Carbon Offset Market to Reach USD 2.4 Trillion by 2035, Growing – openPR.com
Global Carbon Offset Market: A Catalyst for Sustainable Development Goals
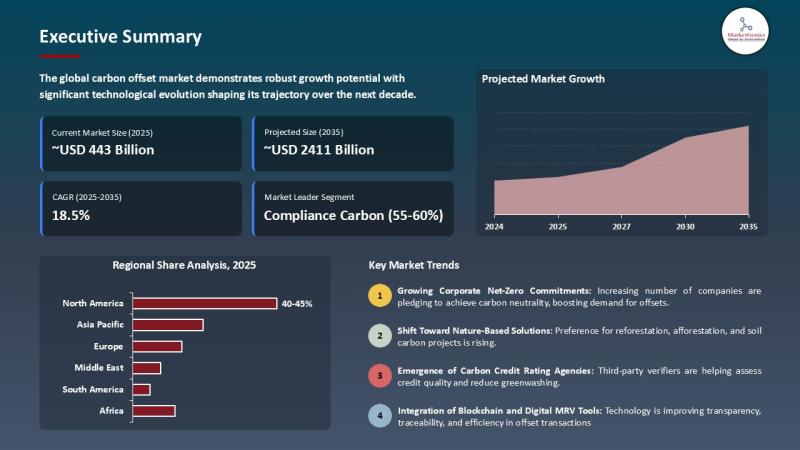
The global carbon offset market is projected to reach USD 2.411 trillion by 2035, demonstrating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 18.5%. This expansion is fundamentally linked to the global pursuit of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly SDG 13 (Climate Action). The market serves as a critical mechanism for corporations and nations to meet climate targets by financing projects that reduce or remove greenhouse gas emissions.
Market Dynamics and Alignment with SDGs
Primary Market Drivers
- Corporate Net-Zero Commitments: A primary driver is the increasing number of corporations committing to net-zero emissions. By purchasing carbon offsets for emissions they cannot eliminate, companies contribute directly to SDG 13 (Climate Action) and adopt more sustainable practices under SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production). A notable example is Microsoft’s purchase of millions of carbon removal credits through reforestation projects, which also supports SDG 15 (Life on Land).
- Regulatory Frameworks: Government regulations are compelling market growth. Vietnam’s emissions trading system, for instance, mandates compliance through offset credits, demonstrating how national policies can advance SDG 13. Such frameworks foster public-private partnerships, aligning with SDG 17 (Partnerships for the Goals).
- Technological Advancements: The integration of digital instruments for monitoring and reporting is enhancing market transparency and buyer confidence. This commitment to innovation directly supports SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure) by building resilient and sustainable systems for climate finance.
Key Trends and Innovations Supporting Sustainability
- Digital Verification Technologies: The market is advancing through digital platforms utilizing blockchain, Artificial Intelligence (AI), and satellite technology. Companies like Pachama use AI and satellite data for real-time forest monitoring, ensuring the integrity of nature-based solutions and bolstering both SDG 15 (Life on Land) and SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure).
- Enhanced Certification Standards: Leading standard-setting bodies such as Verra and Gold Standard are incorporating remote sensing and blockchain registries. These updates improve the credibility and accessibility of high-quality carbon credits, strengthening the global infrastructure required to achieve SDG 13 and fostering trust for SDG 17 (Partnerships for the Goals).
Regional Contributions to Global Climate Action
Regional Market Analysis
- North America: This region leads the market, driven by strong corporate commitments and supportive federal policies like the Inflation Reduction Act. Investments in both nature-based solutions (SDG 15) and engineered carbon removals (SDG 9) are accelerating climate action.
- Europe: The European Union’s Emissions Trading System and ambitious sustainability goals make it a key market. Strong regulatory pressure ensures continuous contributions towards SDG 13.
- Asia Pacific: This region is rapidly emerging, with countries like China and India scaling up government-backed, nature-based solutions. These initiatives diversify the global offset portfolio and advance progress on SDG 15.
Future Outlook and Strategic Developments
Expanding Opportunities for SDG Impact
The future of the carbon offset market lies in its deeper integration into corporate sustainability strategies and the advancement of technology-driven offsets. This evolution will create new pathways for achieving multiple SDGs.
- Corporate Sustainability Integration: As offsets become a fundamental component of corporate net-zero strategies, demand will grow for high-quality credits that deliver verifiable impacts on SDG 13 and co-benefits for other goals like SDG 15.
- Technology-Enabled Solutions: Innovations from platforms like Pachama and Nori are making it easier for smaller landowners and emerging markets to participate in carbon removal projects, promoting inclusive economic growth (SDG 8) and technological innovation (SDG 9).
Recent Strategic Initiatives
- South Pole (April 2025): The company enhanced its carbon offset portfolio with a focus on renewable energy projects (SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy) and reforestation initiatives (SDG 15), improving transparency to meet corporate and regulatory requirements.
- ClimateCare (June 2025): An expanded program was introduced to prioritize community-led renewable energy (SDG 7) and forest conservation projects (SDG 15). This initiative emphasizes social benefits, contributing to SDG 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth) alongside environmental restoration.
Key Market Participants
The growth and integrity of the carbon offset market are supported by numerous organizations committed to facilitating climate action and sustainable development. Key players include:
- 3Degrees
- Bluesource
- Carbon Credit Capital
- Carbonfund.org Foundation
- Climate Impact Partners
- Climate Partner GmbH
- ClimateCare
- EcoAct (Atos Group)
- Enviva Partners
- First Climate
- Gold Standard
- NativeEnergy
- Natural Capital Partners
- Pachama
- Planetly (Part of OneTrust)
- South Pole
- Terrapass
- The CarbonNeutral Company
- Verra
Analysis of the Article in Relation to Sustainable Development Goals
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
-
SDG 13: Climate Action
- The entire article is centered on the carbon offset market, which is a primary mechanism for taking urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts. It discusses corporate net-zero commitments, emissions trading systems, and carbon removal projects, all of which are direct actions to mitigate climate change.
-
SDG 15: Life on Land
- The article explicitly mentions nature-based solutions such as “reforestation and planting of native hardwoods” and “forest conservation projects.” These actions directly contribute to protecting, restoring, and promoting the sustainable use of terrestrial ecosystems and halting deforestation.
-
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
- The text highlights the role of technological innovation in improving the carbon offset market. It mentions “satellite-based remote sensing, using artificial intelligence,” “blockchain protocols,” and “digital platforms” (like Pachama and Nori) that enhance transparency, verification, and scalability, fostering sustainable industrial practices.
-
SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals
- The article describes a complex ecosystem of collaboration between various stakeholders. This includes public-private partnerships (regulatory systems like the EU Emissions Trading System), corporate partnerships (Microsoft purchasing credits from Chestnut Carbon), and collaborations with verification bodies (Verra, Gold Standard) to achieve climate goals.
-
SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
- The article discusses the significant economic growth of the carbon offset market, projecting it to reach “USD 2.4 Trillion by 2035.” This represents a new area of economic activity that aims to decouple economic growth from environmental degradation by creating financial value for emissions reduction and carbon removal.
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
-
Under SDG 13 (Climate Action):
- Target 13.2: Integrate climate change measures into national policies, strategies and planning. The article points to this target by mentioning “regulatory developments” such as “the Vietnam-based emissions trading system,” the “EU Emissions Trading System,” and supportive U.S. policies like the “Inflation Reduction Act,” which integrate climate action into national and regional frameworks.
-
Under SDG 15 (Life on Land):
- Target 15.2: Promote the implementation of sustainable management of all types of forests, halt deforestation, restore degraded forests and substantially increase afforestation and reforestation globally. This is directly addressed through examples like Microsoft’s purchase of “carbon removal credits in the United States through reforestation and planting of native hardwoods” and ClimateCare’s focus on “forest conservation projects.”
-
Under SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure):
- Target 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable, with increased resource-use efficiency and greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies. The article discusses the “advancement of digital platforms and verification technologies,” including “blockchain, AI, and satellite technology,” which are being adopted to make the industry of carbon offsetting more transparent, efficient, and credible.
-
Under SDG 17 (Partnerships for the Goals):
- Target 17.17: Encourage and promote effective public, public-private and civil society partnerships. The entire market structure described in the article, involving “large corporations” (Microsoft), project developers (South Pole), technology startups (Pachama), verification standards (Verra), and government regulations (Vietnam, EU), exemplifies the multi-stakeholder partnerships needed to achieve sustainable development.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
-
Financial Flows and Market Growth:
- The article provides a direct financial indicator for the growth of climate action initiatives. The projection that the “global carbon offset market is projected to surpass USD 2411 Bn by 2035” serves as a quantifiable measure of the financial resources being mobilized for climate mitigation.
-
Corporate Climate Commitments:
- The article implies an indicator related to corporate action through its reference to “large corporations making net-zero commitments.” The number of companies adopting such pledges and purchasing offsets is a measure of the private sector’s integration of climate change measures.
-
Volume of Carbon Credits:
- Progress can be measured by the volume of carbon offsets transacted. The article mentions “millions of carbon removal credits” purchased by Microsoft, indicating that the quantity of verified carbon credits is a key metric for tracking the scale of mitigation and removal activities.
-
Adoption of Technology for Verification:
- An indicator for innovation is the adoption of advanced technologies. The article implies this by stating that verification bodies like “Verra and Gold Standard are working to update their certification processes to include remote sensing technologies and blockchain-based registries.” The number of projects verified using these technologies can measure progress in transparency and credibility.
-
Number of Climate Policies and Regulations:
- The article points to the establishment of regulatory frameworks as a key driver. The existence and enforcement of policies like “the Vietnam-based emissions trading system” and “state-level carbon programs” in the U.S. serve as an indicator of government action and integration of climate policies (Target 13.2).
4. Summary Table of SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators Identified in the Article |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 13: Climate Action | Target 13.2: Integrate climate change measures into national policies, strategies and planning. |
|
| SDG 15: Life on Land | Target 15.2: Promote sustainable management of forests, halt deforestation, restore degraded forests and increase afforestation and reforestation. |
|
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure | Target 9.4: Upgrade industries to make them sustainable… with greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies. |
|
| SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals | Target 17.17: Encourage and promote effective public, public-private and civil society partnerships. |
|
| SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth | Target 8.4: Improve global resource efficiency… and decouple economic growth from environmental degradation. |
|
Source: openpr.com
What is Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0

















































































