Cleanup Progress Paves Way for Industry Growth in Oak Ridge – Department of Energy (.gov)

Report on Environmental Remediation and Sustainable Development at Oak Ridge
Executive Summary
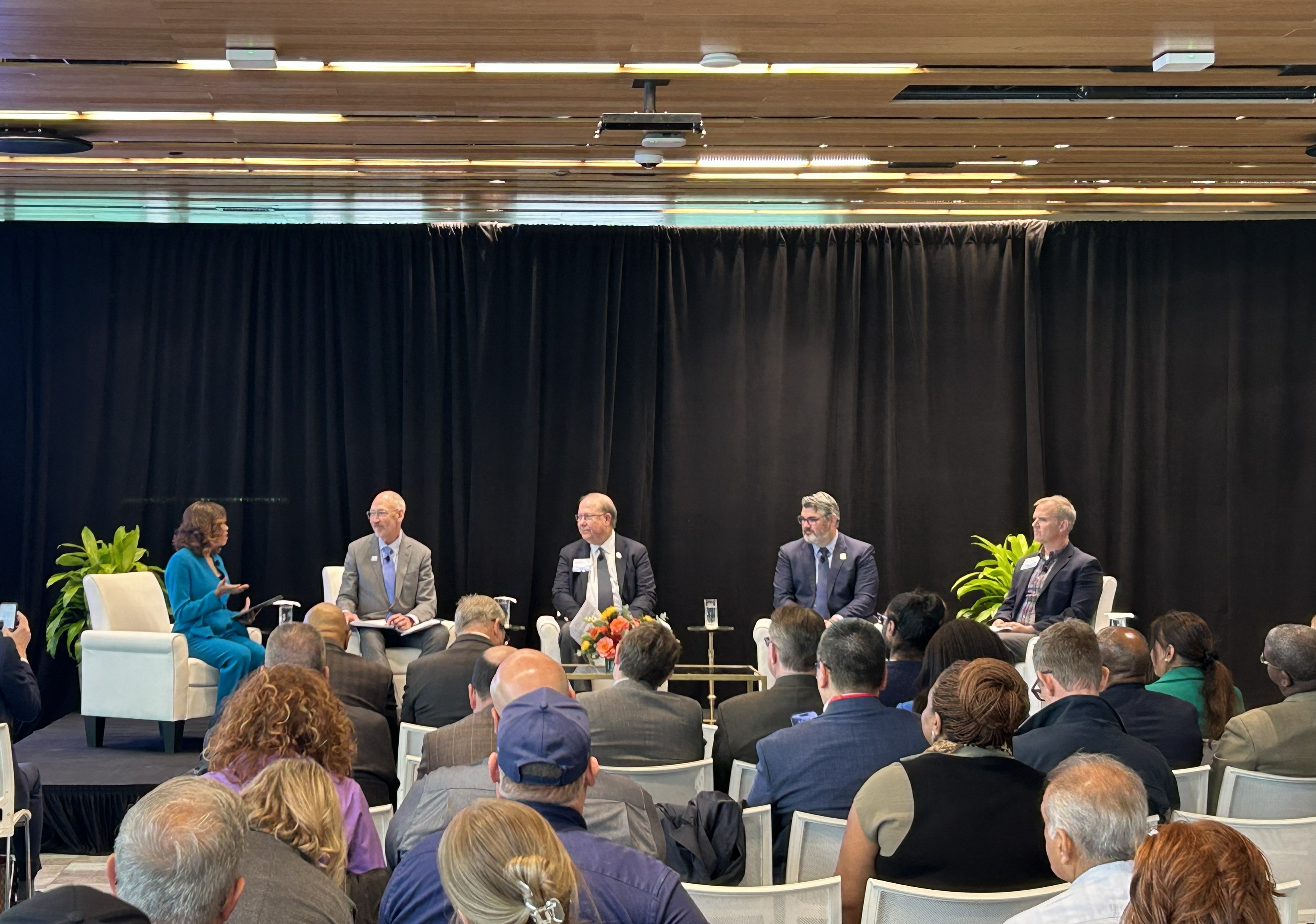
A recent conference panel, “Cleanup Today for a Nuclear Tomorrow,” highlighted the significant progress in environmental remediation at the Oak Ridge site and its direct contributions to regional economic development and the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The successful cleanup of the East Tennessee Technology Park (ETTP) has catalyzed its transformation from a former government uranium enrichment complex into a private industrial park, serving as a national hub for nuclear innovation. This report details how the project’s outcomes align with key SDGs, including those related to economic growth, innovation, sustainable communities, and clean energy.
Contribution to Economic Growth and Decent Work (SDG 8)
The redevelopment of the ETTP following extensive environmental cleanup has generated substantial economic opportunities and promoted inclusive and sustainable economic growth in the region. This directly supports the objectives of SDG 8.
- Capital Investment: The site is home to more than 25 businesses, representing a projected capital investment of $7 billion.
- Job Creation: The redevelopment is expected to generate 1,700 new private-sector jobs.
- Economic Transformation: The project has successfully converted a government liability into a thriving economic asset, fostering a business boom since 2018.
Fostering Innovation and Sustainable Infrastructure (SDG 9 & SDG 7)
The Oak Ridge cleanup initiative is a model for building resilient infrastructure and fostering innovation, which are central to SDG 9. By clearing land for advanced energy research, it also contributes to SDG 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy).
- Nuclear Innovation Hub: Successful remediation at the ETTP has enabled the establishment of the nation’s first nuclear innovation hub, which will play a crucial role in the future of national energy.
- Infrastructure Modernization: Cleanup projects at the Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) and the Y-12 National Security Complex are clearing aging, contaminated structures to make way for new infrastructure that will support future innovation and national security.
- Advancing Clean Energy: The focus on nuclear energy development within the new industrial park supports the advancement of low-carbon energy technologies.
Enhancing Community Sustainability and Responsible Land Management (SDG 11 & SDG 12)
The project exemplifies the principles of sustainable land use and responsible management of hazardous materials, contributing to safer and more resilient communities (SDG 11) and responsible production patterns (SDG 12).
- Completion of Remediation: OREM and UCOR crews have finished demolition and completed soil remediation at the ETTP.
- Historic Decommissioning: The project marked the first-ever removal of a former uranium enrichment complex in the world, addressing a significant legacy of environmental contamination.
- Land Reuse: Since 2018, 730 acres of remediated land have been transferred for economic reuse and development, transforming the site into a productive industrial park.
Multi-Stakeholder Partnerships for Sustainable Goals (SDG 17)
The success of the Oak Ridge transformation was achieved through a robust partnership between public and private sector entities, demonstrating the effectiveness of collaboration as outlined in SDG 17.
- Key Partners: The initiative involved close collaboration among government and corporate entities, including:
- OREM (Oak Ridge Office of Environmental Management)
- UCOR
- Orano USA
- Oak Ridge Corridor Development Corporation
Analysis of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in the Article
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
- SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
- SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
- SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
- SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
- SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
-
SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
- Target 7.a: By 2030, enhance international cooperation to facilitate access to clean energy research and technology, including renewable energy, energy efficiency and advanced and cleaner fossil-fuel technology, and promote investment in energy infrastructure and clean energy technology.
- Explanation: The article highlights the development of a “hub for nuclear energy development” and a “nuclear innovation hub” which will play a “crucial role in the nation’s energy future.” This directly relates to promoting investment and innovation in energy infrastructure and technology.
-
SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
- Target 8.2: Achieve higher levels of economic productivity through diversification, technological upgrading and innovation, with a focus on high-value added and labour-intensive sectors.
- Explanation: The transformation of the site into a hub for the nuclear industry, attracting over 25 businesses and fostering innovation, directly supports achieving higher economic productivity through technological upgrading.
- Target 8.5: By 2030, achieve full and productive employment and decent work for all women and men, including for young people and persons with disabilities, and equal pay for work of equal value.
- Explanation: The article explicitly mentions the expectation to “generate 1,700 new private sector jobs,” which contributes to the goal of achieving productive employment.
-
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
- Target 9.1: Develop quality, reliable, sustainable and resilient infrastructure, including regional and transborder infrastructure, to support economic development and human well-being, with a focus on affordable and equitable access for all.
- Explanation: The article describes clearing away “aging and contaminated structures” to “make way for new infrastructure that will aid innovation.” This redevelopment of a brownfield site into a modern industrial park is a clear example of developing sustainable and resilient infrastructure.
- Target 9.4: By 2030, upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable, with enhanced resource-use efficiency and greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies and industrial processes.
- Explanation: The project involves the “cleanup” and “demolition” of a “former enrichment complex” and transforming it into a “privately owned industrial park” focused on nuclear energy. This retrofitting of an old industrial site for a new, high-tech purpose aligns with this target.
-
SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
- Target 11.6: By 2030, reduce the adverse per capita environmental impact of cities, including by paying special attention to air quality and municipal and other waste management.
- Explanation: The core of the project is the environmental “cleanup” of a contaminated site, including “soil remediation” and the removal of “aging and contaminated structures.” This directly reduces environmental hazards and improves land quality.
- Target 11.a: Support positive economic, social and environmental links between urban, peri-urban and rural areas by strengthening national and regional development planning.
- Explanation: The article emphasizes the connection between “cleanup and economic opportunities happening in the region.” The successful cleanup led to a “business boom” and the transfer of land for “economic reuse and development,” strengthening the regional economy.
-
SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals
- Target 17.17: Encourage and promote effective public, public-private and civil society partnerships, building on the experience and resourcing strategies of partnerships.
- Explanation: The article features a panel with participants from a government office (OREM Manager Erik Olds), a private contractor (UCOR Director Joe Aylor), a private corporation (Orano USA President and CEO Jean-Luc Palayer), and a development corporation (Oak Ridge Corridor Development Corporation President Mike Magill). This collaboration exemplifies a public-private partnership to achieve cleanup and economic development goals.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
-
SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
- Indicator: The article states an “expectation to generate 1,700 new private sector jobs” and a “projected capital investment of $7 billion.” These are direct quantitative measures of economic growth and job creation.
-
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
- Indicator: The establishment of the “nation’s first nuclear innovation hub” and attracting “more than 25 businesses” serve as indicators of progress in fostering innovation and industrial development.
-
SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
- Indicator: Progress is measured by the “730 acres transferred for economic reuse and development.” The completion of “demolition and soil remediation at the ETTP” and the “removal of a former enrichment complex” are milestones that serve as indicators of successful cleanup and land rehabilitation.
4. Table of SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy | 7.a: Enhance international cooperation to facilitate access to clean energy research and technology… and promote investment in energy infrastructure and clean energy technology. | Establishment of a “hub for nuclear energy development” and a “nuclear innovation hub.” |
| SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth | 8.2: Achieve higher levels of economic productivity through… technological upgrading and innovation.
8.5: Achieve full and productive employment and decent work for all. |
Projected capital investment of $7 billion.
Generation of 1,700 new private sector jobs. |
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure | 9.1: Develop quality, reliable, sustainable and resilient infrastructure… to support economic development.
9.4: Upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable. |
Clearing of aging structures to make way for new infrastructure.
Establishment of over 25 businesses on the retrofitted site. |
| SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities | 11.6: Reduce the adverse per capita environmental impact of cities, including by paying special attention to… waste management.
11.a: Support positive economic, social and environmental links… by strengthening national and regional development planning. |
Completion of demolition and soil remediation.
Transfer of 730 acres for economic reuse and development. |
| SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals | 17.17: Encourage and promote effective public, public-private and civil society partnerships. | Collaboration between OREM (public), UCOR (private contractor), Orano USA (private corporation), and Oak Ridge Corridor Development Corporation. |
Source: energy.gov

What is Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0