Bend unveils $1.48B budget plan as city prepares for continued growth – KTVZ
City of Bend 2025-2027 Biennial Budget Report: A Framework for Sustainable Urban Development
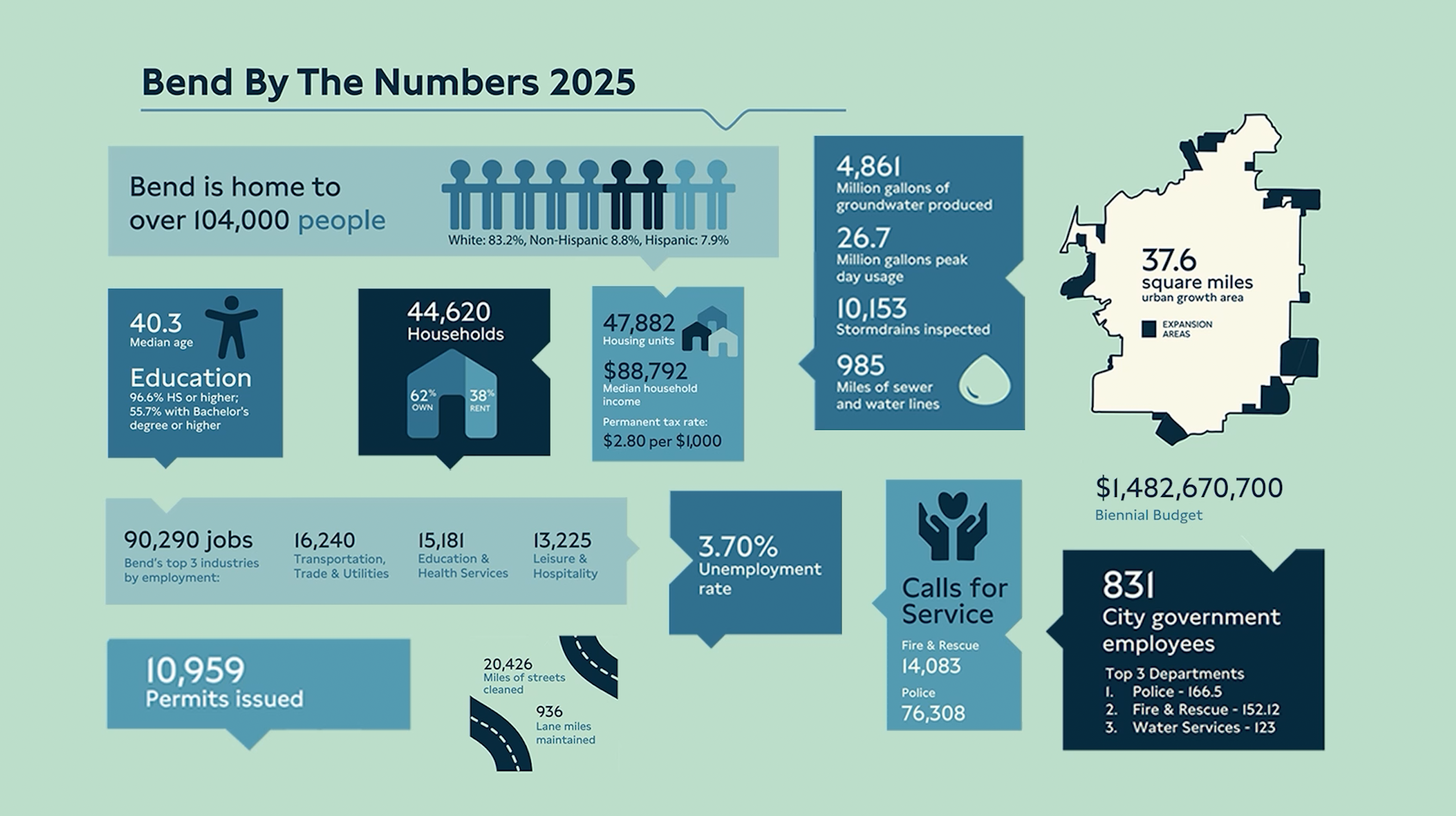
The City of Bend has released its 2025–2027 Budget in Brief, detailing a $1.48 billion spending plan. This budget is designed to manage significant population growth and guide the city’s development in alignment with key Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities).
Socio-Economic Profile and Alignment with SDG 8
The budget operates within a dynamic economic environment, reflecting progress toward SDG 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth). Key indicators include:
- Population: 104,000+ residents
- Households: 44,620 (62% owner-occupied, 38% renter-occupied)
- Median Household Income: Approximately $89,000
- Unemployment Rate: 3.7%
- Regional Job Market: Over 90,000 positions
Budget Allocation and Core Service Delivery
Public Safety and Institutional Strength (SDG 11 & SDG 16)
A primary allocation of funds is directed toward public safety, a cornerstone of creating safe, inclusive communities (SDG 11) and fostering effective, accountable institutions (SDG 16). Staffing and operational metrics include:
- Police Employees: 166
- Fire and Rescue Staff: 152
- Calls for Service (previous cycle): Over 90,000
Infrastructure and Essential Services (SDG 6, SDG 9, & SDG 11)
The budget provides for the maintenance and management of critical urban infrastructure, directly supporting several SDGs. Key operational responsibilities include:
- Water and Sewer Systems: Management of 985 miles of water and sewer lines, contributing to SDG 6 (Clean Water and Sanitation).
- Transportation Networks: Maintenance of nearly 1,000 miles of streets, which supports SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure).
- Urban Development: Issuance of 10,959 permits, reflecting managed development in line with the principles of SDG 11.
Strategic Planning for Sustainable Growth
Urban Growth Management and Housing (SDG 11)
The budget allocates resources for continued urban growth planning, preparing for the expansion of city boundaries to accommodate future housing and service requirements. This forward-looking strategy is essential for achieving the targets of SDG 11, ensuring access to adequate and affordable housing and basic services. The city’s permanent property tax rate remains stable at $2.80 per $1,000 of assessed value, providing a consistent fiscal foundation for these long-term investments.
Governance and Community Engagement (SDG 16)
In adherence to SDG 16, which promotes transparent and inclusive institutions, city officials have affirmed a commitment to ongoing community engagement throughout the budget’s adoption process. The full budget document is publicly available, ensuring accountability and enabling resident participation in planning for a sustainable future.
Analysis of Sustainable Development Goals in the Article
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
-
SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
- The article connects to this goal by providing key economic indicators for the city of Bend. It highlights a low unemployment rate of 3.7% and a substantial job market with over 90,000 positions, which are central themes of promoting sustained, inclusive, and sustainable economic growth and full and productive employment.
-
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure
- This goal is addressed through the budget’s focus on funding essential services and maintaining infrastructure. The article specifically mentions the management of 985 miles of water and sewer lines and nearly 1,000 miles of streets, which are critical components of resilient infrastructure necessary for a community’s functioning and economic development.
-
SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
- This is the most prominent SDG in the article. The entire piece focuses on urban management in a rapidly growing city. Key issues discussed, such as managing population growth, planning for future housing needs, providing public safety (police and fire services), and ensuring community engagement in the budgeting process, directly relate to making cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient, and sustainable.
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
-
SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
- Target 8.5: “By 2030, achieve full and productive employment and decent work for all women and men…” The article’s mention of a low unemployment rate (3.7%) and a large job market directly relates to the goal of achieving full employment within the community.
-
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure
- Target 9.1: “Develop quality, reliable, sustainable and resilient infrastructure… to support economic development and human well-being.” The city’s budget allocation for maintaining nearly 1,000 miles of streets and 985 miles of water and sewer lines is a direct action toward upholding this target.
-
SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
- Target 11.1: “By 2030, ensure access for all to adequate, safe and affordable housing and basic services…” The article addresses this by noting the city’s housing stock (44,620 households) and the provision of basic services like public safety (police and fire departments responding to over 90,000 calls).
- Target 11.3: “By 2030, enhance inclusive and sustainable urbanization and capacity for participatory, integrated and sustainable human settlement planning and management…” This is reflected in the city’s work on “urban growth planning,” preparing to expand boundaries for future housing, and the commitment to “community engagement” in the budget process.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
-
Indicators for SDG 8
- Unemployment Rate: The article explicitly states the unemployment rate is 3.7%. This is a direct measure corresponding to Indicator 8.5.2 (Unemployment rate).
- Number of Jobs: The mention of “more than 90,000 positions across the region” serves as an indicator of the size and health of the local job market.
-
Indicators for SDG 9
- Length of Maintained Infrastructure: The figures of “985 miles of water and sewer lines” and “nearly 1,000 miles of streets cleaned” are quantitative indicators of the scale of infrastructure being managed and maintained by the city, relevant to Target 9.1.
-
Indicators for SDG 11
- Housing Tenure: The data on households being “62% owner-occupied and 38% renter-occupied” is an indicator related to housing conditions and access (Target 11.1).
- Population and Household Count: The figures of “more than 104,000 residents” and “44,620 households” are fundamental indicators for urban planning and service provision (Target 11.3).
- Public Safety Service Levels: The numbers of “166 police employees,” “152 fire and rescue staff,” and “more than 90,000 calls for service” are indicators of the capacity and performance of basic emergency services (Target 11.1).
- Development Activity: The issuance of “10,959 permits” is an implied indicator of the rate of urban development and construction that the city is managing (Target 11.3).
4. Summary Table of SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth | 8.5: Achieve full and productive employment and decent work for all. |
|
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure | 9.1: Develop quality, reliable, sustainable and resilient infrastructure. |
|
| SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities |
11.1: Ensure access for all to adequate, safe and affordable housing and basic services.
11.3: Enhance inclusive and sustainable urbanization and capacity for participatory planning. |
|
Source: ktvz.com
What is Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0















































;Resize=620#)






























