O’Hare: Anticipated TxDOT master plan ‘huge boon’ for Fort Worth-area economic development – Fort Worth Report

Report on the Texas Department of Transportation (TxDOT) Master Plan for the Fort Worth District and its Alignment with Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
Executive Summary
The Texas Department of Transportation (TxDOT) is preparing to launch a new master plan for the Fort Worth district, an initiative aimed at accelerating critical infrastructure projects to support regional growth. This report analyzes the plan’s objectives through the framework of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), highlighting its potential to advance economic prosperity, build resilient infrastructure, and foster sustainable communities through strategic partnerships.
Core Alignment with Sustainable Development Goals
The proposed master plan directly supports several key SDGs, integrating principles of sustainability into regional transportation strategy. The primary goals addressed include:
- SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth: By improving transportation infrastructure, the plan aims to stimulate sustained, inclusive, and sustainable economic growth.
- SDG 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure: The core objective is to build resilient, reliable, and sustainable transportation infrastructure to support economic development and human well-being.
- SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities: The initiative seeks to provide residents with access to safe, affordable, accessible, and sustainable transport systems, thereby making cities and human settlements more inclusive and resilient.
- SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals: The development and implementation of the plan are founded on a multi-stakeholder partnership between state, county, and city officials.
Advancing Economic Growth and Resilient Infrastructure (SDG 8 & SDG 9)
Tarrant County Judge Tim O’Hare has identified the master plan as a crucial driver for the region’s economic future, stating it will be a “huge, huge boon for economic development.” The plan’s focus on upgrading transportation networks is a direct investment in the quality and reliability of regional infrastructure, a key target of SDG 9.
- Elimination of Gridlock: The plan prioritizes reducing traffic congestion, which enhances economic productivity and reduces transportation costs for businesses and commuters, contributing to SDG 8.
- Accelerated Project Delivery: The initiative is modeled after a successful master plan in the Dallas district, which expedited infrastructure projects by an estimated 15 to 20 years. This demonstrates a commitment to efficient and impactful infrastructure development in line with SDG 9.
- Broad Geographic Scope: The plan’s benefits are designed to extend beyond Fort Worth, promoting equitable economic opportunities across the entire district.
Creating Sustainable and Accessible Communities (SDG 11)
A central goal of the master plan is to improve accessibility for residents, which aligns with SDG 11’s target of creating sustainable transport systems for all. By enhancing mobility, the plan will improve quality of life and access to essential services and employment. The comprehensive scope of the plan will impact a wide region, including the following counties:
- Erath
- Hood
- Jack
- Johnson
- Palo Pinto
- Parker
- Somervell
- Tarrant
- Wise
Fort Worth City Council member Michael Crain noted that speeding up transportation improvements is welcome, particularly in underserved areas, reinforcing the plan’s potential to foster more inclusive and equitable community development.
Strengthening Partnerships for Sustainable Development (SDG 17)
The success of the TxDOT master plan hinges on the collaborative efforts of multiple governing bodies and organizations. This multi-stakeholder approach exemplifies SDG 17, which emphasizes partnerships to achieve sustainable goals. Key partners in this initiative include:
- The Texas Department of Transportation (TxDOT)
- Tarrant County officials
- Fort Worth City Council
- The Tarrant Regional Transportation Coalition
This collaboration ensures that transportation development is integrated with local needs and long-term strategic objectives, maximizing the plan’s positive impact.
Conclusion and Next Steps
The forthcoming TxDOT master plan for the Fort Worth district represents a significant step toward building a more prosperous, resilient, and sustainable region. By aligning with key SDGs, the plan moves beyond traditional infrastructure development to address interconnected economic, social, and environmental objectives. Further details are expected to be released within the next month, followed by public meetings to ensure community engagement in this critical initiative.
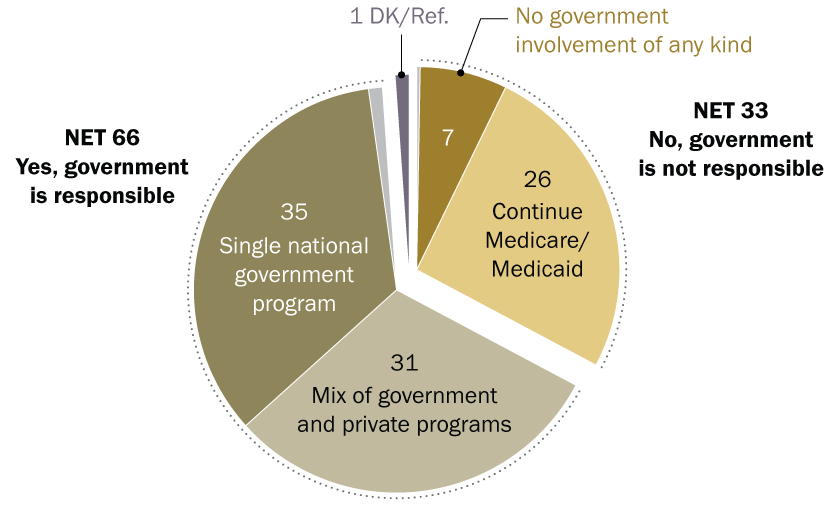
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
The article on the Texas Department of Transportation’s (TxDOT) master plan for the Fort Worth area connects to several Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) focused on infrastructure, economic development, and urban planning.
-
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure
This is the most directly relevant SDG, as the article’s central theme is the development of a master plan for “transportation, highway and road projects.” The plan aims to build and improve regional infrastructure to support the population and local economy.
-
SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
The plan focuses on Fort Worth and its surrounding nine-county district, addressing urban and regional transportation challenges. The goal of “eliminating gridlock” and “making access easier for our people” is fundamental to creating more sustainable and functional urban environments.
-
SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
The article explicitly states that the transportation plan is considered “key to the area’s continuing economic growth” and will be a “huge, huge boon for economic development.” This directly aligns with SDG 8’s objective of promoting sustained, inclusive, and sustainable economic growth.
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
Based on the details provided, several specific SDG targets can be identified:
-
Target 9.1: Develop quality, reliable, sustainable and resilient infrastructure
The article discusses a “TxDOT master plan” designed to “speed up transportation, highway and road projects.” This initiative is a clear example of developing regional infrastructure to support economic development and human well-being by improving transportation networks across a nine-county district.
-
Target 11.2: Provide access to safe, affordable, accessible and sustainable transport systems for all
The plan’s stated goals of “eliminating gridlock” and “making access easier for our people” directly address the need for improved transport systems. By focusing on transportation improvements, the plan aims to create a more accessible and efficient network for residents of Fort Worth and the surrounding areas.
-
Target 11.a: Support positive economic, social and environmental links between urban, peri-urban and rural areas
The master plan is not limited to the city of Fort Worth but encompasses the entire district, including Tarrant County and eight other counties. This represents a form of “regional development planning” that strengthens transportation links between urban (Fort Worth), peri-urban, and rural areas, which is essential for supporting positive economic connections.
-
Target 8.1: Sustain per capita economic growth
County Judge Tim O’Hare explicitly links the infrastructure plan to economic outcomes, stating it is “key to the area’s continuing economic growth” and a “huge, huge boon for economic development.” This aligns with the broader goal of fostering economic growth through strategic investments in infrastructure.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
The article does not mention official SDG indicators, but it implies several metrics that could be used to measure the success of the transportation plan:
-
Implied Indicators for Target 9.1 & 11.2
- Reduction in Traffic Congestion: The goal of “eliminating gridlock” implies that a key success metric would be the measurement of traffic flow and a reduction in congestion levels or average commute times.
- Acceleration of Project Delivery: The article notes that a similar plan in Dallas sped up projects by “15 to 20 years.” This suggests an indicator could be the reduction in the average timeline for the completion of transportation projects.
-
Implied Indicators for Target 8.1
- Rate of Economic Growth: The statement that the plan will be a “huge, huge boon for economic development” implies that progress could be measured by the rate of regional GDP growth, job creation, or the attraction of new business investments to the area following the infrastructure improvements.
4. Table of SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators (Implied from Article) |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure | 9.1: Develop quality, reliable, sustainable and resilient infrastructure…to support economic development and human well-being. | – Reduction in the timeline for completing transportation projects. – Number of new highway and road projects initiated and completed. |
| SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities | 11.2: Provide access to safe, affordable, accessible and sustainable transport systems for all.
11.a: Support positive economic…links between urban, peri-urban and rural areas by strengthening…regional development planning. |
– Reduction in traffic congestion and commute times (“eliminating gridlock”). – Improved transportation connectivity across the nine-county district. |
| SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth | 8.1: Sustain per capita economic growth. | – Increase in the rate of regional economic growth. – Level of new economic investment and development in the region. |
Source: fortworthreport.org

What is Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0


















































.jpg.webp?itok=0ZsAnae9#)