Trade in agricultural goods down 3.2% in 2023
Trade in agricultural goods down 3.2% in 2023 - Eurostat European Commission


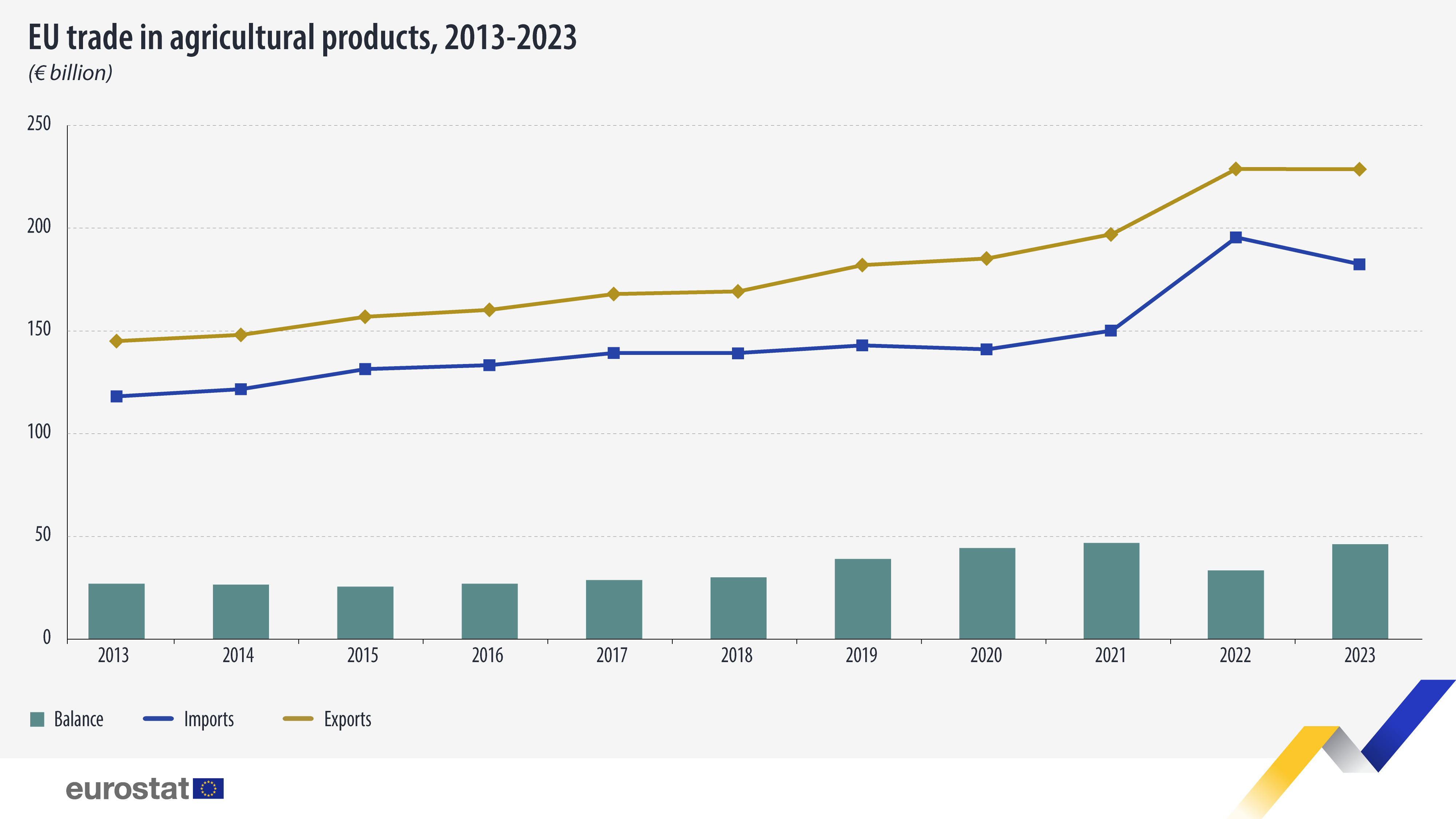
EU Trade in Agricultural Products: 2013-2023
In 2023, the value of trade (imports and exports) of agricultural products between the European Union (EU) and the rest of the world reached €410.9 billion, which is €13.5 billion less than in 2022 (€424.4 billion), resulting in a decrease of 3.2%.
The EU exported €228.6 billion worth of agricultural products and imported €182.3 billion, generating a surplus of €46.3 billion. While the value of exports remained stable between 2022 and 2023, there was a noticeable decrease in the value of imports (-6.8%).
Between 2013 and 2023, EU trade in agricultural products increased by 56.2% (from €263.1 billion to €410.9 billion), with an average annual growth rate of 4.6%. During this period, exports grew faster (4.7%) than imports (4.4%).
Source dataset: ds-045409
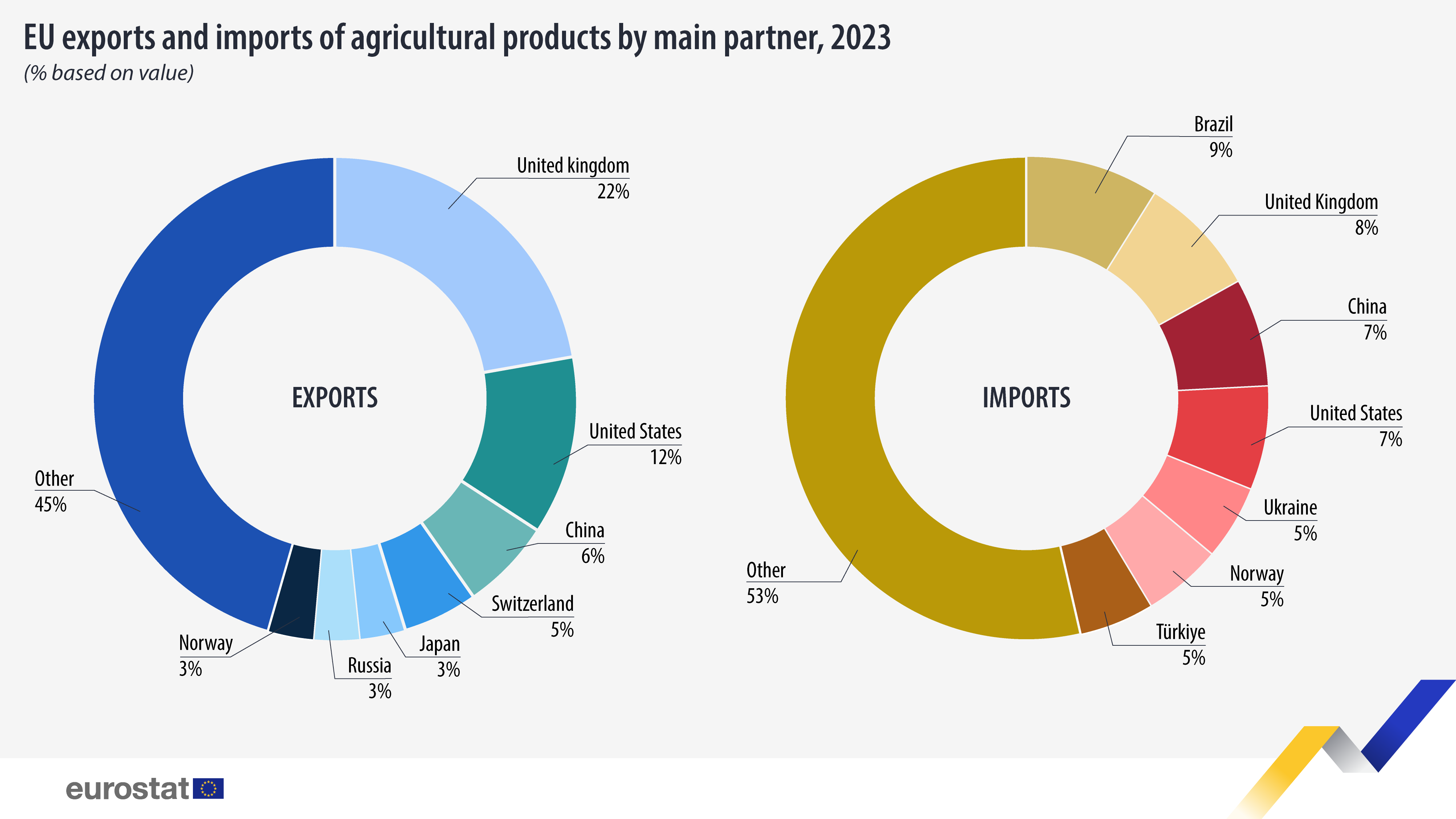
UK and Brazil: Biggest Export and Import Partners
The United Kingdom was the main export partner for the EU, accounting for a 22% share in EU exports of agricultural products (equivalent to €48.6 billion). This was followed by the United States (12%; €27.5 billion), China (6%; €13.5 billion), Switzerland (5%; €12.1 billion), Japan (3%; €7.2 billion), and Russia (3%; €6.6 billion).
EU imports of agricultural products mostly originated from Brazil (9%; €16.9 billion), the United Kingdom (8%; €15.8 billion), China (7%; €13.3 billion), the United States (7%; €13.1 billion), Ukraine (5%; €9.5 billion), and Norway (5%; €9.2 billion).
Source dataset: ds-045409
SDGs, Targets, and Indicators Analysis
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
- SDG 2: Zero Hunger – The article discusses the trade of agricultural products, which is directly related to achieving SDG 2, which aims to end hunger, achieve food security, improve nutrition, and promote sustainable agriculture.
- SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth – The article mentions the value of trade in agricultural products, which is connected to SDG 8’s target of promoting sustained, inclusive, and sustainable economic growth, full and productive employment, and decent work for all.
- SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production – The article highlights the trade of agricultural products between the EU and the rest of the world, which is relevant to SDG 12’s target of ensuring sustainable consumption and production patterns.
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
- SDG 2.3: By 2030, double the agricultural productivity and incomes of small-scale food producers, particularly women, indigenous peoples, family farmers, pastoralists, and fishers.
- SDG 8.1: Sustain per capita economic growth in accordance with national circumstances and, in particular, at least 7 percent gross domestic product growth per annum in the least developed countries.
- SDG 12.2: By 2030, achieve the sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
- Indicator for SDG 2.3: Agricultural productivity and incomes of small-scale food producers.
- Indicator for SDG 8.1: Gross domestic product growth rate.
- Indicator for SDG 12.2: Sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources in agricultural production.
Table: SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 2: Zero Hunger | 2.3: By 2030, double the agricultural productivity and incomes of small-scale food producers, particularly women, indigenous peoples, family farmers, pastoralists, and fishers. | Agricultural productivity and incomes of small-scale food producers. |
| SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth | 8.1: Sustain per capita economic growth in accordance with national circumstances and, in particular, at least 7 percent gross domestic product growth per annum in the least developed countries. | Gross domestic product growth rate. |
| SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production | 12.2: By 2030, achieve the sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources. | Sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources in agricultural production. |
Copyright: Dive into this article, curated with care by SDG Investors Inc. Our advanced AI technology searches through vast amounts of data to spotlight how we are all moving forward with the Sustainable Development Goals. While we own the rights to this content, we invite you to share it to help spread knowledge and spark action on the SDGs.
Fuente: ec.europa.eu

Join us, as fellow seekers of change, on a transformative journey at https://sdgtalks.ai/welcome, where you can become a member and actively contribute to shaping a brighter future.







