374Water AirSCWO Technology Destroys PFAS in Biosolids – The Manila Times

Report on the Eradication of PFAS Contaminants in Biosolids via AirSCWO Technology
Executive Summary
A report from 374Water Inc. confirms the successful deployment of its commercial-scale AirSCWO (Supercritical Water Oxidation) system for the complete destruction of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in municipal biosolids. The technology consistently reduces these “forever chemicals” to non-detectable levels, offering a critical solution to a growing environmental and public health crisis. This innovation directly supports the achievement of several United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly those related to clean water, public health, sustainable communities, and responsible production.
Technological Advancement in Waste Management
The AirSCWO System and its Application
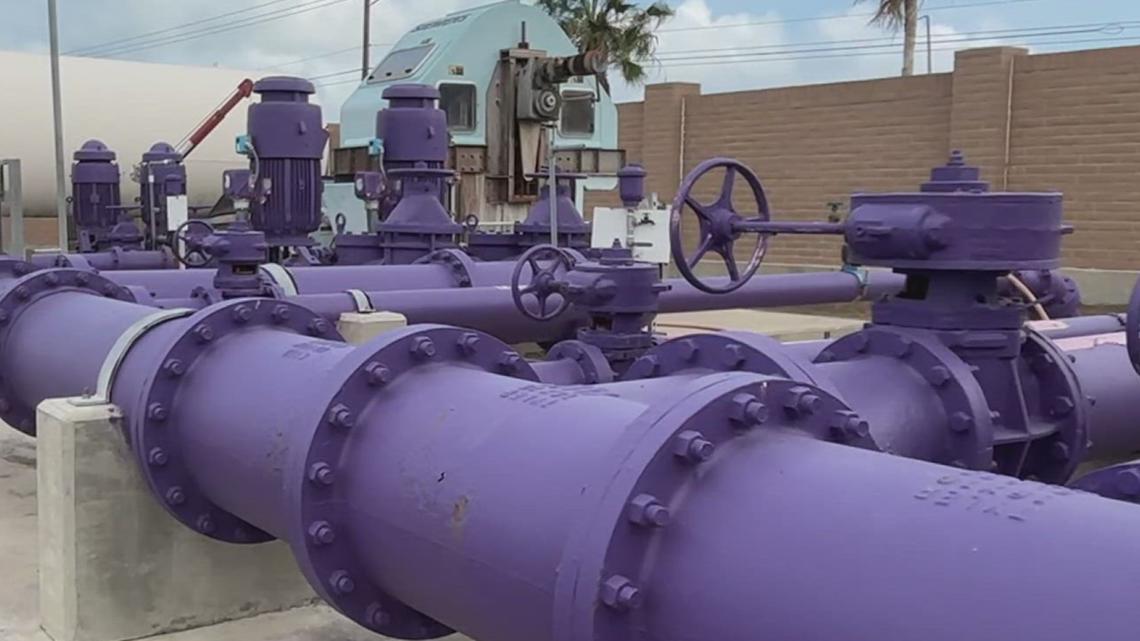
The AirSCWO system, developed by 374Water, is an advanced thermal oxidation technology designed to mineralize organic waste. The process has been validated on biosolids, the organic material remaining after wastewater treatment, which are frequently contaminated with high concentrations of PFAS from industrial and household sources.
Verified Destruction Efficacy
Third-party laboratory analysis of waste streams processed by the AirSCWO system has confirmed its effectiveness. Key performance results include:
- Complete PFAS Destruction: The system consistently reduces PFAS concentrations in treated effluent to non-detectable levels, far exceeding the U.S. EPA’s stringent drinking water standards.
- High Organic Destruction Rate: The technology achieves over 99.99% destruction of organic compounds present in biosolids.
- Versatility: The system has proven effective across a wide range of PFAS-contaminated sludges and biosolids from various sources.
Contribution to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation & SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being
The disposal of PFAS-contaminated biosolids through traditional methods like land application poses a direct threat to water resources and human health. By destroying these persistent chemicals, the AirSCWO technology makes a significant contribution to:
- Protecting Water Sources: It prevents PFAS from leaching into groundwater and surface water, safeguarding water quality for communities and ecosystems (Target 6.3).
- Reducing Health Risks: By eliminating a primary pathway of human exposure to toxic “forever chemicals,” the technology helps reduce the incidence of diseases linked to PFAS contamination (Target 3.9).
- Ensuring Safe Sanitation: It provides wastewater treatment facilities with a method to manage their byproducts safely and sustainably, closing the loop on sanitation management (Target 6.2).
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure & SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
This technological solution addresses critical infrastructure gaps in waste management, fostering more resilient and sustainable urban environments.
- Innovative Infrastructure (SDG 9): The AirSCWO system represents a significant technological upgrade for waste treatment infrastructure, promoting clean and environmentally sound industrial processes (Target 9.4).
- Sustainable Waste Management (SDG 11): It offers municipalities a viable alternative to landfills and land application, helping cities reduce their adverse environmental impact and manage waste more effectively (Target 11.6).
SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production & SDG 14/15: Life Below Water and on Land
The technology fundamentally alters the lifecycle of hazardous waste, promoting responsible management and protecting ecosystems.
- Environmentally Sound Management of Chemicals (SDG 12): The system provides a method for the complete destruction of hazardous chemicals, aligning with goals for their sound management throughout their life cycle to minimize adverse impacts (Target 12.4).
- Protection of Ecosystems (SDG 14 & 15): By preventing the release of PFAS into the environment, the technology directly protects terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems from pollution, preserving biodiversity and ecological health (Targets 14.1 and 15.1).
Market Outlook and Conclusion
Addressing a Growing National Issue
With states and municipalities increasingly restricting conventional disposal methods for biosolids, the demand for effective destruction technologies is rising across municipal, federal, and industrial sectors. The limitations of landfills and the rising costs of transportation and disposal fees are accelerating the need for innovative, on-site solutions.
Conclusion
The successful deployment of 374Water’s AirSCWO technology marks a pivotal advancement in the global effort to combat PFAS contamination. By providing a scalable and effective method for destroying “forever chemicals,” this innovation offers a clear pathway for achieving key targets within the Sustainable Development Goals, ensuring cleaner water, healthier communities, and a more sustainable future.
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
The article on 374Water’s AirSCWO technology for destroying PFAS in biosolids addresses several interconnected Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The primary focus is on water quality, waste management, and technological innovation, which directly links to the following SDGs:
- SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being: The article highlights the “major public health and environmental risks” associated with PFAS “forever chemicals,” which are described as “toxic” and “hazardous.” By destroying these chemicals, the technology helps reduce human exposure and related health problems.
- SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation: This is a central theme. The technology treats biosolids, a byproduct of wastewater treatment, to prevent the contamination of “groundwater.” The goal is to produce “safe dischargeable water streams,” directly contributing to water quality and sanitation.
- SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure: The article introduces an “innovative waste destruction technology” (AirSCWO) developed by a company to solve a pressing issue for municipal and industrial wastewater treatment facilities. This represents an advancement in sustainable infrastructure and clean technology.
- SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production: The core issue is the management of hazardous waste (PFAS-contaminated biosolids). The technology provides a method for the “environmentally sound management of chemicals and all wastes,” as described in the goal’s targets.
- SDG 15: Life on Land: The article explicitly states that the common disposal method of land application for biosolids can “contaminate soil, crops… and livestock.” By destroying the contaminants before disposal, the technology helps protect terrestrial ecosystems from pollution.
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
Based on the specific problems and solutions presented in the article, the following SDG targets are directly relevant:
-
SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being
- Target 3.9: “By 2030, substantially reduce the number of deaths and illnesses from hazardous chemicals and air, water and soil pollution and contamination.” The article’s focus on destroying “toxic PFAS” that pose “major public health… risks” directly aligns with reducing illness from chemical contamination in water and soil.
-
SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation
- Target 6.3: “By 2030, improve water quality by reducing pollution, eliminating dumping and minimizing release of hazardous chemicals and materials, halving the proportion of untreated wastewater and substantially increasing recycling and safe reuse globally.” The AirSCWO system is designed to “destroy PFAS in biosolids to non-detectable levels,” thus preventing the release of these hazardous chemicals into groundwater and improving overall water quality.
-
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
- Target 9.4: “By 2030, upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable, with increased resource-use efficiency and greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies and industrial processes…” The article presents the AirSCWO system as an “innovative solution” and an “environmentally sound technology” for wastewater treatment facilities, which are a key part of municipal and industrial infrastructure.
-
SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
- Target 12.4: “By 2020, achieve the environmentally sound management of chemicals and all wastes throughout their life cycle… and significantly reduce their release to air, water and soil in order to minimize their adverse impacts on human health and the environment.” The technology offers a solution for the “disposal of PFAS contaminated biosolids,” which is a critical waste management challenge. The process aims to “fully eliminate and destroy PFAS contaminated biosolids,” directly addressing the sound management of chemical waste.
-
SDG 15: Life on Land
- Target 15.1: “By 2020, ensure the conservation, restoration and sustainable use of terrestrial and inland freshwater ecosystems and their services…” The article notes that land application of contaminated biosolids pollutes “soil, crops, groundwater, and livestock.” Preventing this contamination through technology helps conserve and protect terrestrial ecosystems from degradation.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
Yes, the article mentions several specific, measurable indicators that can be used to track progress towards the identified targets.
- Indicator for PFAS Destruction Efficiency: The article provides a direct quantitative measure of the technology’s effectiveness. It states that the system “consistently achiev[es] over 99.99% destruction of organic compounds.” This percentage serves as a clear indicator for Target 12.4 (sound management of waste) and Target 6.3 (reducing pollution).
- Indicator for Water Quality: Progress towards Target 6.3 can be measured by the quality of the treated water. The article specifies that the technology produces “effluent with PFAS concentrations at non-detectable levels” or “below the U.S. EPA’s drinking water standards.” The concentration of PFAS in the effluent is a precise indicator.
- Indicator for Waste Management Improvement: An implied indicator for Target 12.4 is the reduction in the volume of hazardous waste being sent to landfills or used in land applications. The article mentions that “landfills are accepting less of this form of waste” and the technology can “eliminate the need for further downstream processing.” Measuring the volume of biosolids treated by this technology versus traditional disposal methods would indicate progress.
- Indicator for Adoption of Clean Technology: For Target 9.4, an indicator would be the rate of adoption of this technology by the target markets. The article mentions “increased market demand” and the company’s effort to “convert our pipeline to actionable backlog,” suggesting that the number of AirSCWO units deployed in municipal, federal, and industrial facilities is a key metric of progress.
4. Table of SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators Identified in the Article |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being | 3.9: Substantially reduce illnesses from hazardous chemicals and pollution. | Reduction in public exposure to “toxic PFAS ‘forever chemicals'” that pose “major public health risks.” |
| SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation | 6.3: Improve water quality by reducing pollution and minimizing the release of hazardous chemicals. | Concentration of PFAS in treated effluent being at “non-detectable levels” or “below the U.S. EPA’s drinking water standards.” |
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure | 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure and industries with clean and environmentally sound technologies. | Adoption rate of the AirSCWO system by municipal, federal, and industrial facilities to manage waste. |
| SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production | 12.4: Achieve environmentally sound management of chemicals and all wastes. | The destruction efficiency of the technology, specifically “over 99.99% destruction of organic compounds.” |
| SDG 15: Life on Land | 15.1: Ensure the conservation and sustainable use of terrestrial and inland freshwater ecosystems. | Reduction in the land application of contaminated biosolids, thereby preventing pollution of “soil, crops, groundwater, and livestock.” |
Source: manilatimes.net

What is Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0