CO2 worsens wildfires by helping plants grow
CO2 worsens wildfires by helping plants grow | UCR News | UC Riverside UC Riverside


Fueling the Severity and Frequency of Wildfires: The Role of Carbon Dioxide
Introduction
A recent study conducted by UC Riverside has revealed that carbon dioxide (CO2) is a major driver behind the increasing severity and frequency of wildfires. While climate change is often blamed for the surge in wildfires, the study suggests that the impact of rising CO2 levels on plant growth plays a significant role.
The Impact of CO2 on Plant Growth
Plants require CO2 for photosynthesis, the process through which they convert light into food. With the burning of fossil fuels, the atmosphere is being filled with increasing levels of CO2. This additional CO2 allows plants to produce more carbohydrates, leading to an increase in biomass that becomes fuel for wildfires.
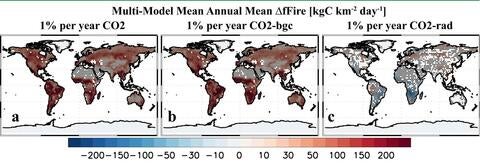
Model Experiments and Findings
The study conducted eight model experiments to analyze the effects of increasing CO2 concentrations since 1850 on wildfire activity. The models accounted for various factors such as different plant types, the increase in atmospheric CO2, and the impact of heat waves and drought on plant withering and flammability. The findings revealed that while warming and drying conditions are still important factors in promoting wildfires, the increase in fires during hotter seasons is primarily driven by the abundance of fuel rather than an increase in “fire weather” days.
Implications and Recommendations
The researchers emphasize the need for further studies to understand the factors contributing to the increase in wildfires. Additionally, they urge policymakers to recognize the urgent need to reduce CO2 emissions. While implementing better fire control measures and prescribed burns can help manage fuel load, the most effective way to decrease wildfires is by mitigating carbon dioxide emissions.
Conclusion
The study highlights the significant impact of carbon dioxide on the severity and frequency of wildfires. By focusing on the Sustainable Development Goal of Climate Action (SDG 13), it becomes evident that urgent action is required to reduce CO2 emissions and mitigate the devastating effects of wildfires on ecosystems and communities.
(Cover image: Toa55/iStock/Getty)
SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
- SDG 13: Climate Action
- SDG 15: Life on Land
The article discusses the impact of carbon dioxide on wildfires, which is directly related to climate change and the degradation of land ecosystems.
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
- SDG 13.1: Strengthen resilience and adaptive capacity to climate-related hazards and natural disasters
- SDG 15.1: By 2020, ensure the conservation, restoration, and sustainable use of terrestrial and inland freshwater ecosystems and their services, in particular forests, wetlands, mountains, and drylands, in line with obligations under international agreements
- SDG 15.2: By 2020, promote the implementation of sustainable management of all types of forests, halt deforestation, restore degraded forests, and substantially increase afforestation and reforestation globally
The article highlights the need to strengthen resilience and adaptive capacity to wildfires caused by increased carbon dioxide levels. It also emphasizes the importance of conserving and restoring terrestrial ecosystems, particularly forests, to mitigate the severity and frequency of wildfires.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
- Indicator for SDG 13.1: Number of deaths, missing persons, and directly affected persons attributed to disasters per 100,000 population
- Indicator for SDG 15.1: Forest area as a proportion of total land area
- Indicator for SDG 15.2: Proportion of important sites for terrestrial and freshwater biodiversity that are covered by protected areas, by ecosystem type
The article does not explicitly mention specific indicators, but these indicators can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets. The number of deaths, missing persons, and directly affected persons attributed to wildfires can indicate the resilience and adaptive capacity to climate-related hazards. The forest area as a proportion of total land area can measure the conservation and restoration efforts of terrestrial ecosystems. The proportion of important sites for biodiversity covered by protected areas can reflect the sustainable management and restoration of forests.
SDGs, Targets, and Indicators Table
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 13: Climate Action | 13.1: Strengthen resilience and adaptive capacity to climate-related hazards and natural disasters | Number of deaths, missing persons, and directly affected persons attributed to disasters per 100,000 population |
| SDG 15: Life on Land | 15.1: By 2020, ensure the conservation, restoration, and sustainable use of terrestrial and inland freshwater ecosystems and their services, in particular forests, wetlands, mountains, and drylands, in line with obligations under international agreements | Forest area as a proportion of total land area |
| 15.2: By 2020, promote the implementation of sustainable management of all types of forests, halt deforestation, restore degraded forests, and substantially increase afforestation and reforestation globally | Proportion of important sites for terrestrial and freshwater biodiversity that are covered by protected areas, by ecosystem type |
Behold! This splendid article springs forth from the wellspring of knowledge, shaped by a wondrous proprietary AI technology that delved into a vast ocean of data, illuminating the path towards the Sustainable Development Goals. Remember that all rights are reserved by SDG Investors LLC, empowering us to champion progress together.
Source: news.ucr.edu

Join us, as fellow seekers of change, on a transformative journey at https://sdgtalks.ai/welcome, where you can become a member and actively contribute to shaping a brighter future.