World of Change: El Niño, La Niña, and Rainfall – NASA Science (.gov)
Global Temperature Analysis for 2024: A Report on Climate Trends and Sustainable Development Goal Implications
Executive Summary
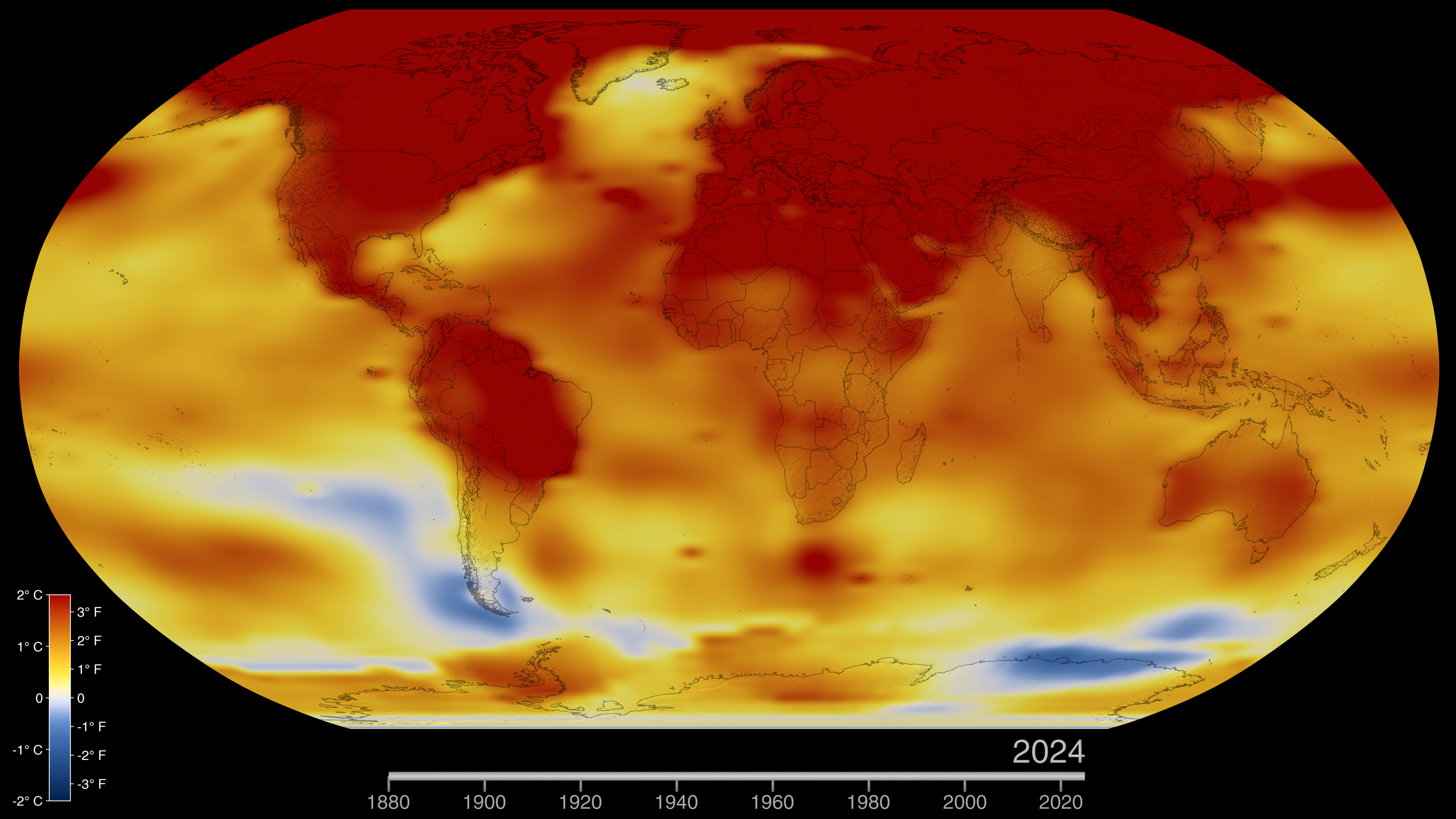
A comprehensive analysis led by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) confirms that 2024 was the warmest year since record-keeping began in 1880. The persistent and accelerating rise in global temperatures presents a direct and critical challenge to the achievement of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), most notably SDG 13 (Climate Action). This report details the key findings, causal factors, and the cascading impacts on various global sustainability targets.
Record-Breaking Temperatures and the Challenge to SDG 13 (Climate Action)
The data for 2024 indicates a significant deviation from historical averages, pushing the global climate system further from the stability required to meet the targets of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. The failure to curb this warming trend directly undermines SDG 13, which calls for urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts.
Key Temperature Metrics for 2024
- The average surface temperature was 1.28 degrees Celsius (2.30 degrees Fahrenheit) above the 1951-1980 baseline.
- Temperatures were approximately 1.47 degrees Celsius (2.65 degrees Fahrenheit) warmer than the pre-industrial average (1850-1900).
- For over half of 2024, average temperatures surpassed the 1.5 degrees Celsius threshold outlined in the Paris Agreement, a key framework for achieving SDG 13.
- The year concluded a 15-month period of unprecedented consecutive monthly temperature records, from June 2023 through August 2024.
Causal Factors and the Imperative for SDG 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy)
The primary drivers of this long-term warming trend are anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions, which directly links the climate crisis to global energy systems. This underscores the critical importance of accelerating the transition outlined in SDG 7.
Primary Drivers of Warming
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions: The warming is driven by heat-trapping gases, including carbon dioxide and methane. Recent analyses show record increases in carbon dioxide emissions from fossil fuels, highlighting a lack of progress toward SDG 7’s goal of increasing the share of renewable energy.
- Natural Climate Fluctuations: The strong El Niño event that began in 2023 contributed to the record temperatures, although the heat surge continued to exceed expectations even after the event abated.
- Other Contributing Factors: Researchers are investigating additional factors, such as the atmospheric effects of the 2022 Tonga volcanic eruption and changes in aerosol pollution.
Widespread Impacts on Global Sustainability Targets
The consequences of record global temperatures are not abstract; they manifest as tangible threats to human well-being, ecosystems, and infrastructure, impacting a wide range of SDGs.
Observed and Projected Consequences
- SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities): Increased risk of extreme rainfall and flooding, alongside the threat of wildfires, directly endangers urban and rural settlements, challenging the goal of making human communities resilient and safe.
- SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-being): The increasing frequency and intensity of extreme heat waves pose a significant risk to human health.
- SDG 14 (Life Below Water) & SDG 15 (Life on Land): Rising sea surface temperatures threaten marine ecosystems, while changing climate patterns and wildfires degrade terrestrial habitats.
Data Collaboration as a Model for SDG 17 (Partnerships for the Goals)
The confirmation of these climate records relies on robust international cooperation, demonstrating the principles of SDG 17. The analysis is built on a foundation of shared data and independent verification.
Methodology and Corroboration
- Data Collection: NASA’s temperature record is assembled from surface air temperature data from tens of thousands of meteorological stations and sea surface temperature data from ships and buoys.
- Independent Verification: Analyses by NOAA, Berkeley Earth, the Hadley Centre, and Copernicus Climate Services independently concluded that 2024 was the warmest year on record, reinforcing the certainty of the findings. This multi-agency effort to consolidate and analyze data serves as a functional example of the global partnerships required to address complex challenges like climate change.
Analysis of Sustainable Development Goals in the Article
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
The primary Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) addressed in the article is:
-
SDG 13: Climate Action
The entire article is dedicated to the issue of climate change, which is the central theme of SDG 13. It provides detailed evidence of a warming planet, discussing record-breaking global average surface temperatures, the role of greenhouse gas emissions, and the long-term warming trend. The article explicitly references the “Paris Agreement on climate change,” a key international framework for climate action, and discusses the goal of limiting warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius. The impacts mentioned, such as “wildfires,” “extreme rainfall, heat waves, and increased flood risk,” are direct consequences of climate change that SDG 13 aims to mitigate.
While SDG 13 is the main focus, the impacts discussed implicitly connect to other goals, although they are not the article’s central topic:
- SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities: The mention of “urban heating effects” and “increased flood risk” directly impacts the sustainability and safety of human settlements.
- SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being: Extreme weather events like “heat waves” pose significant risks to human health.
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
Based on the article’s focus on climate change, the following specific targets under SDG 13 are directly relevant:
-
Target 13.1: Strengthen resilience and adaptive capacity to climate-related hazards and natural disasters in all countries.
The article supports the relevance of this target by highlighting the increasing severity of climate-related hazards. It states, “We’re already seeing the impact in extreme rainfall, heat waves, and increased flood risk, which are going to keep getting worse as long as emissions continue.” The mention of “wildfires currently threatening our centers and workforce in California” is a concrete example of a climate-related hazard that requires enhanced resilience and adaptive capacity.
-
Target 13.2: Integrate climate change measures into national policies, strategies and planning.
This target is central to the article’s narrative. The text explicitly references the “Paris Agreement on climate change” and its goal to “remain below 1.5 degrees Celsius over the long term.” The analysis showing that “for more than half of 2024, average temperatures were more than 1.5 degrees Celsius above the baseline” serves as a direct assessment of the world’s progress (or lack thereof) in meeting the objectives set by international climate policy. The article’s data-driven approach is intended to provide “decision-makers with one location for data and analysis,” which is essential for policy integration.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
Yes, the article mentions several explicit and implied indicators that can be used to measure progress:
-
Indicator for Target 13.2: Global Average Temperature Anomaly.
This is the most prominent indicator in the article. It provides precise measurements to track warming against historical baselines, which is fundamental to assessing the Paris Agreement goals. Specific data points include:
- “Global temperatures in 2024 were 2.30 degrees Fahrenheit (1.28 degrees Celsius) above the agency’s 20th-century baseline (1951-1980).”
- “Earth in 2024 was about 2.65 degrees Fahrenheit (1.47 degrees Celsius) warmer than the mid-19th century average (1850-1900).”
-
Indicator for Target 13.2: Greenhouse Gas Concentrations.
The article identifies the root cause of the warming trend and provides a key indicator for it. It states that the warming is “driven by heat-trapping carbon dioxide, methane, and other greenhouse gases.” It quantifies the change in this indicator: “The concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere has increased from pre-industrial levels in the 18th century of approximately 278 parts per million to about 420 parts per million today.”
-
Indicator for Target 13.1: Occurrence and Impact of Climate-Related Hazards (Implied).
While the article does not provide specific statistics on the number of disasters or people affected, it clearly implies that the frequency and intensity of these events are key indicators of climate impact. It mentions “wildfires,” “extreme rainfall, heat waves, and increased flood risk” as observable consequences of the measured temperature rise. These events serve as qualitative, if not quantitative, indicators of the growing need for resilience and adaptation.
4. Summary Table of SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 13: Climate Action | 13.1: Strengthen resilience and adaptive capacity to climate-related hazards and natural disasters in all countries. | Implied Indicator: Increased occurrence and intensity of extreme weather events (e.g., “wildfires,” “extreme rainfall, heat waves, and increased flood risk”). |
| SDG 13: Climate Action | 13.2: Integrate climate change measures into national policies, strategies and planning. |
|
Source: nasa.gov
What is Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0












































































