Assessing Hannon Armstrong Sustainable Infrastructure Capital’s (HASI) Valuation Following Recent Investor Interest – simplywall.st
Report on HA Sustainable Infrastructure Capital (HASI) Market Performance and SDG Alignment
Executive Summary
This report provides an analysis of the recent market performance and financial valuation of HA Sustainable Infrastructure Capital (HASI). The company’s investment focus on sustainable infrastructure positions it as a key contributor to achieving several United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Recent volatility in its share price reflects shifting market sentiment regarding the valuation of assets critical for climate action and sustainable development. The analysis examines conflicting valuation metrics in the context of HASI’s role in financing projects aligned with SDG 7, SDG 9, SDG 11, and SDG 13.
Market Performance Analysis
Share Price Volatility and Returns
Recent trading activity for HASI indicates fluctuating investor sentiment towards sustainable infrastructure assets. While the long-term success of such investments is crucial for meeting global climate targets (SDG 13), short-term market dynamics present a mixed performance record.
- 1-Day Gain: 2.66%
- Year-to-Date Return: 6.52%
- 1-Year Shareholder Return: Negative
- 3-Year Shareholder Return: Positive
This performance suggests that while the market recognizes the long-term potential of SDG-aligned infrastructure, near-term risk assessment continues to evolve.
Financial Valuation Assessment
Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio Analysis
The P/E ratio provides a snapshot of how the market values a company’s earnings. For an entity like HASI, whose mission is tied to sustainable outcomes, the P/E ratio can reflect a market premium for its positive environmental impact.
- HASI P/E Ratio: 17.6x
- US Diversified Financial Industry Average P/E: 16.5x
- Estimated Fair P/E Ratio: 14.9x
The analysis indicates that HASI’s shares trade at a premium compared to both the industry average and its calculated fair ratio, suggesting that investors may be factoring in the non-financial value of its contributions to SDG 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy) and SDG 13 (Climate Action). This valuation points to a potential overvaluation based on current earnings alone.
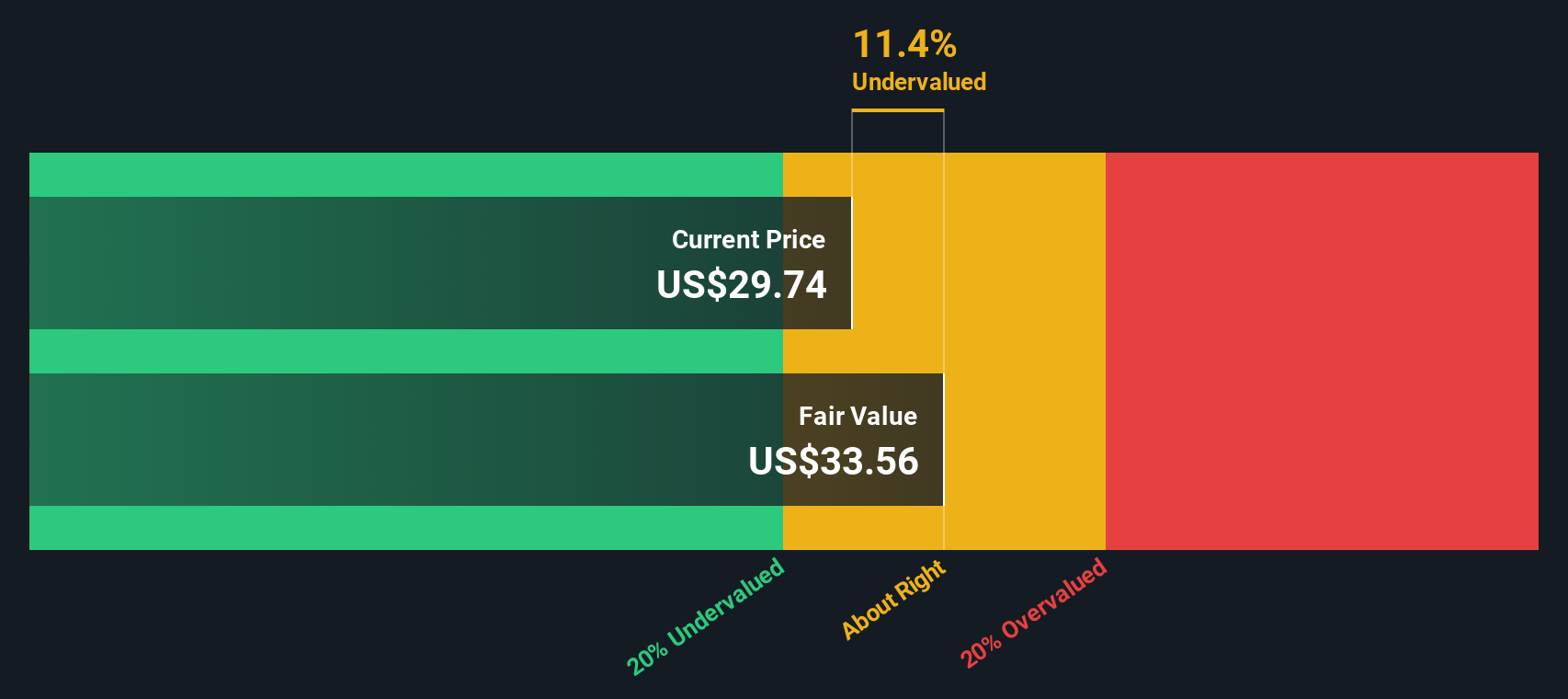
Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Model Perspective
In contrast to the P/E ratio, the DCF model evaluates the company based on its projected future cash flows. This long-term perspective is particularly relevant for infrastructure assets that generate stable returns over extended periods.
- DCF Valuation Finding: The model estimates that HASI is trading approximately 11% below its intrinsic fair value.
- Implication: This suggests the stock may be undervalued when considering its long-term cash-generating potential from sustainable infrastructure projects.
The divergence between the P/E and DCF models highlights the complexity of valuing companies whose core business is facilitating the transition to a sustainable economy as envisioned by the SDGs.
Alignment with Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
Core Business Strategy and SDG Impact
HASI’s investment strategy is fundamentally aligned with the global sustainability agenda. The company finances projects that are essential for making progress on several key SDGs.
- SDG 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy): HASI directly enables the growth of renewable energy sources by financing solar, wind, and other clean energy projects.
- SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure): The firm’s portfolio is composed of resilient, sustainable, and innovative infrastructure projects that are foundational to a modern, low-carbon economy.
- SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities): Investments in energy efficiency, distributed generation, and sustainable land use contribute to making cities and human settlements more inclusive, safe, resilient, and sustainable.
- SDG 13 (Climate Action): The primary objective of HASI’s investments is to finance climate solutions, making it a direct instrument for taking urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts.
Conclusion
HA Sustainable Infrastructure Capital presents a complex valuation case. While short-term metrics like the P/E ratio suggest a potential overvaluation, long-term models such as the DCF indicate the company may be undervalued. This discrepancy underscores the market’s ongoing efforts to price the intrinsic value of companies dedicated to advancing the Sustainable Development Goals. HASI’s future performance is inextricably linked to the global commitment to climate action and the continued deployment of capital towards building a sustainable and resilient infrastructure for the future.
Analysis of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in the Article
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
- SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth: The article’s core focus is on the financial performance, revenue growth, and valuation of HA Sustainable Infrastructure Capital. This directly relates to economic growth, investment, and the financial health of a company operating in a key sector.
- SDG 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure: The company’s name, “HA Sustainable Infrastructure Capital,” and its description as an “infrastructure-focused” entity explicitly connect the article to this goal. The entire analysis revolves around a company whose purpose is to invest in and develop infrastructure.
- SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities: While not explicitly mentioned, investment in “sustainable infrastructure” is a foundational component for developing sustainable cities and communities. This includes infrastructure for transport, utilities, and public services.
- SDG 13: Climate Action: The term “sustainable infrastructure” strongly implies projects that are designed to be resilient to climate change and contribute to mitigation efforts, such as renewable energy or green buildings. Investment in such a company is a form of climate finance.
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
- Target 8.2: Achieve higher levels of economic productivity through diversification, technological upgrading and innovation. The article’s discussion of “solid revenue growth” and market reassessment of “growth and risk in the infrastructure sector” points to the economic productivity and financial viability of companies in this innovative field.
- Target 9.1: Develop quality, reliable, sustainable and resilient infrastructure, including regional and transborder infrastructure, to support economic development and human well-being, with a focus on affordable and equitable access for all. The company’s entire business model, as implied by its name “HA Sustainable Infrastructure Capital,” is aligned with this target. The financial analysis in the article is an assessment of a key player in achieving this goal.
- Target 9.4: By 2030, upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable, with increased resource-use efficiency and greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies and industrial processes. The focus on “sustainable” infrastructure implies that the company’s investments are directed towards projects that align with this target of making industries and infrastructure more environmentally sound.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
- The article does not mention any official SDG indicators. However, it uses several financial and market-based indicators to measure the performance and viability of a company dedicated to sustainable infrastructure. These can be seen as proxy indicators for private sector investment and economic activity in this area.
-
Implied Financial Indicators:
- Share Price Return: The article mentions the “year-to-date share price return sits at 6.52%,” which indicates investor confidence and the financial performance of the sustainable infrastructure sector.
- Revenue Growth: The mention of “solid revenue growth” serves as a direct measure of the company’s economic expansion and the market demand for sustainable infrastructure projects.
- Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio: The analysis of the P/E ratio (17.6x) is used to gauge market valuation and growth expectations for the company, reflecting how the market values investment in this sector.
- Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Valuation: The use of a DCF model to estimate fair value is another indicator of the underlying financial health and long-term investment potential in sustainable infrastructure.
4. Table of SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators (Implied from the article) |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth | 8.2: Achieve higher levels of economic productivity. | Solid revenue growth reported by the company. |
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure | 9.1: Develop quality, reliable, sustainable and resilient infrastructure. 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable. |
Share price return (e.g., 6.52% year-to-date). Price-to-Earnings (P/E) ratio (17.6x) as a measure of market valuation. Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) as a measure of estimated fair value. |
| SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities | (Implied) Investment in infrastructure that supports sustainable communities. | The existence and financial analysis of an investment firm named “HA Sustainable Infrastructure Capital” implies capital flow towards this goal. |
| SDG 13: Climate Action | (Implied) Investment in infrastructure that contributes to climate change mitigation and adaptation. | Market sentiment and investor interest in a “sustainable infrastructure” company. |
Source: simplywall.st
What is Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0















































































