EU,’ and ‘Industrie 4.0′” as key drivers, which are examples of public-private partnerships to achieve technological and industrial goals.
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
-
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure
- Target 9.2: Promote inclusive and sustainable industrialization. The article’s focus on the global expansion of Industry 4.0, including rapid growth in the “Asia-Pacific” region, supports the goal of increasing the industry’s contribution to the economy.
- Target 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable. This is directly addressed through mentions of “Sustainable Manufacturing Initiatives,” “energy-efficient processes,” “green automation,” and the need to “optimize asset utilization.”
- Target 9.5: Enhance scientific research and upgrade technological capabilities. The entire article is a testament to this target, detailing advancements in “IIoT, AI & Machine Learning, Blockchain, AR/VR, Additive Manufacturing, and Digital Twin” and noting that key players are emphasizing “R&D.”
-
SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
- Target 8.2: Achieve higher levels of economic productivity through technological upgrading and innovation. The article states that a key driver for adopting Industry 4.0 is the “Need for Operational Efficiency,” which aims to “enhance workforce productivity” through “intelligent automation” and “advancements in Robotics and AI.”
-
SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
- Target 12.2: Achieve the sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources. The drive to “reduce downtime, optimize asset utilization” and implement “energy-efficient processes” directly contributes to this target by ensuring resources are used more effectively.
-
SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
- Target 7.3: Double the global rate of improvement in energy efficiency. The article highlights that the “Energy & Utilities” sector is using Industry 4.0 for “energy optimization” and that “energy-efficient processes” are a key part of sustainable manufacturing initiatives.
-
SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals
- Target 17.17: Encourage and promote effective public-private partnerships. The article identifies “Government Initiatives & Policies” like “Smart Factory EU” and “Industrie 4.0” as key market drivers, showcasing collaboration between governments and private industry to accelerate “digital transformation.”
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
- Market Value and Growth Rate: The projection of the market’s growth from “USD 86.45 billion in 2023 to USD 309.45 billion by 2032” at a “CAGR of 14.80%” serves as a quantitative indicator for Target 9.2 (contribution of industry to GDP).
- Technology Adoption Rate: The statistic that “Industrial IoT accounted for nearly 48% of the revenue share in 2021” is a specific indicator of technology adoption, relevant to Target 9.5. The segmentation of the market by technology (AI, Blockchain, etc.) further implies that adoption rates for each can be tracked.
- Investment in R&D and Innovation: The article implies that investment in research and development is a key activity for market leaders (“key players emphasizing R&D, AI integration”). This serves as a qualitative indicator for Target 9.5.
- Implementation of Sustainable Practices: The identification of “Sustainable Manufacturing Initiatives” and “energy-efficient processes” as a “key market opportunity” implies that the adoption of these practices is a measurable indicator for Targets 9.4, 12.2, and 7.3.
- Existence of Government-Industry Programs: The mention of specific programs like “‘Make in India,’ ‘Smart Factory EU,’ and ‘Industrie 4.0′” serves as a concrete indicator of public-private partnerships (Target 17.17) being in place to support industrial development.
4. Table of SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators Identified in the Article |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure | 9.2: Promote inclusive and sustainable industrialization. 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable. 9.5: Enhance scientific research and upgrade technological capabilities. |
– Market value growth from USD 86.45 billion to USD 309.45 billion. – Adoption of “Sustainable Manufacturing Initiatives” and “green automation.” – Investment in R&D by key players and development of new technologies (IIoT, AI, Digital Twin). |
| SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth | 8.2: Achieve higher levels of economic productivity through technological upgrading and innovation. | – Adoption of technologies to “enhance workforce productivity” and achieve “operational efficiency.” – Use of “intelligent automation” and “collaborative robots” to reshape factories. |
| SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production | 12.2: Achieve the sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources. | – Focus on initiatives to “optimize asset utilization” and “reduce downtime.” – Implementation of “energy-efficient processes.” |
| SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy | 7.3: Double the global rate of improvement in energy efficiency. | – Use of Industry 4.0 for “energy optimization” and “smart grids” in the Energy & Utilities sector. – Adoption of “energy-efficient processes” in manufacturing. |
| SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals | 17.17: Encourage and promote effective public-private partnerships. | – Existence of supportive government frameworks like “Make in India,” “Smart Factory EU,” and “Industrie 4.0.” |
Source: openpr.com

What is Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0






























_2.png?#)