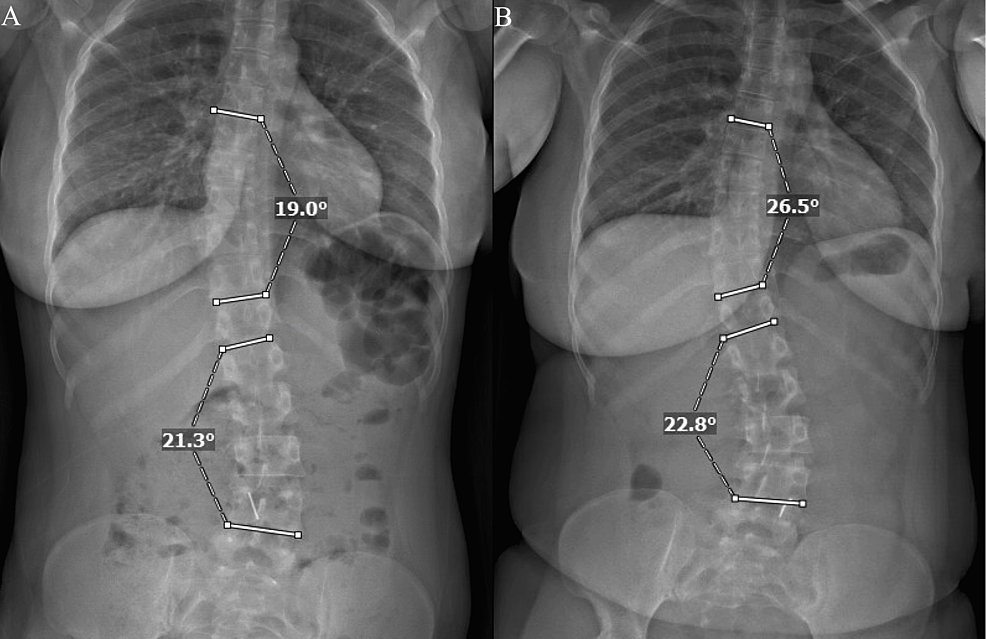
Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis and Pregnancy
Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis and Pregnancy | Article Cureus


Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and their Significance
Introduction
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are a set of 17 global goals established by the United Nations in 2015. These goals aim to address various social, economic, and environmental challenges faced by countries around the world. The SDGs provide a framework for sustainable development and serve as a guide for governments, organizations, and individuals to work towards a more inclusive and sustainable future.
Significance of the SDGs
The SDGs are significant for several reasons:
- Comprehensive Approach: The SDGs cover a wide range of issues, including poverty, hunger, health, education, gender equality, clean water and sanitation, affordable and clean energy, decent work and economic growth, industry innovation and infrastructure, reduced inequalities, sustainable cities and communities, responsible consumption and production, climate action, life below water, life on land, peace, justice and strong institutions, and partnerships for the goals. This comprehensive approach ensures that no aspect of sustainable development is overlooked.
- Global Collaboration: The SDGs provide a common language and framework for countries to collaborate on addressing global challenges. By working together towards the SDGs, countries can share knowledge, resources, and best practices to achieve common goals.
- Measurable Targets: Each SDG has specific targets and indicators that allow for monitoring and evaluation of progress. These targets provide a clear roadmap for action and enable stakeholders to track their efforts towards achieving the goals.
- Interconnectedness: The SDGs recognize the interconnected nature of social, economic, and environmental issues. They emphasize the need for integrated approaches and cross-sectoral collaboration to address complex challenges.
- Inclusivity: The SDGs prioritize leaving no one behind. They aim to ensure that all individuals, regardless of their background or circumstances, have equal access to opportunities and benefits of sustainable development.
Conclusion
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are a crucial framework for achieving a sustainable and inclusive future. By addressing a wide range of social, economic, and environmental challenges, the SDGs provide a roadmap for action and collaboration. It is essential for governments, organizations, and individuals to prioritize the SDGs and work towards their achievement to create a better world for present and future generations.
H2: Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), Targets, and Indicators Analysis
H3: 1. SDGs Addressed or Connected to the Issues Highlighted in the Article
– SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being
– SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
– SDG 13: Climate Action
Explanation:
The article discusses issues related to health, cities, and climate change, which are connected to the following SDGs:
1. SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being – The article highlights the importance of addressing health issues, specifically related to the specialty mentioned in the image. This aligns with SDG 3, which aims to ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages.
2. SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities – The article mentions cities and their role in addressing the highlighted issues. SDG 11 focuses on making cities inclusive, safe, resilient, and sustainable.
3. SDG 13: Climate Action – The article indirectly refers to climate change by discussing the need for sustainable development. SDG 13 aims to take urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts.
H3: 2. Specific Targets Under Those SDGs Identified Based on the Article’s Content
– Target 3.4: By 2030, reduce by one-third premature mortality from non-communicable diseases through prevention and treatment and promote mental health and well-being.
– Target 11.3: By 2030, enhance inclusive and sustainable urbanization and capacity for participatory, integrated, and sustainable human settlement planning and management in all countries.
– Target 13.1: Strengthen resilience and adaptive capacity to climate-related hazards and natural disasters in all countries.
Explanation:
Based on the article’s content, the following targets can be identified:
1. Target 3.4 under SDG 3 focuses on reducing premature mortality from non-communicable diseases and promoting mental health and well-being. The article mentions the specialty related to health, indicating the importance of prevention and treatment to achieve this target.
2. Target 11.3 under SDG 11 emphasizes enhancing inclusive and sustainable urbanization. The article mentions cities and their role in addressing the highlighted issues, highlighting the need for participatory and sustainable human settlement planning and management.
3. Target 13.1 under SDG 13 aims to strengthen resilience and adaptive capacity to climate-related hazards and natural disasters. Although not explicitly mentioned, the article implies the need for climate action and sustainable development, aligning with this target.
H3: 3. Indicators Mentioned or Implied in the Article to Measure Progress towards the Identified Targets
– Indicator 3.4.1: Mortality rate attributed to cardiovascular disease, cancer, diabetes, or chronic respiratory disease.
– Indicator 11.3.1: Ratio of land consumption rate to population growth rate.
– Indicator 13.1.1: Number of deaths, missing persons, and directly affected persons attributed to disasters per 100,000 population.
Explanation:
The article does not explicitly mention indicators, but based on the identified targets, the following indicators can be used to measure progress:
1. Indicator 3.4.1 under SDG 3 measures the mortality rate attributed to non-communicable diseases. This indicator aligns with the target of reducing premature mortality from such diseases.
2. Indicator 11.3.1 under SDG 11 measures the ratio of land consumption rate to population growth rate. This indicator helps assess the sustainability of urbanization and human settlement planning.
3. Indicator 13.1.1 under SDG 13 measures the impact of disasters on population, including deaths, missing persons, and directly affected individuals. This indicator reflects the need to strengthen resilience and adaptive capacity to climate-related hazards.
H3: 4. Table: SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|——————————–|———————————————————————————————————-|——————————————————————————————————————–|
| SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being | Target 3.4: By 2030, reduce by one-third premature mortality from non-communicable diseases through prevention and treatment and promote mental health and well-being. | Indicator 3.4.1: Mortality rate attributed to cardiovascular disease, cancer, diabetes, or chronic respiratory disease. |
| SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities | Target 11.3: By 2030, enhance inclusive and sustainable urbanization and capacity for participatory, integrated, and sustainable human settlement planning and management in all countries. | Indicator 11.3.1: Ratio of land consumption rate to population growth rate. |
| SDG 13: Climate Action | Target 13.1: Strengthen resilience and adaptive capacity to climate-related hazards and natural disasters in all countries. | Indicator 13.1.1: Number of deaths, missing persons, and directly affected persons attributed to disasters per 100,000 population. |
Behold! This splendid article springs forth from the wellspring of knowledge, shaped by a wondrous proprietary AI technology that delved into a vast ocean of data, illuminating the path towards the Sustainable Development Goals. Remember that all rights are reserved by SDG Investors LLC, empowering us to champion progress together.
Source: cureus.com

Join us, as fellow seekers of change, on a transformative journey at https://sdgtalks.ai/welcome, where you can become a member and actively contribute to shaping a brighter future.







