Global Screw Pumps Market Set to Reach $3.72 Billion by 2028, Driven by Booming Oil and Gas Industry and Continuous Innovation
Global Screw Pumps Market Set to Reach $3.72 Billion by 2028, Driven by Booming Oil and Gas Industry and Continuous Innovation Yahoo Finance


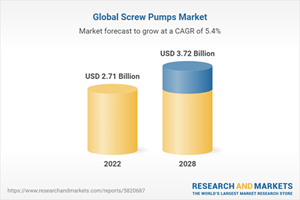
Global Screw Pumps Market

The “Screw Pumps Market by Screw Configuration, Max. Pressure, Distribution Channel, End Use, and Region 2023-2028” report has been added to ResearchAndMarkets.com’s offering.
The global screw pumps market has achieved significant milestones, reaching a market size of US$ 2.71 billion in 2022. The market is poised for further expansion, forecasted to grow to US$ 3.72 billion by 2028, exhibiting a commendable compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.30% during the period from 2023 to 2028.
Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
The global screw pumps market aligns with several Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) set by the United Nations:
- SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
- SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
- SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
- SDG 13: Climate Action
- SDG 14: Life Below Water
- SDG 15: Life on Land
These goals highlight the importance of sustainable energy, innovation, responsible production, climate action, and the preservation of marine and terrestrial ecosystems.
Screw Pumps Market Trends:
Several trends are shaping the global screw pumps market:
- Oil and Gas Industry Growth: The substantial expansion of the global oil and gas industry is driving the demand for screw pumps. These pumps provide continuous fluid flow, making them crucial for various applications, including crude oil transfer, pipeline boosting, and drilling mud transfer.
- Refinery Applications: Screw pumps are widely adopted in refineries to transfer solids between tanks or vessels without altering valve configurations, contributing to market growth.
- Advanced Materials: The introduction of screw pumps manufactured using advanced materials resistant to wear and corrosion enhances longevity and reliability, stimulating market growth.
- Wastewater Treatment: Screw pumps are increasingly used in wastewater treatment for precise chemical dosing and the pumping of activated sludge or stormwater, driving market expansion.
- Eccentric Screw Pumps: The launch of eccentric screw pumps designed for shear-sensitive materials and precise flow control is positively impacting market growth.
- Energy Efficiency: Growing demand for energy-efficient pumps, coupled with their widespread adoption in the F & B industry, is driving market growth.
- Government Initiatives: Various government initiatives aimed at reducing emissions and enhancing energy efficiency are contributing to market expansion.
Key Market Segmentation:
The market analysis includes key segments:
- Screw Configuration:
- Single Screw/Eccentric Screw/Progressive Cavity Pumps
- Twin Screw Pumps
- Three Screw Pumps
- Multiple Screw Pumps (Single Screw/Eccentric Screw/Progressive Cavity Pumps represented the largest segment)
- Max. Pressure:
- Distribution Channel:
- End Use:
Regional Insights:
The market analysis covers major regional markets:
- North America: (United States and Canada)
- North America leads the screw pumps market, driven by the demand for data privacy and security, the increase in cyberattacks
SDGs, Targets, and Indicators Analysis
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
- SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
- SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
- SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
- SDG 13: Climate Action
- SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals
The article discusses the global screw pumps market, which is connected to several SDGs. The use of screw pumps in various industries, including oil and gas, power generation, water treatment, chemicals, and food and beverage, contributes to SDG 7 by promoting affordable and clean energy. The continuous product innovations and extensive research and development activities mentioned in the article align with SDG 9, which focuses on industry, innovation, and infrastructure. Additionally, the article mentions the importance of advanced materials and energy efficiency, which are relevant to SDG 12 (responsible consumption and production) and SDG 13 (climate action). Finally, the mention of government initiatives and the need for partnerships in reducing emissions and enhancing energy efficiency connects to SDG 17 (partnerships for the goals).
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
- Target 7.2: Increase substantially the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix.
- Target 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable.
- Target 12.2: Achieve sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources.
- Target 13.2: Integrate climate change measures into national policies, strategies, and planning.
- Target 17.17: Encourage and promote effective public, public-private, and civil society partnerships.
Based on the issues discussed in the article, the following targets can be identified. Target 7.2 focuses on increasing the share of renewable energy, which aligns with the promotion of affordable and clean energy in the screw pumps market. Target 9.4 aims to upgrade infrastructure and industries to make them sustainable, which relates to the continuous product innovations and research and development activities mentioned in the article. Target 12.2 emphasizes sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources, which is relevant to the use of advanced materials and energy efficiency in screw pumps. Target 13.2 highlights the integration of climate change measures into policies and planning, which connects to the need for climate action in the industry. Finally, target 17.17 emphasizes the importance of partnerships, which is mentioned in relation to government initiatives and reducing emissions.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
- Indicator 7.2.1: Renewable energy share in the total final energy consumption.
- Indicator 9.4.1: CO2 emissions per unit of value added.
- Indicator 12.2.1: Material footprint, material footprint per capita, and material footprint per GDP.
- Indicator 13.2.1: Number of countries that have communicated their first or second nationally determined contributions.
- Indicator 17.17.1: Amount of United States dollars committed to public-private and civil society partnerships.
The article does not explicitly mention these indicators, but they can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets. Indicator 7.2.1 measures the renewable energy share in the total final energy consumption, which reflects progress towards increasing the share of renewable energy. Indicator 9.4.1 measures CO2 emissions per unit of value added, which indicates progress in upgrading infrastructure and industries to reduce emissions. Indicator 12.2.1 measures the material footprint, which can be used to assess progress in achieving sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources. Indicator 13.2.1 measures the number of countries that have communicated their contributions to climate change mitigation, reflecting progress in integrating climate change measures into policies and planning. Indicator 17.17.1 measures the amount of financial commitments to partnerships, which indicates progress in promoting effective partnerships.
4. Table: SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
SDGs Targets Indicators SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy Target 7.2: Increase substantially the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix. Indicator 7.2.1: Renewable energy share in the total final energy consumption. SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure Target 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable. Indicator 9.4.1: CO2 emissions per unit of value added. SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production Target 12.2: Achieve sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources. Indicator 12.2.1: Material footprint, material footprint per capita, and material footprint per GDP. SDG 13: Climate Action Target 13.2: Integrate climate change measures into national policies, strategies, and planning. Indicator 13.2.1: Number of countries that have communicated their first or second nationally determined contributions. SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals Target 17.17: Encourage and promote effective public, public-private, and civil society partnerships. Indicator 17.17.1: Amount of United States dollars committed to public-private and civil society partnerships. Behold! This splendid article springs forth from the wellspring of knowledge, shaped by a wondrous proprietary AI technology that delved into a vast ocean of data, illuminating the path towards the Sustainable Development Goals. Remember that all rights are reserved by SDG Investors LLC, empowering us to champion progress together.
Source: finance.yahoo.com

Join us, as fellow seekers of change, on a transformative journey at https://sdgtalks.ai/welcome, where you can become a member and actively contribute to shaping a brighter future.
- North America leads the screw pumps market, driven by the demand for data privacy and security, the increase in cyberattacks