E-Waste Management Industry Research 2024-2034
E-Waste Management Market – A Global and Regional Analysis: Focus on Application, Product, and Region – Analysis and Forecast, 2024-2034
Dublin, Oct. 14, 2024 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) — The “E-Waste Management Market – A Global and Regional Analysis: Focus on Application, Product, and Region – Analysis and Forecast, 2024-2034” report has been added to ResearchAndMarkets.com’s offering.
Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
- Goal 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
- Goal 13: Climate Action
- Goal 15: Life on Land
Introduction
The e-waste management market is projected to reach $71.58 billion by 2034 from $17.12 billion in 2023, growing at a CAGR of 14.22% during the forecast period 2024-2033.
Impact on Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
The e-waste management market significantly impacts various industries by promoting environmental sustainability and resource efficiency. As electronic waste volumes grow due to rapid technological advancements and increased consumption, effective e-waste management becomes crucial. This market fosters innovation in recycling technologies and processes, leading to improved recovery of valuable materials such as metals and plastics. Consequently, industries such as electronics manufacturing benefit from the reduced need for raw materials, decreasing extraction pressures on natural resources.
Europe’s Leadership in E-Waste Management
Europe is at the forefront of the global e-waste management market, setting a benchmark for effective e-waste recycling practices. In 2022, Europe led the world in both e-waste generation and recycling efficiency. The region generated 17.6 kg of e-waste per capita, the highest globally, yet it also demonstrated robust recycling capabilities by formally collecting and recycling 7.5 kg per capita. This represents a recycling rate of 42.8%, significantly higher than other regions. This high rate underscores Europe’s advanced regulatory framework and its commitment to sustainable waste management practices. Europe’s leadership in e-waste management showcases the impact of stringent regulations coupled with public and private sector commitment to environmental sustainability.
Environmental and Economic Benefits
Furthermore, compliance with stringent global regulations on waste disposal enhances corporate responsibility and brand reputation while potentially reducing regulatory penalties. Overall, the e-waste management market not only mitigates environmental damage but also contributes to economic efficiencies through material recovery and recycling, positioning it as a critical component in sustainable industrial practices.
Market Segmentation
Recycled E-Waste to Lead the Market
In the e-waste management market, recycling is the predominant application and is pivotal in addressing the escalating issue of electronic waste globally. Recycling of e-waste not only mitigates the environmental impact caused by hazardous chemicals and materials such as lead, mercury, and cadmium, but it also conserves natural resources by recovering valuable materials such as gold, silver, and copper. This recovery process is crucial for reducing the reliance on virgin material extraction, thus lowering the carbon footprint associated with mining and manufacturing new electronics.
The process involves several stages, including collection, sorting, dismantling, and material recovery, which are integral to ensuring that valuable components are efficiently recycled and reused. This systematic approach helps in diverting substantial amounts of waste from landfills, significantly reducing the leaching of toxins into the environment and improving overall public health outcomes.
As the market matures, the demand for recycled materials is expected to grow, driven by increasing consumer awareness and stricter regulatory frameworks that mandate recycling and proper e-waste management. This trend positions recycling not just as a necessary environmental action but as a lucrative segment within the broader e-waste management industry, promoting sustainable practices while contributing to economic growth.
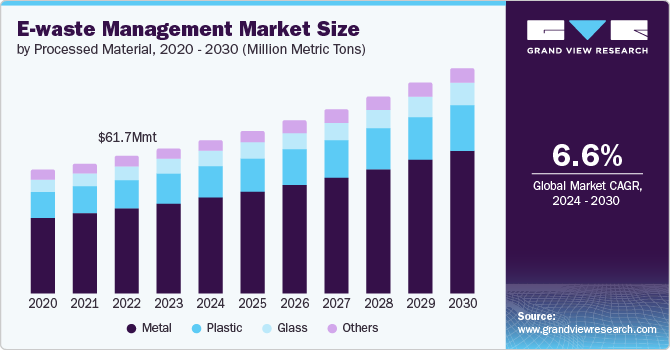
Metal to Hold the Largest Share in the E-Waste Management Market (by Material)
In 2022, the e-waste management market was predominantly led by metal, which accounts for 31 billion kg of the total e-waste generated. This figure significantly outweighs the 17 billion kg of plastics and 14 billion kg of other materials such as minerals, glass, and composites. Metals, particularly iron, played a crucial role, with high quantities present in e-waste and excellent recycling efficiencies across most management routes, resulting in approximately 19 billion kg being recycled into secondary resources.
Despite their lower quantities, platinum-group and precious metals also contributed notably to the value recovered from e-waste recycling, with several thousand kilograms reprocessed through both formal and informal methods. However, the recovery and recycling of rare earth elements, essential for modern technologies and renewable energy solutions, remains economically unviable. This is due to low market prices and the complex production chains concentrated in a few countries, limiting commercial recycling operations to about 1% of current demand.
This discrepancy emphasizes the necessity for enhanced recycling technologies and better economic incentives to address the recovery of valuable yet under-recycled materials such as rare earth elements.
Consumer Electronics to Hold the Largest Share in the E-Waste Management Market (by Source)
Consumer electronics are set to dominate the e-waste management market, driven by the rapid proliferation of devices such as smartphones, tablets, laptops, and household gadgets. The constant innovation in this sector leads to shorter product lifecycles, resulting in increased disposal rates. As consumers frequently upgrade to the latest technology, the volume of discarded electronics continues to grow exponentially.
Furthermore, the high turnover rate of consumer electronics is exacerbated by planned obsolescence and the integration of sophisticated components that quickly become outdated. Consequently, the need for effective e-waste management systems becomes more pressing. Consumer electronics contain valuable materials, including precious metals and rare earth elements, which present substantial opportunities for resource recovery through recycling.
In response, governments and industry stakeholders are intensifying efforts to implement robust e-waste management frameworks. These include extended producer responsibility (EPR) programs, public awareness campaigns, and the development of advanced recycling technologies. By focusing on consumer electronics, the e-waste management market can address one of the most significant sources of electronic waste, promoting sustainability and resource efficiency in the process.
Market Dynamics Overview
Market Drivers
- Increasing E-Waste Generation
- Rising Awareness of E-Waste as a Hazard
- Shift toward Circular Economy
Trends: Current and Future Impact Assessment
- Growing Government Regulations toward E-Waste Management
- Investments in E-Waste Recycling Infrastructure
Market Restraints
- High Recycling Cost
- Limited Recycling Infrastructure
Market Opportunities
- Advancements in Recycling Technologies
- Growing Adoption of Secondary Metals in Electronics, Jewelry, and Automotive Industries
Supply Chain Overview
- Value Chain Analysis
- Market Map
- E-Waste Management Market (by Material)
- Metal
- Plastic
- Glass
- Others
- Pricing Forecast
Research and Development Review
- Patent Filing Trend (by Country)
Regulatory Landscape
- Consortiums and Associations
- Regulations
Stakeholder Analysis
- Use Cases
- End User and Buying Criteria
Major Developments and Ongoing Projects
Competitive Benchmarking & Company Profiles
- Sims Limited
- Aurubis AG
- ENVIRO HUB HOLDINGS PTE LTD
- Umicore
- ERI
- Tetronics Environmental Technology Company
- Boliden
- Stena Metall AB
- SK tes
- Desco Electronic Recyclers
- Sembcorp Industries
- MBA Polymers Inc.
- Enviorncom Group
- Quantum Lifecycle Partners
- TRIPLE M METAL LP
Market Statistics
| Report Attribute | Details |
| No. of Pages | 123 |
| Forecast Period | 2024 – 2034 |
| Estimated Market Value (USD) in 2024 | $18.93 Billion |
| Forecasted Market Value (USD) by 2034 | $71.58 Billion |
| Compound Annual Growth Rate | 14.2% |
| Regions Covered | Global |
About ResearchAndMarkets.com
ResearchAndMarkets.com is the world’s leading source for international market research reports and market data. We provide you with the latest data on international and regional markets, key industries, the top companies, new products, and the latest trends.
Attachment

For more information about this report visit https://www.researchandmarkets.com/r/nbcq01
SDGs, Targets, and Indicators in the Article
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
- SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
- SDG 13: Climate Action
- SDG 15: Life on Land
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
- SDG 12.4: By 2020, achieve the environmentally sound management of chemicals and all wastes throughout their life cycle, in accordance with agreed international frameworks, and significantly reduce their release to air, water, and soil in order to minimize their adverse impacts on human health and the environment.
- SDG 12.5: By 2030, substantially reduce waste generation through prevention, reduction, recycling, and reuse.
- SDG 13.3: Improve education, awareness-raising, and human and institutional capacity on climate change mitigation, adaptation, impact reduction, and early warning.
- SDG 15.3: By 2030, combat desertification, restore degraded land and soil, including land affected by desertification, drought, and floods, and strive to achieve a land degradation-neutral world.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
- Indicator 12.4.1: Number of parties to international multilateral environmental agreements on hazardous waste, including electronic waste, and other chemicals that meet their commitments and obligations in transmitting information as required by each relevant agreement.
- Indicator 12.5.1: National recycling rate, tons of material recycled.
- Indicator 13.3.1: Number of countries that have communicated the strengthening of institutional, systemic, and individual capacity-building to implement adaptation, mitigation, and technology transfer, and development actions.
- Indicator 15.3.1: Proportion of land that is degraded over total land area.
Table: SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production | 12.4: By 2020, achieve the environmentally sound management of chemicals and all wastes throughout their life cycle, in accordance with agreed international frameworks, and significantly reduce their release to air, water, and soil in order to minimize their adverse impacts on human health and the environment. | 12.4.1: Number of parties to international multilateral environmental agreements on hazardous waste, including electronic waste, and other chemicals that meet their commitments and obligations in transmitting information as required by each relevant agreement. |
| SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production | 12.5: By 2030, substantially reduce waste generation through prevention, reduction, recycling, and reuse. | 12.5.1: National recycling rate, tons of material recycled. |
| 12.5: By 2030, substantially reduce waste generation through prevention, reduction, recycling, and reuse. | 12.5.1: National recycling rate, tons of material recycled. | |
| SDG 13: Climate Action | 13.3: Improve education, awareness-raising, and human and institutional capacity on climate change mitigation, adaptation, impact reduction, and early warning. | 13.3.1: Number of countries that have communicated the strengthening of institutional, systemic, and individual capacity-building to implement adaptation, mitigation, and technology transfer, and development actions. |
| SDG 15: Life on Land | 15.3: By 2030, combat desertification, restore degraded land and soil, including land affected by desertification, drought, and floods, and strive to achieve a land degradation-neutral world. | 15.3.1: Proportion of land that is degraded over total land area. |
Source: globenewswire.com








