House Prices to Income – Substack
Economic Analysis of Housing Affordability and its Implications for Sustainable Development Goals
Executive Summary
This report analyzes newly released 2024 wage and income data in the United States to assess the ratio of house prices to incomes. This ratio serves as a critical indicator for monitoring progress towards several Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly those concerning poverty, economic equality, and sustainable communities. The findings indicate that house prices remain significantly elevated relative to key income metrics, posing substantial challenges to achieving targets outlined in the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
Analysis of Median Household Income vs. House Prices
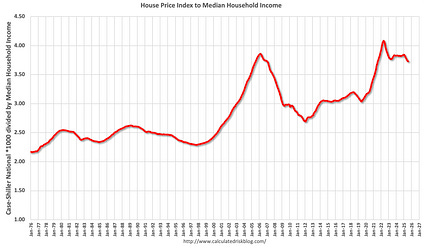
An assessment of the ratio between the Case-Shiller house price index and median household income reveals persistent affordability challenges. This metric is fundamental to evaluating progress towards SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities), which calls for access to adequate, safe, and affordable housing for all.
- The U.S. Census Bureau reported that the nominal median household income for 2024 was $83,730, an increase of 3.87% from $80,610 in 2023.
- Despite this income growth, the ratio of house prices to median income remains high, indicating that housing costs are outpacing the earnings of a typical household.
- Based on this measure, house prices are currently only 3% below the previous housing bubble peak and approximately 9% below the most recent peak.
- This disparity directly impacts SDG 1 (No Poverty) and SDG 10 (Reduced Inequalities), as housing is a primary expenditure, and its high cost can strain household budgets, prevent wealth accumulation, and exacerbate economic inequality.
Analysis of National Average Wage Index vs. House Prices
A second analysis utilizes the National Average Wage Index, released by the Social Security Administration, to corroborate the findings. This ratio provides insight into the affordability of housing for the average wage earner, a key component of SDG 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth).
- The ratio of the national Case-Shiller house price index to the National Average Wage Index confirms that housing remains expensive relative to wages.
- With 2025 data estimated, this ratio is positioned well above the historical median and is approaching the levels seen during the peak of the last housing bubble.
- This trend suggests that the benefits of economic growth are not translating into improved living standards for many workers, as wage gains are insufficient to keep pace with escalating housing costs.
Implications for Sustainable Development Goals
The elevated ratio of house prices to income has direct and significant implications for the achievement of several SDGs:
- SDG 1: No Poverty
- High housing costs are a major contributor to financial instability and can push households into poverty.
- SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
- The gap between wage growth and housing inflation indicates that economic growth is not inclusive, failing to provide decent living standards for all workers.
- SDG 10: Reduced Inequalities
- Housing unaffordability disproportionately affects low- and middle-income households, widening the wealth and opportunity gap.
- SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
- The data clearly indicates a failure to meet Target 11.1, which aims to ensure access to adequate and affordable housing for all citizens by 2030.
Conclusion
The 2024 data confirms that U.S. house prices remain elevated when measured against both median household income and the national average wage. This persistent affordability crisis presents a formidable barrier to progress on core Sustainable Development Goals, including the reduction of poverty and inequality, the promotion of decent work, and the development of sustainable communities. The findings underscore an urgent need for policy interventions aimed at aligning housing costs with household incomes to ensure sustainable and equitable development.
Analysis of Sustainable Development Goals in the Article
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
- SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities: The article’s primary focus is on the affordability of housing, which is a central theme of SDG 11. The analysis of the “ratio of house prices to incomes” directly addresses the challenge of ensuring access to adequate and affordable housing for all. The conclusion that “house prices are still elevated” highlights a key issue related to sustainable urban development.
- SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth: The article relies heavily on economic data related to wages and income, such as the “median household income” and the “National Average Wage Index.” These metrics are fundamental to assessing economic growth and the quality of work, which are core components of SDG 8. The discussion of income growth (e.g., “up 3.87% from $80,610 in 2023”) is directly relevant to this goal.
- SDG 10: Reduced Inequalities: The article implicitly addresses income inequality by choosing to use median income over average income. It explicitly states that “the average total income is skewed by the income of a few people.” This methodological choice demonstrates an awareness of and focus on the economic condition of the typical household, rather than an average that can mask significant disparities, which aligns with the goal of reducing inequality.
- SDG 1: No Poverty: While not the main focus, the issue of housing affordability is intrinsically linked to poverty. The article references the Census Bureau’s report on “Income, Poverty and Health Insurance Coverage,” establishing a direct connection between the income data being discussed and the broader issue of poverty. Unaffordable housing is a major factor that can push households into poverty or prevent them from escaping it.
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
- Target 11.1: “By 2030, ensure access for all to adequate, safe and affordable housing and basic services and upgrade slums.” The entire article is an analysis of housing affordability. The construction of a “ratio of the house price indexes to some measure of income” is a direct attempt to quantify progress (or lack thereof) towards this target.
- Target 8.5: “By 2030, achieve full and productive employment and decent work for all women and men… and equal pay for work of equal value.” The article’s use of the “National Average Wage Index” and “median household income” as key data points relates to the “pay” and “decent work” aspects of this target. It assesses whether income growth is keeping pace with major living costs like housing.
- Target 10.2: “By 2030, empower and promote the social, economic and political inclusion of all…” The article’s deliberate use of median income to avoid the skew caused by high earners is an analytical approach that aligns with understanding the economic reality for the majority of the population. This focus on the typical household’s financial situation is relevant to measuring broad economic inclusion and inequality.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
- Ratio of house price to income: This is the central metric developed and analyzed in the article. It serves as a direct, practical indicator for Target 11.1. The article uses the Case-Shiller house price index against both median household income and the National Average Wage Index to create this ratio, concluding that “house prices are still elevated.”
- Median household income: The article explicitly states the median household income for 2024 was “$83,730,” citing the U.S. Census Bureau. This is a key statistical indicator used to measure the economic well-being of a typical household and is relevant for tracking progress under SDG 8 and SDG 10.
- National Average Wage Index: This is another specific indicator mentioned in the article, sourced from the Social Security Administration. It is used to track the trend in wages over time and is a crucial component in the second graph’s analysis of housing affordability, making it a relevant indicator for Target 8.5.
SDGs, Targets, and Indicators Summary
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities | 11.1: Ensure access for all to adequate, safe and affordable housing. | The ratio of house prices to income, constructed using the Case-Shiller house price index and income data. |
| SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth | 8.5: Achieve full and productive employment and decent work for all… and equal pay for work of equal value. | National Average Wage Index; Median household income ($83,730 in 2024). |
| SDG 10: Reduced Inequalities | 10.2: Empower and promote the social, economic and political inclusion of all. | The use of median household income as a metric to avoid the skew of high earners and better represent the typical household’s economic situation. |
| SDG 1: No Poverty | (Implied) 1.2: Reduce at least by half the proportion of men, women and children of all ages living in poverty in all its dimensions. | The article’s reference to the “Income, Poverty and Health Insurance Coverage” report links the analysis of income and housing costs to the broader context of poverty measurement. |
Source: calculatedrisk.substack.com
What is Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0











































































