Paducah a finalist for national AI Data Center and Energy Infrastructure Initiative – Lane Report

Report on the Selection of Paducah, KY for AI and Energy Infrastructure Development in Alignment with Sustainable Development Goals
1.0 Introduction and Project Overview
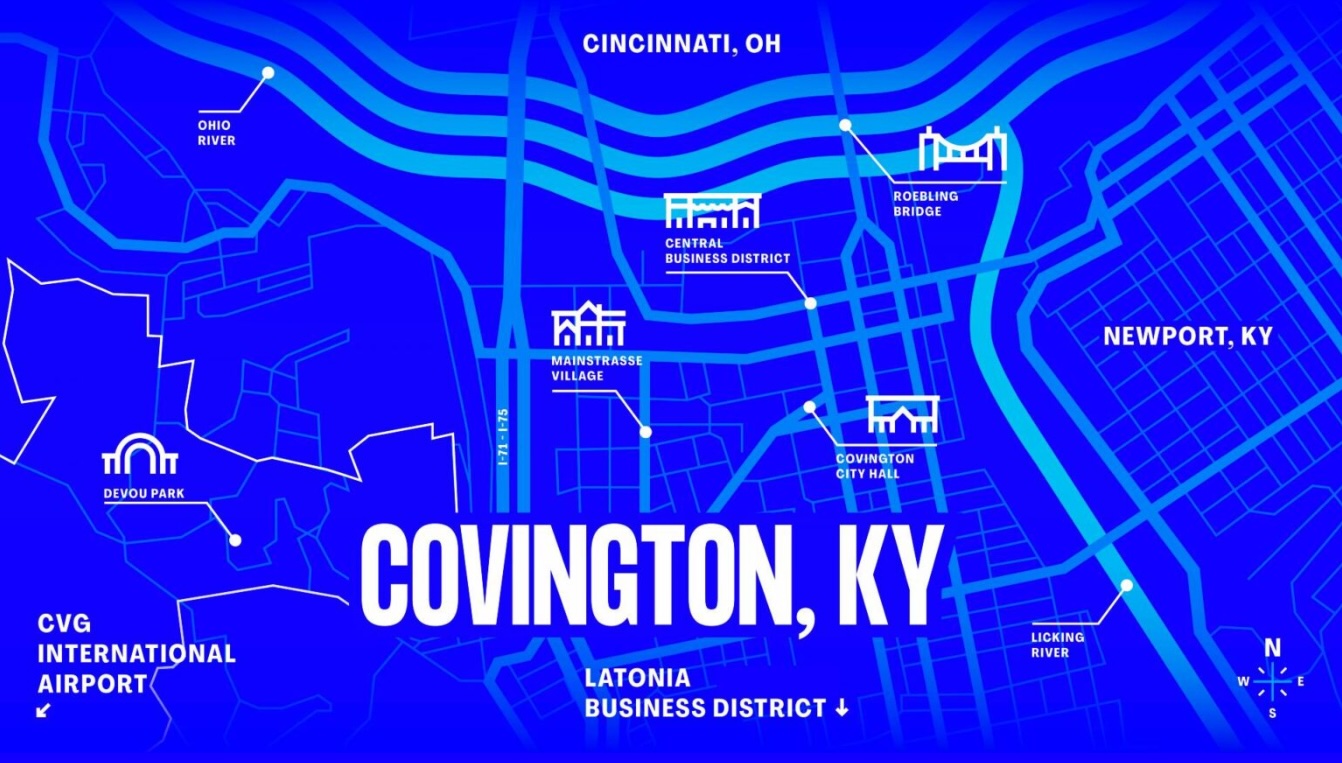
The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) has designated the Paducah Gaseous Diffusion Plant site in Kentucky as one of four national finalists for the development of Artificial Intelligence (AI) Data Centers and related energy infrastructure. This initiative is poised to make substantial contributions toward achieving several United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) by repurposing a legacy federal asset for modern technological and energy needs.
2.0 Alignment with Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
The proposed development in Paducah demonstrates a strong commitment to multiple SDGs, transforming a site undergoing environmental remediation into a hub for future-focused technology and sustainable energy.
- SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy: A central component of the proposal is the potential construction of a modern nuclear power reactor. This directly addresses the significant energy requirements of AI data centers with a reliable, carbon-free energy source, supporting the global transition to sustainable energy systems.
- SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure: The project is fundamentally focused on building resilient, next-generation infrastructure (data centers) and fostering technological innovation (AI). It leverages existing assets, including extensive electrical infrastructure and a strong fiber network, to create a foundation for future industrial and technological growth.
- SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth: The projected multibillion-dollar investment is expected to catalyze significant local and regional economic growth. It promises the creation of new, high-quality jobs, thereby promoting sustained, inclusive, and sustainable economic development for the community.
- SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities: By repurposing a former industrial site that has been the subject of extensive environmental cleanup, the project contributes directly to industrial and community regeneration. This revitalization effort enhances the economic resilience and long-term sustainability of the Paducah region.
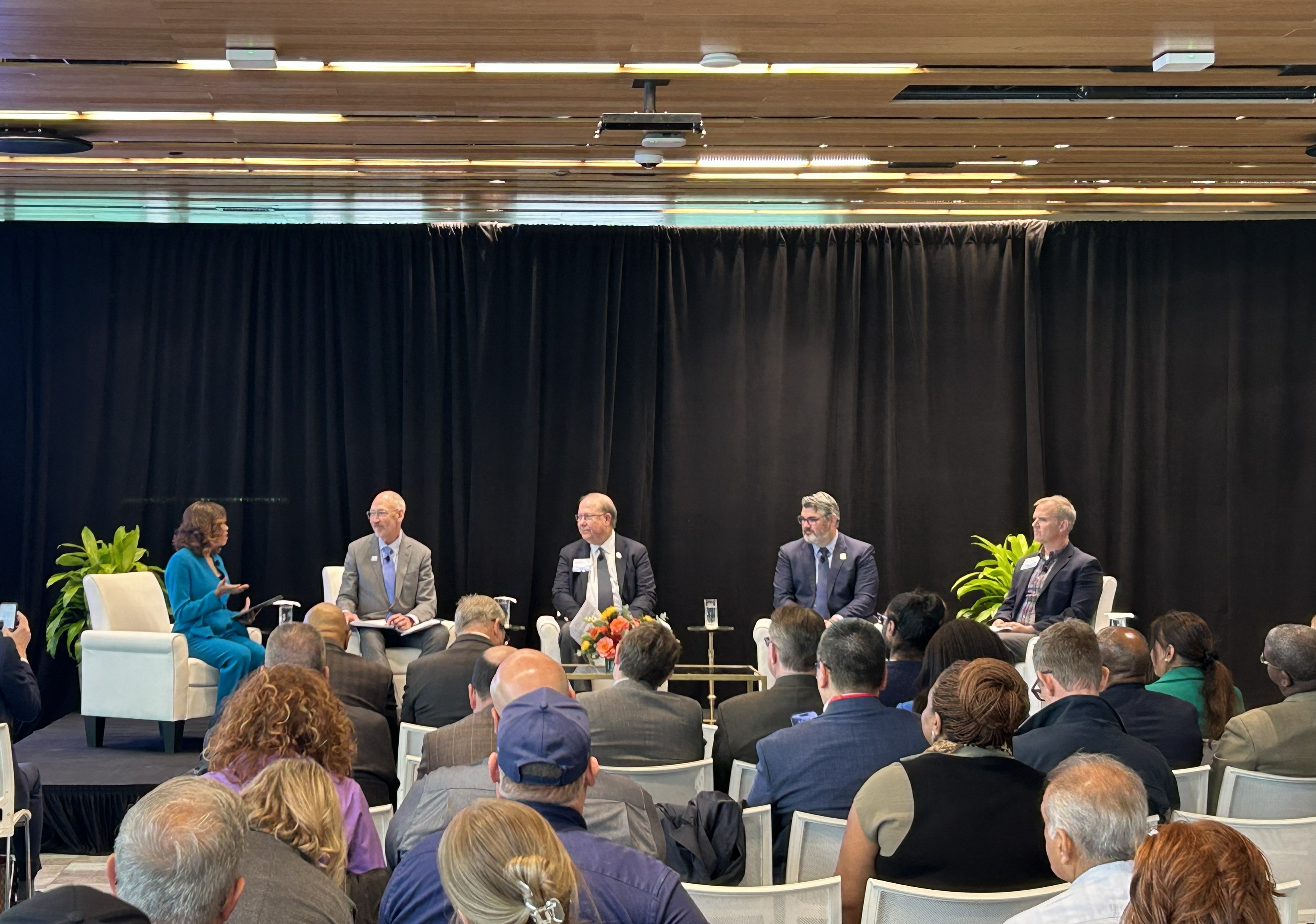
- SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals: The successful bid exemplifies a multi-stakeholder partnership involving the DOE, federal, state, and local governments, utility partners, and community organizations. This collaborative model is critical for implementing and achieving complex sustainable development objectives.
3.0 Site Selection and Strategic Attributes
Paducah was selected from a competitive field alongside three other DOE-managed locations. The choice was predicated on the site’s unique capacity to support large-scale, energy-intensive development in a sustainable manner.
3.1 Finalist Locations
- Paducah Gaseous Diffusion Plant, Kentucky
- Idaho National Laboratory, Idaho
- Oak Ridge Reservation, Tennessee
- Savannah River Site, South Carolina
3.2 Paducah’s Strategic Assets for Sustainable Development
The community’s bid highlighted its strategic advantages, which are well-aligned with the infrastructure and innovation targets of SDG 9.
- Unparalleled electrical infrastructure
- Access to significant natural gas capacity
- A robust fiber optic network
- A skilled labor force with capacity for growth
- A unified community vision designating the area as “nuclear-friendly”
4.0 Site History and Future Vision
The Paducah Gaseous Diffusion Plant, operational since 1952, is currently managed by the DOE’s Environmental Management program, which oversees extensive cleanup and decommissioning activities. This project charts a new, forward-looking course for the site.
- Legacy Operations: The site historically produced enriched uranium for national defense and commercial power before commercial operations ceased in 2013.
- Environmental Stewardship (SDG 12): Ongoing environmental remediation, waste management, and decontamination efforts reflect a commitment to responsible consumption and production patterns through the safe management of a legacy industrial site.
- Future Vision: The community and its partners aim to establish Paducah as a global leader in the nuclear energy ecosystem, from enrichment to power generation, contributing to both national energy security and global AI leadership.
5.0 Next Steps and Conclusion
Greater Paducah Economic Development (GPED) will maintain close collaboration with the DOE during engagement with private sector developers and energy providers. Final project partner selections are anticipated by the end of the year. This initiative firmly positions Paducah at the nexus of national efforts to build secure, sustainable infrastructure for the AI era, serving as a powerful example of how the Sustainable Development Goals can be applied to foster economic prosperity and technological leadership.
Analysis of SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
- SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
- SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
- SDG 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure
- SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
- SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
-
SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
- Target 7.1: By 2030, ensure universal access to affordable, reliable and modern energy services. The article mentions that the initiative aims to “lower energy costs” and provide power for new AI data centers, which require significant and reliable energy.
- Target 7.a: By 2030, enhance international cooperation to facilitate access to clean energy research and technology, including renewable energy, energy efficiency and advanced and cleaner fossil-fuel technology, and promote investment in energy infrastructure and clean energy technology. The project involves deploying “Advanced Nuclear Reactor Technologies” and investing in “Energy Infrastructure,” reflecting a focus on advanced, clean energy technology.
-
SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
- Target 8.2: Achieve higher levels of economic productivity through diversification, technological upgrading and innovation, including through a focus on high-value added and labour-intensive sectors. The project focuses on high-tech sectors like AI and advanced nuclear energy, which represent technological upgrading and innovation.
- Target 8.3: Promote development-oriented policies that support productive activities, decent job creation, entrepreneurship, creativity and innovation. The article explicitly states the community welcomes “capital investment, economic development, and job growth.”
-
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure
- Target 9.1: Develop quality, reliable, sustainable and resilient infrastructure, including regional and transborder infrastructure, to support economic development and human well-being. The core of the project is the development of “AI Data Center and Energy Infrastructure” and leveraging the site’s “unparalleled electrical infrastructure.”
- Target 9.4: By 2030, upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable, with enhanced resource-use efficiency and greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies and industrial processes. The project involves redeveloping the Paducah Gaseous Diffusion Plant, a former industrial site, with modern, advanced technologies like AI data centers and nuclear reactors.
-
SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
- Target 11.3: By 2030, enhance inclusive and sustainable urbanization and capacity for participatory, integrated and sustainable human settlement planning and management in all countries. The selection of Paducah was supported by a “community letter of interest and support” involving local leadership, utility partners, and community organizations, demonstrating participatory planning for community development.
- Target 11.a: Support positive economic, social and environmental links between urban, peri-urban and rural areas by strengthening national and regional development planning. The project is a national initiative by the DOE that directly impacts the Paducah region, aiming to foster economic development and job growth by leveraging the area’s unique assets.
-
SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals
- Target 17.17: Encourage and promote effective public, public-private and civil society partnerships, building on the experience and resourcing strategies of partnerships. The article highlights extensive collaboration between the Department of Energy (public), “private-sector data center developers” (private), and “state and local governments,” “utility partners,” and “community organizations” (civil society).
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
-
SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
- Indicator (Implied): Amount of investment in clean energy. The article mentions a potential “multibillion-dollar investment” in a modern nuclear power reactor.
- Indicator (Implied): The proportion of the population with access to electricity. The project aims to build energy infrastructure to meet the “rapidly growing electric power demand for AI data centers.”
-
SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
- Indicator (Implied): Job creation. The project is expected to lead to “job growth in our community.”
- Indicator (Implied): Inflow of investment. The article mentions the community welcomes “capital investment” and the project itself is a “multibillion-dollar investment.”
-
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure
- Indicator (Implied): Development of new infrastructure. The project is explicitly for “AI Data Center and Energy Infrastructure development.”
- Indicator (Implied): Adoption of new technologies. The project involves “Advanced Nuclear Reactor Technologies” and infrastructure for “AI dominance.”
-
SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
- Indicator (Implied): Redevelopment of contaminated or industrial sites. The project is located at the Paducah Gaseous Diffusion Plant, a site undergoing “environmental cleanup activities.”
- Indicator (Implied): Level of community and stakeholder participation. Progress can be measured by the successful collaboration mentioned between the DOE, local governments, and community stakeholders.
-
SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals
- Indicator (Implied): Number and quality of multi-stakeholder partnerships. The article details a partnership involving the DOE, congressional and state delegations, local leadership, utility partners, private developers, and community organizations.
4. Table of SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy |
|
|
| SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth |
|
|
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure |
|
|
| SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities |
|
|
| SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals |
|
|
Source: lanereport.com

What is Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0