Biofuel, solar power plants proposed for Pearl Harbor would demolish historic structures
Biofuel, solar power plants proposed for Pearl Harbor would demolish historic structures Stars and Stripes

The Navy’s Plan for Biofuel and Solar Energy Plants on Joint Base Pearl Harbor-Hickam
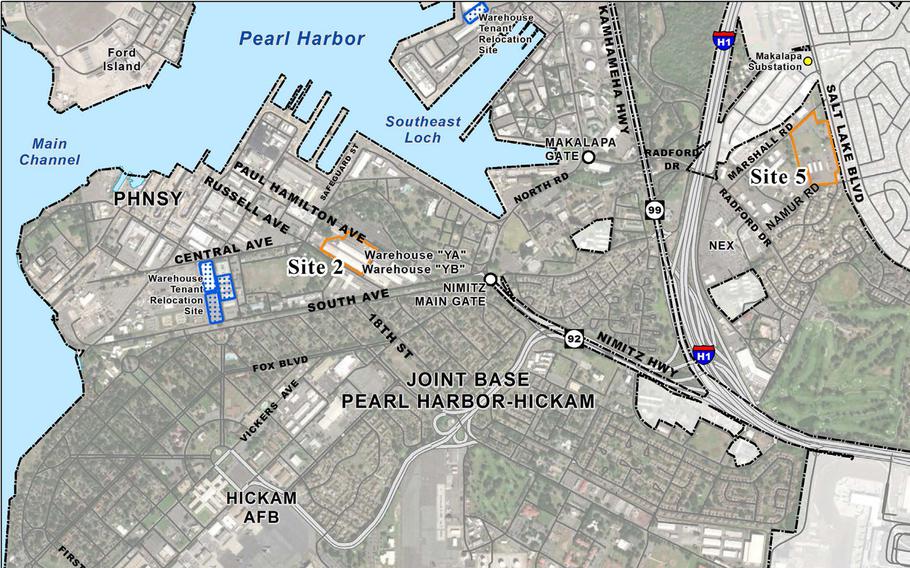
The Navy plans to lease out two sites on Joint Base Pearl Harbor-Hickam, Hawaii, outlined in orange, for construction of biofuel and solar energy plants intended to give the service greater energy resiliency. (U.S. Navy)
Introduction
The Navy plans to lease out 25 acres on Joint Base Pearl Harbor-Hickam for the construction of biofuel and solar energy plants. These plants are expected to be operational by 2027 and will contribute to the Navy’s energy resiliency and support the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
Project Details
- The Navy is seeking public comment on a draft environmental assessment for the construction of the biofuel and solar energy plants.
- The projects will involve two separate land leases on the Oahu joint base.
- Three historic buildings at Pearl Harbor will be demolished, while six others will be reused for the projects.
- One 10-acre site will house a biofuel-powered generation plant, while a separate 15 acres will hold a photovoltaic solar generating system.
- Both sites will also include lithium-ion battery storage systems.
- The plants will be connected to the existing distribution system operated by Hawaiian Electric Co., which provides 95% of the state’s electricity.
- Ameresco Inc., a renewable energy firm, was selected to develop the project.
- The land lease could last up to 37 years, with the option to negotiate new lease terms or decommission the system at the end of the lease.
Benefits and Goals
The construction of these plants aims to improve the joint base’s energy security, strategic flexibility, and energy resiliency. It will also support the installation’s renewable energy goals and contribute to Hawaii’s Clean Energy Initiative’s target of generating 100% of the state’s energy from renewable sources by 2045.
Addressing Energy Security Gaps
The new plants will address the Navy’s critical energy security gaps by providing energy resiliency to the entire base in the event of a grid outage. The joint base’s electrical distribution system is currently characterized as aging, undersized, and overloaded.
Historical Considerations
The proposed projects will have to navigate around historically significant structures on the joint base. Pearl Harbor, designated as a National Historic Landmark district, will be altered through the construction of new facilities, demolition of three historic properties, and reuse of six historic properties.
Conclusion
The Navy’s plan to lease out land on Joint Base Pearl Harbor-Hickam for the construction of biofuel and solar energy plants is a significant step towards achieving the SDGs and improving energy resiliency. Public comments on the draft environmental assessment can be submitted until May 2.
Sources
- Draft Environmental Assessment
- Email: NFPAC-Receive2@navy.mil
- Mail: Department of the Navy, NAVFAC Atlantic, Attn: Project Manager for JBPHH EUL Energy EA (EV21), 6506 Hampton Blvd., Norfolk VA 23508
SDGs, Targets, and Indicators Analysis
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
- SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
- SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
- SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
- SDG 13: Climate Action
The article discusses the Navy’s plans to lease out land for the construction of biofuel and solar energy plants. This aligns with SDG 7, which focuses on ensuring access to affordable, reliable, sustainable, and modern energy for all. It also relates to SDG 9, which aims to build resilient infrastructure, promote inclusive and sustainable industrialization, and foster innovation. Additionally, the projects contribute to SDG 11 by promoting sustainable cities and communities through the use of renewable energy sources. Finally, the initiatives support SDG 13 by addressing climate change through the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions.
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
- SDG 7.2: Increase substantially the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix
- SDG 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable
- SDG 11.6: Reduce the adverse per capita environmental impact of cities
- SDG 13.2: Integrate climate change measures into national policies, strategies, and planning
The article mentions the construction of biofuel and solar energy plants, which contribute to increasing the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix (SDG 7.2). The projects also involve the upgrade of infrastructure to make it sustainable (SDG 9.4). By utilizing renewable energy sources, the initiatives help reduce the adverse environmental impact of cities (SDG 11.6). Furthermore, the integration of these climate-friendly measures aligns with SDG 13.2.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
- Percentage of renewable energy in the energy mix
- Investment in renewable energy infrastructure
- Reduction in greenhouse gas emissions
- Number of sustainable energy projects implemented
The article does not explicitly mention specific indicators. However, progress towards the identified targets can be measured using indicators such as the percentage of renewable energy in the energy mix, the amount of investment in renewable energy infrastructure, the reduction in greenhouse gas emissions resulting from the projects, and the number of sustainable energy projects implemented.
Table: SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy | Increase substantially the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix (7.2) | Percentage of renewable energy in the energy mix |
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure | Upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable (9.4) | Investment in renewable energy infrastructure |
| Build resilient infrastructure, promote inclusive and sustainable industrialization, and foster innovation (9.1) | Number of sustainable energy projects implemented | |
| SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities | Reduce the adverse per capita environmental impact of cities (11.6) | Reduction in greenhouse gas emissions |
| SDG 13: Climate Action | Integrate climate change measures into national policies, strategies, and planning (13.2) | Number of sustainable energy projects implemented |
Behold! This splendid article springs forth from the wellspring of knowledge, shaped by a wondrous proprietary AI technology that delved into a vast ocean of data, illuminating the path towards the Sustainable Development Goals. Remember that all rights are reserved by SDG Investors LLC, empowering us to champion progress together.
Source: stripes.com

Join us, as fellow seekers of change, on a transformative journey at https://sdgtalks.ai/welcome, where you can become a member and actively contribute to shaping a brighter future.







