Earth just had its hottest year on record — climate change is to blame
Earth just had its hottest year on record — climate change is to blame Nature.com


The Hottest Year on Record: Impacts of Global Warming
The past 12 months were the hottest on record. Some 7.3 billion people worldwide were exposed, for at least 10 days, to temperatures that were heavily influenced by global warming, with one-quarter of people facing dangerous levels of extreme heat over the past 12 months, according to a report by the non-profit organization Climate Central.
Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
- Goal 13: Climate Action
- Goal 3: Good Health and Well-being
- Goal 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
“These impacts are only going to grow as long as we continue to burn coal oil and natural gas,” says Andrew Pershing, the vice-president for science at Climate Central.
Cities must protect people from extreme heat

Calculating the Impact of Climate Change
Researchers have previously estimated the influence of climate change on specific extreme weather events, a process known as climate attribution. Now, scientists have calculated the impact of human-induced climate change on daily air temperatures in 175 countries and 920 cities from November 2022 to the start of October 2023.
They found that the average global temperature over the past 12 months was 1.32 ºC above that during the pre-industrial baseline period of 1850 to 1900, surpassing the previous record of 1.29 ºC that was set from October 2015 to September 2016 (see ‘Heating planet’). The report comes as the European Union’s Copernicus Climate Change Service predicted that 2023 will be the hottest calendar year on record, with the average temperature up to October being 1.43 ºC above the pre-industrial average.
Source: Climate Central
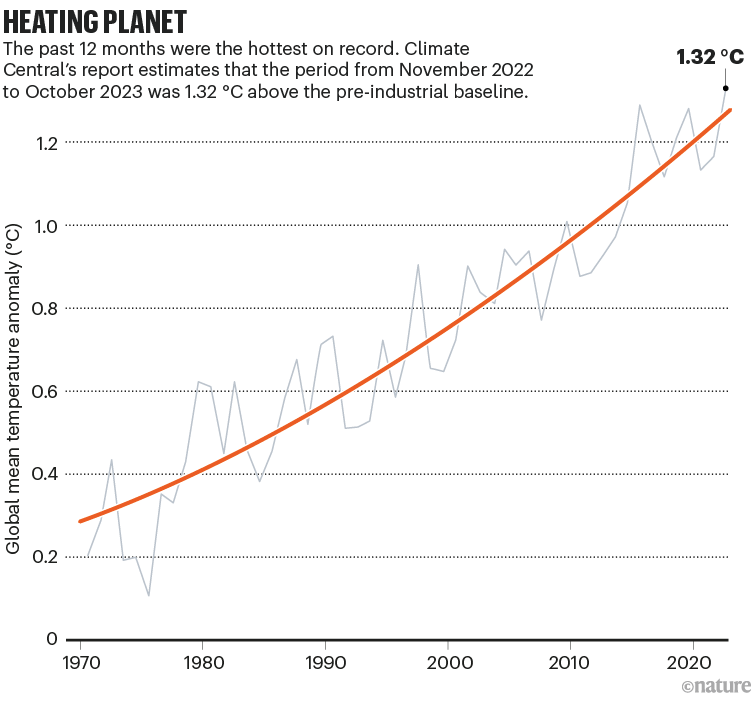
“This is the hottest temperature that our planet has experienced in something like 125,000 years,” says Pershing, the vice-president for science at Climate Central.
Most of this warming, about 1.28 ºC, results from human-induced climate change, with natural variation in the climate caused by processes such as the ongoing ocean-warming event El Niño contributing much less, says climate researcher Friederike Otto at Imperial College London.
By analysing daily air-temperature data and using computational climate models, the team calculated the effect of climate change on daily temperatures worldwide using a measure called the Climate Shift Index (CSI). The CSI scale runs from –5 to 5. A CSI value of zero means there is no detectable influence of human-caused climate change on the daily temperature, whereas a positive CSI value indicates how much more likely climate change made the daily temperature. A negative CSI value means climate change made the observed temperature less likely.
Earth’s hottest month: these charts show what happened in July and what comes next

Global Impacts of Extreme Heat
The researchers found that 7.3 billion people worldwide were exposed, for at least 10 days, to temperatures that were strongly impacted by climate change. In the first half of the past 12 months, tropical regions across South America, Africa and the Malay archipelago experienced the most days with temperatures that were strongly attributable to climate change, defined as having a CSI value of three or higher. These effects were felt even more strongly in the second half of the year-long period.
In Jamaica, the country where global warming had the greatest impact on daily temperatures, people experienced temperatures that were made over 4.5 times more likely by climate change. Guatemala and Rwanda also experienced temperatures that were made more than four times more likely by climate change.
The researchers also estimated the extent to which 700 cities with populations of at least 1 million experienced extreme heat over the past 12 months, defined as daily temperatures that are expected to occur less than 1% of the time in that region. They did this by comparing recent temperature data with data collected over a reference period of 1991–2020.
Join us, as fellow seekers of change, on a transformative journey at https://sdgtalks.ai/welcome, where you can become a member and actively contribute to shaping a brighter future.








