How La Niña and El Niño impact Arkansas weather | Weather Wise – thv11.com
Analysis of Oceanic Temperature Variations and Their Alignment with Sustainable Development Goals
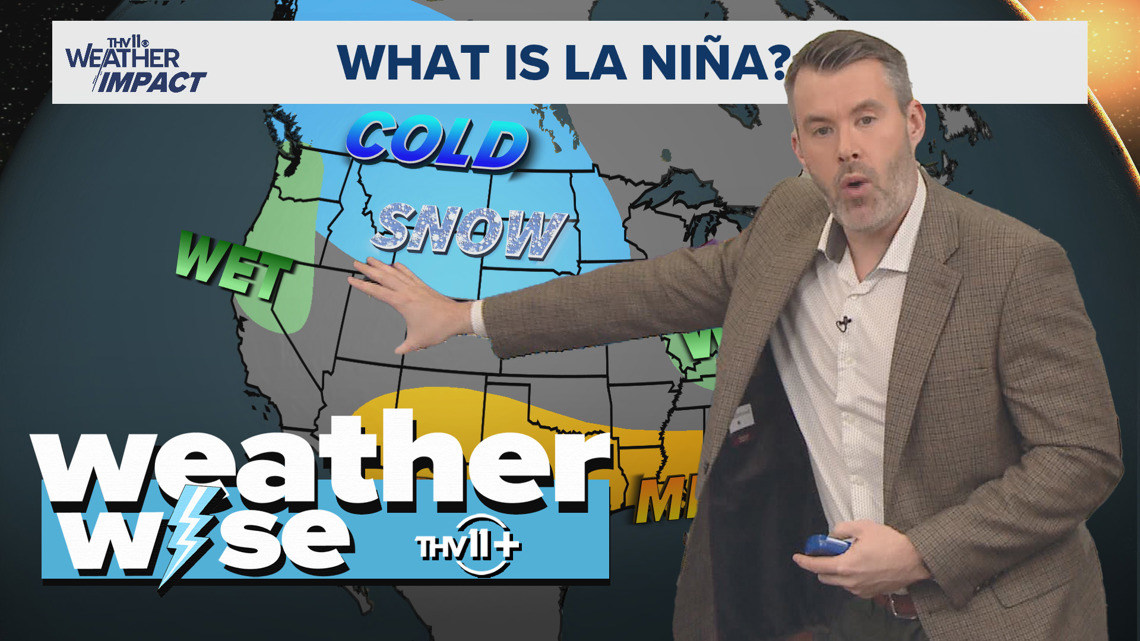
A report issued on November 4, 2025, examines the climatic phenomena of La Niña and El Niño, driven by oceanic temperature fluctuations. This analysis highlights the critical intersection of these weather patterns with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly those concerning climate, environmental stability, and human well-being.
Climatic Drivers and SDG 13: Climate Action
The El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) cycle, which includes both El Niño and La Niña events, represents a significant driver of global weather variability. Understanding these patterns is fundamental to achieving SDG 13 (Climate Action), as their frequency and intensity are influenced by broader climate change. Effective climate action requires robust monitoring and forecasting of such events to mitigate their adverse impacts on communities and ecosystems.
- Monitoring sea surface temperatures is crucial for early warning systems.
- Predictive models help inform policy and disaster preparedness strategies.
- These phenomena underscore the need for global cooperation to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and limit global temperature rise.
Impact on Marine Ecosystems and SDG 14: Life Below Water
The core mechanism of ENSO—the warming or cooling of the Pacific Ocean—has direct consequences for marine life, directly impacting the objectives of SDG 14 (Life Below Water). The health of marine ecosystems is intrinsically linked to stable oceanic conditions.
- Ocean Warming: El Niño events can lead to widespread coral bleaching, threatening marine biodiversity and the livelihoods dependent on it.
- Fisheries Disruption: Changes in ocean currents and temperature alter the distribution and abundance of fish stocks, affecting food security and economic stability for coastal communities.
- Ecosystem Resilience: Protecting and restoring marine habitats is essential to enhance their resilience to climate-related shocks like El Niño.
Socio-Economic Impacts and Broader SDG Linkages
The cascading effects of ENSO-driven weather events, such as altered precipitation patterns, have profound implications for several other SDGs. An early analysis of potential November snowfall, for instance, connects directly to community preparedness and infrastructure resilience.
Key Affected Sustainable Development Goals:
- SDG 2 (Zero Hunger): Extreme weather, including droughts and floods linked to ENSO, disrupts agricultural production, threatening food security and rural livelihoods.
- SDG 6 (Clean Water and Sanitation): ENSO cycles can lead to severe water shortages or, conversely, overwhelming floods, jeopardizing access to safe drinking water.
- SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities): Forecasting unusual weather events, such as unseasonal snow, is vital for urban planning, infrastructure maintenance, and ensuring the safety and resilience of human settlements.
Analysis of Sustainable Development Goals in the Article
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
-
SDG 13: Climate Action
- The article’s core topic is the effect of ocean temperature on weather patterns like La Niña and El Niño. These are large-scale climate phenomena. Discussing their impact on local weather directly relates to understanding and taking action on climate-related hazards.
-
SDG 14: Life Below Water
- The article explicitly mentions “the temperature of the ocean” as the driving factor for the weather events discussed. Ocean temperature is a critical vital sign for the health of marine ecosystems. Changes in ocean temperature, a key aspect of climate change, directly impact life below water.
-
SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
- The article discusses how climate patterns “impact our weather,” including “November snow chances.” Extreme and unpredictable weather events pose significant risks to human settlements, infrastructure, and safety, making community resilience a relevant theme.
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
-
Target 13.1: Strengthen resilience and adaptive capacity to climate-related hazards and natural disasters in all countries.
- The article explains phenomena (La Niña, El Niño) that cause climate-related hazards such as extreme weather. Understanding these impacts is the first step toward building resilience and adapting to them.
-
Target 14.3: Minimize and address the impacts of ocean acidification, including through enhanced scientific cooperation at all levels.
- While the article mentions ocean temperature and not acidification specifically, this target broadly concerns the changing physical and chemical conditions of the ocean due to climate change. Ocean warming, as mentioned in the article, is a primary stressor on marine ecosystems and is directly linked to the same root causes as acidification.
-
Target 11.5: By 2030, significantly reduce the number of deaths and the number of people affected and substantially decrease the direct economic losses relative to global gross domestic product caused by disasters…
- The weather impacts resulting from El Niño and La Niña can lead to natural disasters (e.g., severe storms, floods, droughts). The article, by providing information on these weather patterns, contributes to the public awareness needed to prepare for and mitigate the effects of such disasters.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
-
Ocean Temperature
- The article explicitly states “the temperature of the ocean” as a key factor. This is a direct, measurable indicator used globally to track climate change (SDG 13) and its effects on marine environments (SDG 14).
-
Frequency and Intensity of Climate Patterns (Implied)
- By focusing on “La Niña and El Niño,” the article implies the importance of monitoring these climate patterns. Tracking their frequency, duration, and intensity serves as an indicator of climate variability and change, which is crucial for assessing risks to communities (SDG 11) and strengthening climate resilience (SDG 13).
-
Public Weather and Climate Information (Implied)
- The article itself is a piece of public information that “breaks down” complex weather phenomena. The dissemination of such reports can be seen as an implied indicator of progress in raising awareness and providing early warnings about climate-related hazards, contributing to Target 13.3 (Improve education, awareness-raising…) and Target 11.5.
Summary Table of SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 13: Climate Action | 13.1: Strengthen resilience and adaptive capacity to climate-related hazards and natural disasters. | Frequency and intensity of climate patterns like El Niño/La Niña (Implied). |
| SDG 14: Life Below Water | 14.3: Minimize and address the impacts of ocean acidification… | Ocean Temperature (Explicitly mentioned). |
| SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities | 11.5: Significantly reduce the number of deaths and the number of people affected… by disasters. | Dissemination of public weather reports and early warnings (Implied by the article’s existence). |
Source: thv11.com
What is Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0









































































