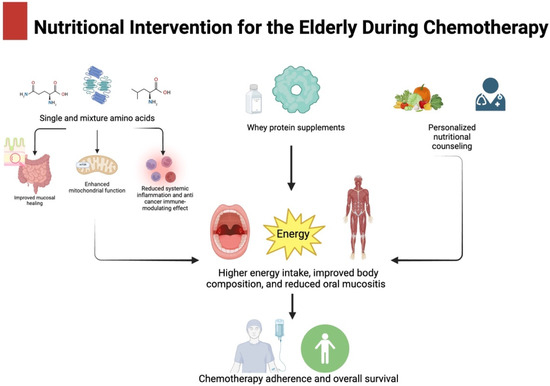
El Niño desert orchid is a tough, unique hybrid – Teche Today

Horticultural Assessment of Chitalpa ‘El Niño’ and its Contribution to Sustainable Development Goals
1.0 Introduction
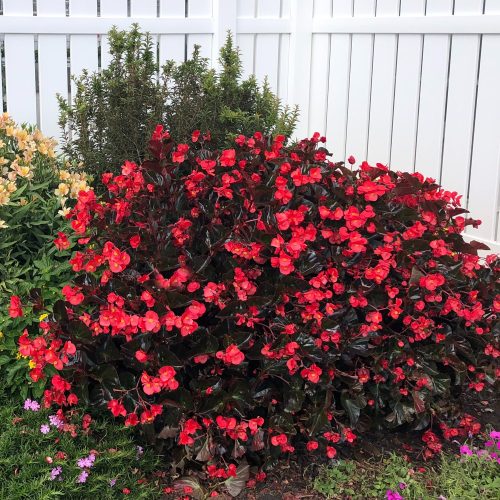
A new woody ornamental shrub, Chitalpa ‘El Niño’, has been introduced, demonstrating significant potential for resilient landscaping. This report details the botanical characteristics, cultivation requirements, and notable resilience of the plant. A primary focus is placed on its alignment with several United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly in the context of climate action, biodiversity, and sustainable communities.
The shrub is the result of a notable intergeneric hybridization between two native North American genera: Catalpa and Chilopsis (desert willow). This breeding achievement has produced a plant with exceptional hardiness and ornamental value.
2.0 Botanical and Cultivation Profile
Observations from trials at the LSU AgCenter Botanic Gardens at Burden and the Hammond Research Station provide the following profile:
- Flowers: Produces fragrant, pink-to-violet, frilly blooms from late spring through summer.
- Foliage: Features opposite-arranged, pointed leaves that create a distinct architectural structure.
- Size: A fast-growing, deciduous shrub reaching approximately 10 feet in height with a spread of 4 to 6 feet.
- Sun Exposure: Performs optimally in full sun but tolerates partial sun conditions.
- Maintenance: Requires minimal upkeep after establishment.
3.0 Environmental Resilience and Sustainability Impact
Chitalpa ‘El Niño’ exhibits a high degree of resilience, making it a valuable asset for sustainable landscaping practices. Its key attributes include:
- Climate Resilience: The plant has demonstrated tolerance to a wide range of environmental stressors, including drought, heavy precipitation, and record freezing temperatures.
- Pest and Wildlife Resistance: Trials indicate the shrub is highly resistant to deer damage.
- Support for Pollinators: The fragrant, long-lasting blooms are a significant attractant for pollinator species.
4.0 Alignment with Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
The characteristics of Chitalpa ‘El Niño’ directly support the advancement of several key SDGs.
SDG 15: Life on Land
- Halting Biodiversity Loss: By attracting and providing a consistent food source for pollinators, the shrub actively supports local ecosystem health and biodiversity.
- Sustainable Use of Terrestrial Ecosystems: The plant’s development from native species showcases an innovative and sustainable use of genetic resources. Its deer resistance helps protect landscapes from degradation in areas with high deer populations.
SDG 13: Climate Action
- Climate Change Adaptation: The shrub’s proven tolerance to extreme weather events, such as drought and unseasonal freezes, makes it a climate-resilient species suitable for gardens and landscapes adapting to changing climatic conditions.
SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
- Resilient and Sustainable Urban Green Spaces: As a low-maintenance and hardy plant, it is ideal for public and private landscaping, reducing the resource burden (water, labor) on communities. Its unique aesthetic qualities enhance the value of urban green spaces.
SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation
- Sustainable Water Management: The plant’s significant drought tolerance reduces the need for supplemental irrigation, conserving vital freshwater resources, a key target for sustainable water management in residential and municipal settings.
Analysis of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in the Article
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
-
SDG 15: Life on Land
This goal is relevant because the article focuses on a new plant hybrid that supports local ecosystems. It explicitly mentions that the El Niño desert orchid attracts pollinators, which is a critical component of biodiversity and terrestrial ecosystem health. The discussion of creating a hybrid from native plants also touches upon the conservation and sustainable use of plant genetic resources.
-
SDG 13: Climate Action
This goal is addressed through the plant’s resilience to extreme weather events. The article highlights its ability to handle “droughts, heavy rain” and survive “record freezing temperatures.” This demonstrates the plant’s adaptive capacity to climate-related hazards, making it a suitable choice for creating climate-resilient gardens and landscapes.
-
SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
This goal is connected as the article promotes the plant for use in “Louisiana gardens” and public spaces like the “AgCenter Botanic Gardens at Burden.” By introducing a low-maintenance, resilient, and pollinator-friendly shrub, it contributes to the development of sustainable, resilient, and biodiverse urban and suburban green spaces.
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
-
Target 15.5: Take urgent and significant action to reduce the degradation of natural habitats, halt the loss of biodiversity…
The article supports this target by highlighting that the El Niño shrub is “drawing in a lot of pollinators.” Promoting plants that provide food and habitat for pollinators is a direct action to support and halt the loss of biodiversity in local environments like gardens.
-
Target 13.1: Strengthen resilience and adaptive capacity to climate-related hazards and natural disasters in all countries.
The article directly relates to this target by describing the plant’s toughness and ability to withstand extreme weather. The text states it “can handle droughts, heavy rain and everything in between. It even survived Louisiana’s record freezing temperatures this past winter.” This showcases the plant as a tool for building climate-resilient landscapes.
-
Target 11.7: By 2030, provide universal access to safe, inclusive and accessible, green and public spaces…
While not about access, the article contributes to the quality and sustainability of green spaces. By promoting a “tough-as-nails, easycare shrub” that is also deer-resistant and thrives in various conditions, it helps ensure that gardens and public green spaces can be maintained sustainably, enhancing their ecological value and appeal.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
-
Indicator for Pollinator Support (Implied)
The statement that the plant is “drawing in a lot of pollinators” implies that progress can be measured by observing and quantifying the number and diversity of pollinator species attracted to the El Niño shrub in gardens and research stations. This is a direct measure of its contribution to local biodiversity.
-
Indicator for Climate Resilience (Implied)
The article mentions the plant’s survival through “record freezing temperatures” and its tolerance for drought and heavy rain. This implies an indicator related to the survival and health rate of the plant under documented extreme weather conditions. The trials conducted at Burden and the Hammond Research Station are actively measuring this.
-
Indicator for Sustainable Landscaping (Implied)
The promotion of this “low maintenance” and “deer resistant” plant for local gardens suggests an indicator could be the rate of adoption or the total area planted with this resilient and ecologically beneficial shrub in residential and public landscapes. This would measure the integration of sustainable practices in community greening efforts.
4. Summary Table of SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators (Mentioned or Implied) |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 15: Life on Land | Target 15.5: Halt biodiversity loss. | The number and diversity of pollinator species attracted to the plant. |
| SDG 13: Climate Action | Target 13.1: Strengthen resilience and adaptive capacity to climate-related hazards. | The survival and growth rate of the plant under extreme weather conditions (drought, heavy rain, freeze). |
| SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities | Target 11.7: Enhance the quality and sustainability of green spaces. | The adoption rate or area of cultivation of low-maintenance, resilient plants in local gardens. |
Source: techetoday.com

What is Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0