3 Agriculture – Products Stocks to Watch in a Promising Industry
3 Agriculture - Products Stocks to Watch in a Promising Industry Yahoo Finance


The Zacks Agriculture – Products Industry: A Report
The Zacks Agriculture – Products industry will benefit from the stable demand for food, supported by an increasing population. Rising consumer awareness regarding food ingredients and the preference for healthier alternatives will continue to boost the industry’s growth prospects. Alternative and innovative agricultural technologies like hydroponics and vertical farming are expected to be other key catalysts, given their inherent benefits.
Players like Bunge Limited BG, The Andersons, Inc. ANDE and Arcadia Biosciences RKDA are poised to gain from strong end-market demand and their ongoing growth initiatives.
Industry Description
The Zacks Agriculture – Products industry comprises companies that are either involved in storing agricultural commodities, distributing ingredients to others or engaged in farming crops, livestock and poultry products. Some are engaged in purchasing, storing, transporting, processing and selling agricultural commodities or products derived from the same. They operate grain elevators, where income is generated from commodities bought and sold using these elevators or held as inventory. Some companies provide nutrients, advanced indoor and greenhouse lighting, environmental control systems and accessories for hydroponic gardening — the method of growing plants using mineral nutrient solutions in a water solvent instead of soil. A few players offer innovative, plant-based health and wellness products. Companies producing lumber also fall under this industry.
Trends Shaping the Future of the Agriculture – Products Industry
Solid Demand to Support Industry: Demand for food is directly influenced by population and demographic changes besides income growth and income distribution. Per the United Nations, the global population will rise to 8.5 billion in 2030 and 9.7 billion in 2050. This would lead to a 50% increase in global food demand. In response to growing consumer demand for healthier food alternatives, several agricultural and food-based companies are investing in innovation and augmenting their product and market strategies to bring new quality and healthy food ingredients to the market. Ongoing improvements in grain-handling techniques and investment in larger storage spaces will likely support the industry. Plus, stable earnings across all cycles are ensured, considering the industry’s products are always in demand, irrespective of the condition of the economy.
Hydroponics & Cannabis Are Key Catalysts: Hydroponics is gaining popularity as it gives growers the ability to regulate better and control nutrient delivery, light, air, water, humidity, pests and temperature in an indoor setting. It can help produce crops faster with higher yields than traditional soil-based growers. It is being utilized in new and emerging industries, including the cultivation of cannabis and hemp. Vertical farms producing organic fruits and vegetables also utilize hydroponics due to a rising shortage of farmland and environmental vulnerabilities. Also, vertical farming is the latest agricultural technology, wherein companies use shelves and artificial light to grow produce, minimizing land and water consumption. Total sales for the hydroponic equipment industry are projected to surpass $16 billion by 2025. Even though the cannabis industry is undergoing a rough patch due to an oversupply, its long-term prospects are intact. In the United States, several states have legalized cannabis for medical or recreational use, representing the largest market in the world. By 2027, spending on legal cannabis is expected to reach $47.3 billion in North America.
Cost-Saving Actions to Aid Margins: Players in the industry are facing rising labor, packaging and distribution costs, among other expenses. Companies engaged in animal products have been facing increasing production costs for a while due to elevated feed ingredient prices. However, feed prices have eased lately. The industry continues to navigate a tight labor market with a spike in wages and higher distribution costs. Recently, industry players have been reporting improvements in the supply-chain issues that have been plaguing them so far. They have been making efforts to bolster their financial conditions, conserve cash and improve profitability by implementing pricing and cost-reduction actions, which are likely to help sustain margins in the future.
Zacks Industry Rank Indicates Bright Prospects
The Zacks Agriculture – Products industry is part of the broader Zacks Basic Materials sector. The industry currently carries a Zacks Industry Rank #55, which places it in the top 22% of the 251 Zacks industries.
The group’s Zacks Industry Rank, basically the average of the Zacks Rank of all the member stocks, indicates bright prospects in the near term. Our research shows that the top 50% of the Zacks-ranked industries outperform the bottom 50% by a factor of more than 2 to 1.
Before we present a few stocks worth considering for your portfolio, let’s look at the industry’s recent stock market performance and valuation.
Industry Versus Broader Market
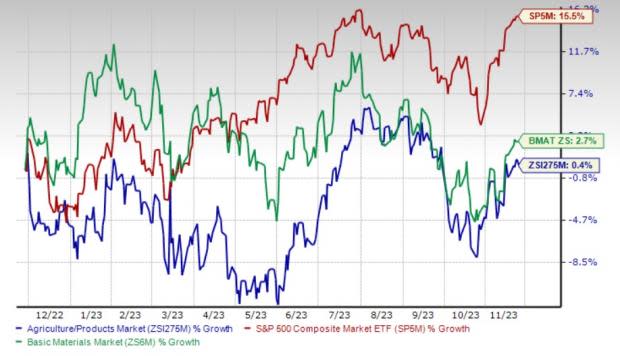
The Zacks Agriculture – Products industry has underperformed its sector and the Zacks S&P 500 composite over the past 12 months. Stocks in this industry have moved up 0.4% in the past 12 months compared with the S&P 500’s growth of 15.5% and the Basic Materials sector’s rise of 2.7%.
One-Year Price Performance

Industry’s Current Valuation
On the basis of the trailing 12-month EV/EBITDA ratio, a commonly used multiple for valuing Agriculture – Products stocks, we see that the industry is currently trading at 4.86X compared with the S&P 500’s 13.21X. The Basic Materials sector’s trailing 12-month EV/EBITDA is 11.14X. This is
SDGs, Targets, and Indicators Analysis
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
- SDG 2: Zero Hunger
- SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being
- SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
- SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
- SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
- SDG 13: Climate Action
- SDG 15: Life on Land
The article discusses the agriculture industry, which is directly related to SDG 2 (Zero Hunger) as it focuses on food production and distribution. It also mentions the rising demand for healthier food alternatives, which connects to SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-being). The industry’s growth prospects and the need for innovative agricultural technologies align with SDG 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth) and SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure). The article also mentions hydroponics and vertical farming, which contribute to SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production) by promoting sustainable farming practices. Additionally, the mention of environmental vulnerabilities and the need for cost-saving actions relates to SDG 13 (Climate Action) and SDG 15 (Life on Land).
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
- Target 2.1: By 2030, end hunger and ensure access by all people, in particular the poor and people in vulnerable situations, including infants, to safe, nutritious, and sufficient food all year round.
- Target 3.4: By 2030, reduce by one-third premature mortality from non-communicable diseases through prevention and treatment and promote mental health and well-being.
- Target 8.2: Achieve higher levels of economic productivity through diversification, technological upgrading, and innovation, including through a focus on high-value added and labor-intensive sectors.
- Target 9.4: By 2030, upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable, with increased resource-use efficiency and greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies and industrial processes.
- Target 12.2: By 2030, achieve the sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources.
- Target 13.3: Improve education, awareness-raising, and human and institutional capacity on climate change mitigation, adaptation, impact reduction, and early warning.
- Target 15.1: By 2020, ensure the conservation, restoration, and sustainable use of terrestrial and inland freshwater ecosystems and their services.
Based on the article’s content, the identified targets are aligned with the SDGs mentioned above. These targets focus on ending hunger, promoting good health, achieving economic growth through innovation, upgrading infrastructure for sustainability, managing natural resources efficiently, addressing climate change, and conserving ecosystems.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
- Indicator 2.1.1: Prevalence of undernourishment
- Indicator 3.4.1: Mortality rate attributed to cardiovascular disease, cancer, diabetes, or chronic respiratory disease
- Indicator 8.2.1: Annual growth rate of real GDP per employed person
- Indicator 9.4.1: CO2 emission per unit of value added
- Indicator 12.2.1: Material footprint, material footprint per capita, and material footprint per GDP
- Indicator 13.3.1: Number of countries that have communicated the strengthening of institutional, systemic, and individual capacity-building to implement adaptation, mitigation, and technology transfer
- Indicator 15.1.1: Forest area as a proportion of total land area
The article does not explicitly mention these indicators, but they can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets. These indicators focus on measuring undernourishment, mortality rates from non-communicable diseases, economic growth, CO2 emissions, material footprint, capacity-building for climate change, and forest conservation.
SDGs, Targets, and Indicators Table
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 2: Zero Hunger | Target 2.1: By 2030, end hunger and ensure access by all people, in particular the poor and people in vulnerable situations, including infants, to safe, nutritious, and sufficient food all year round. | Indicator 2.1.1: Prevalence of undernourishment |
| SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being | Target 3.4: By 2030, reduce by one-third premature mortality from non-communicable diseases through prevention and treatment and promote mental health and well-being. | Indicator 3.4.1: Mortality rate attributed to cardiovascular disease, cancer, diabetes, or chronic respiratory disease |
| SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth | Target 8.2: Achieve higher levels of economic productivity through diversification, technological upgrading, and innovation, including through a focus on high-value added and labor-intensive sectors. | Indicator 8.2.1: Annual growth rate of real GDP per employed person |
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure | Target 9.4: By 2030, upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable, with increased resource-use efficiency and greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies and industrial processes. | Indicator 9.4.1: CO2 emission per unit of value added |
| SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production | Target 12.2: By 2030, achieve the sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources. | Indicator 12.2.1: Material footprint, material footprint per capita, and material footprint per GDP |
| SDG 13: Climate Action |

Join us, as fellow seekers of change, on a transformative journey at https://sdgtalks.ai/welcome, where you can become a member and actively contribute to shaping a brighter future.







