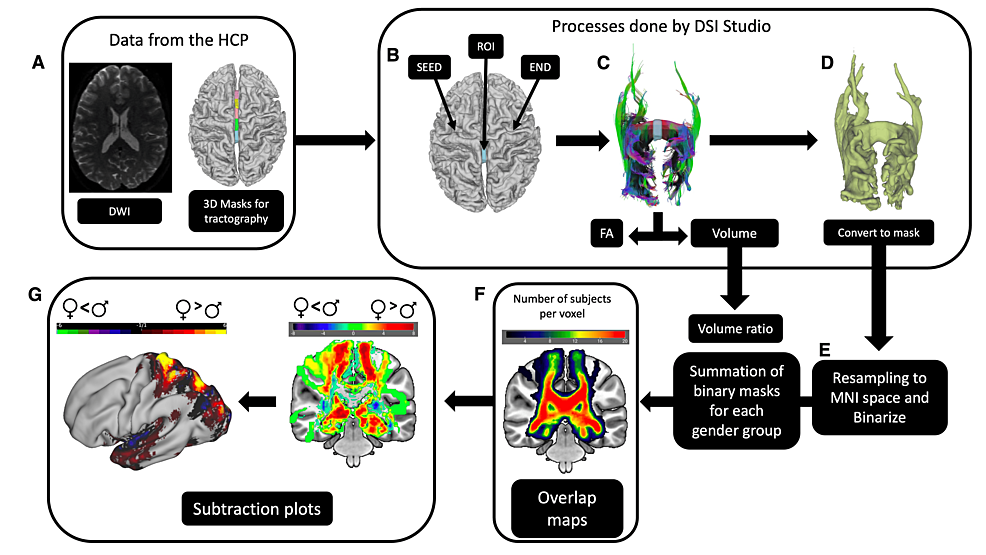
Gender Differences in the Cortical Distribution of Corpus Callosum Fibers
Gender Differences in the Cortical Distribution of Corpus Callosum Fibers Cureus


Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and their Significance
Introduction
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are a set of 17 global goals established by the United Nations in 2015. These goals aim to address various social, economic, and environmental challenges faced by the world, with the ultimate objective of achieving sustainable development for all.
Significance of SDGs
The SDGs provide a comprehensive framework for countries, organizations, and individuals to work towards a more sustainable future. By focusing on key areas such as poverty eradication, quality education, gender equality, clean energy, and climate action, the SDGs address some of the most pressing issues of our time.
SDGs and Sustainable Development
The SDGs are closely aligned with the concept of sustainable development, which emphasizes the need to meet present needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. By integrating social, economic, and environmental dimensions, the SDGs promote a holistic approach to development that ensures long-term sustainability.
SDGs in Action
- No Poverty: The first goal aims to end poverty in all its forms and dimensions. This includes eradicating extreme poverty, reducing inequality, and ensuring social protection for the most vulnerable populations.
- Quality Education: Goal 4 focuses on ensuring inclusive and equitable quality education for all. This involves promoting lifelong learning opportunities, improving educational infrastructure, and enhancing educational outcomes.
- Gender Equality: Goal 5 aims to achieve gender equality and empower all women and girls. This includes eliminating discrimination, promoting equal opportunities, and ensuring women’s participation in decision-making processes.
- Clean Energy: Goal 7 emphasizes the need for affordable, reliable, sustainable, and modern energy for all. This involves increasing the share of renewable energy sources, improving energy efficiency, and expanding access to electricity.
- Climate Action: Goal 13 focuses on urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts. This includes strengthening resilience, implementing mitigation strategies, and mobilizing financial resources for climate-related projects.
Conclusion
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) provide a roadmap for achieving a more sustainable and equitable world. By addressing key challenges such as poverty, education, gender inequality, clean energy, and climate change, the SDGs offer a comprehensive framework for promoting sustainable development. It is crucial for governments, organizations, and individuals to actively work towards these goals to ensure a better future for all.
H2 SDGs, Targets, and Indicators Analysis
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being – The article discusses the importance of specialty healthcare in improving health outcomes and well-being.
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
Target 3.8: Achieve universal health coverage, including financial risk protection, access to quality essential healthcare services, and access to safe, effective, quality, and affordable essential medicines and vaccines.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
Indicator 3.8.1: Coverage of essential health services – The article emphasizes the need for access to quality essential healthcare services.
Indicator 3.8.2: Proportion of the population with large household expenditures on health as a share of total household expenditure or income – The article indirectly implies the importance of financial risk protection and affordability of healthcare services.
4. SDGs, Targets, and Indicators Table:
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|——|———|————|
| SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being | Target 3.8: Achieve universal health coverage, including financial risk protection, access to quality essential healthcare services, and access to safe, effective, quality, and affordable essential medicines and vaccines. | Indicator 3.8.1: Coverage of essential health services |
| | | Indicator 3.8.2: Proportion of the population with large household expenditures on health as a share of total household expenditure or income |
Behold! This splendid article springs forth from the wellspring of knowledge, shaped by a wondrous proprietary AI technology that delved into a vast ocean of data, illuminating the path towards the Sustainable Development Goals. Remember that all rights are reserved by SDG Investors LLC, empowering us to champion progress together.
Source: cureus.com

Join us, as fellow seekers of change, on a transformative journey at https://sdgtalks.ai/welcome, where you can become a member and actively contribute to shaping a brighter future.







