PACT is requisite for prostate cancer cell proliferation – Nature
Executive Summary
This report details an investigation into the role of the Protein Kinase RNA Activator (PACT) in prostate cancer (PCa) proliferation. The study aligns with Sustainable Development Goal 3 (Good Health and Well-being) by seeking novel therapeutic targets for a significant non-communicable disease. Key findings indicate that PACT is essential for PCa cell proliferation. Its depletion leads to cell cycle arrest and reveals a network of downstream genes, including the clinically relevant Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA), that could serve as new therapeutic targets. The research utilizes innovative methodologies, contributing to SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure), and proposes a foundation for developing advanced siRNA-based therapies.
Introduction: Contextualizing Prostate Cancer Research within Global Health Goals
Prostate cancer (PCa) represents a major global health challenge, contributing significantly to cancer-related mortality in men. This burden directly impedes the achievement of SDG 3, Target 3.4, which aims to reduce premature mortality from non-communicable diseases. Current treatments for advanced PCa, particularly castrate-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC), face limitations due to inevitable drug resistance. This clinical need underscores the importance of scientific research and innovation, a cornerstone of SDG 9, to develop more effective and sustainable therapeutic strategies. This report examines the function of the PACT protein as a potential therapeutic target, addressing the urgent need for novel treatments to improve health outcomes and promote well-being.
Key Findings and Implications for SDG 3
The study employed a loss-of-function approach to elucidate the role of PACT in PCa, yielding results with direct implications for advancing cancer treatment and supporting SDG 3.
PACT is a Pro-Proliferative Factor in Prostate Cancer
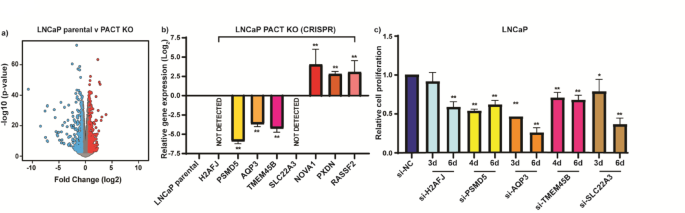
- Depletion of PACT via both siRNA and CRISPR-Cas9 methods consistently resulted in a significant reduction in cell proliferation across multiple PCa cell lines.
- Loss of PACT induced cell cycle arrest at the G0/G1 phase and increased apoptosis.
- These results identify PACT as a critical driver of PCa growth, making it a promising target for therapies aimed at controlling non-communicable diseases.
Genomic and Pathway Analysis Reveals PACT’s Regulatory Network
RNA-sequencing analysis of cells lacking PACT (PACT KO) identified 718 differentially expressed genes, revealing a broad impact on cellular function. Pathway analysis showed a significant depletion of biological processes in PACT KO cells related to:
- Cell cycle and division
- Mitochondrial function and metabolic pathways
- Nuclear receptor (NR) response pathways, including androgen response
This comprehensive analysis provides a molecular blueprint for understanding how PACT supports cancer progression, offering multiple avenues for therapeutic intervention in line with SDG 3.
Identification of Novel Therapeutic Targets Downstream of PACT
The study validated several key genes that were significantly downregulated in the absence of PACT. Targeting these genes individually was shown to reduce PCa cell proliferation.
- KLK3 (PSA): A well-known androgen-regulated gene, its downregulation highlights PACT’s role in hormone-driven cancer growth.
- H2AFJ, PSMD5, AQP3, TMEM45B, and SLC22A3: siRNA-mediated knockdown of these genes mimicked the anti-proliferative effects of PACT depletion.
This discovery expands the portfolio of potential drug targets for PCa, contributing to the development of new health technologies as envisioned by the SDGs.
PACT Modulates Response to Androgen-Targeted Therapies
- In PACT KO cells, the hormonal upregulation of PSA was diminished.
- The effect of the AR antagonist enzalutamide was enhanced in PACT KO cells, suggesting that targeting PACT could improve the efficacy of existing therapies.
- This finding is crucial for overcoming drug resistance, a major barrier to achieving the health targets of SDG 3.
Methodological Innovation and Contribution to SDG 9
This research leverages advanced scientific tools, reflecting a commitment to innovation as outlined in SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure).
- CRISPR-Cas9 Genome Editing: Utilized for the stable knockout of the PRKRA gene, providing a robust model for studying PACT function.
- RNA-Sequencing (RNA-seq): Employed for a comprehensive, unbiased analysis of the transcriptome, enabling the identification of entire gene networks regulated by PACT.
- siRNA Therapeutics: The study validates the use of siRNA as a tool to target PACT and its downstream effectors, laying the groundwork for developing next-generation RNA-based medicines.
These technological applications enhance scientific research capabilities and support the development of innovative health solutions.
Conclusion and Future Directions for Sustainable Health
This report establishes a pro-proliferative role for the PACT protein in prostate cancer, mediated through its influence on the cell cycle, metabolic processes, and androgen receptor signaling. The findings strongly support the potential of PACT as a novel therapeutic target. The identification of downstream genes that also regulate PCa proliferation opens new avenues for combination therapies. From a global health perspective, this research directly contributes to SDG 3 by advancing the knowledge base needed to combat a prevalent non-communicable disease. The potential development of siRNA-based therapeutics targeting PACT or PSA represents a significant step towards more effective and personalized cancer treatments. Future work should focus on translating these findings into preclinical and clinical settings, furthering the goal of ensuring healthy lives and promoting well-being for all.
Analysis of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in the Article
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
-
SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being
This is the primary SDG addressed. The article focuses entirely on prostate cancer (PCa), a significant non-communicable disease. It investigates the molecular mechanisms of the disease to identify new therapeutic targets. The introduction explicitly states that PCa “is the fourth most commonly diagnosed cancer worldwide, and in 2020 accounted for 3.8% cancer related death in men,” highlighting a major global health challenge. The research aims to address the “unmet clinical need for new PCa therapeutics,” directly contributing to the goal of promoting health and well-being.
-
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
This goal is connected through its emphasis on scientific research and technological innovation. The study employs advanced scientific techniques such as “RNA-sequencing (RNA-seq) analysis,” “CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing,” and explores novel therapeutic approaches like “siRNA-based therapies.” This represents a direct contribution to enhancing scientific research and upgrading technological capabilities in the medical field, which is a key aspect of SDG 9.
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
-
Target 3.4: Reduce premature mortality from non-communicable diseases
The article’s central theme is to understand and find new treatments for prostate cancer, a major non-communicable disease (NCD). By investigating the pro-proliferative role of the PACT protein and suggesting it as a therapeutic target, the research directly aims to develop more effective treatments. The conclusion suggests that targeting PACT “could be of benefit to overall PCa patient survival,” which aligns perfectly with the goal of reducing premature mortality from NCDs like cancer.
-
Target 3.b: Support the research and development of vaccines and medicines for the communicable and non-communicable diseases
This target is explicitly supported by the article, which is a fundamental piece of scientific research aimed at developing new medicines. The study’s conclusion proposes that “siRNA therapeutic targeting of PACT, or downregulated genes with PACT KO, could represent a new therapeutic approach.” This directly embodies the spirit of supporting research and development for new treatments for NCDs.
-
Target 9.5: Enhance scientific research, upgrade the technological capabilities of industrial sectors in all countries
The research described in the article is a clear example of enhancing scientific research. The “Materials and methods” section details the use of sophisticated technologies like “RNA-sequencing (RNA-seq),” “CRISPR-Cas 9,” and “flow cytometry.” The discussion also points towards future technological applications, such as using “nanoparticle- or microbubble-guided ultrasound technologies” for site-specific delivery of siRNA therapeutics. This showcases the upgrading of technological capabilities to tackle complex health problems.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
-
Indicator for Target 3.4 (Implied)
The official indicator is 3.4.1 (Mortality rate attributed to cancer). The article provides baseline data relevant to this indicator by stating that in 2020, prostate cancer “accounted for 3.8% cancer related death in men.” The success of the therapeutic approaches proposed in the article would be measured by a reduction in this mortality rate over time.
-
Indicator for Target 3.b (Implied)
While the article does not provide data on official indicators like R&D spending, the publication of this research itself serves as a qualitative indicator of ongoing research and development efforts. The study’s findings, which identify a “new therapeutic approach,” represent a measurable step in the R&D pipeline for new cancer medicines.
-
Indicator for Target 9.5 (Implied)
The article serves as an output indicator for enhanced scientific research. The successful application of advanced technologies like “RNA-sequencing” and “CRISPR-Cas9” to identify a novel therapeutic target in prostate cancer is a direct measure of upgraded technological and research capabilities within the scientific community studying this disease.
4. Summary Table of Findings
| SDGs, Targets and Indicators | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being |
|
|
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure |
|
|
Source: nature.com
What is Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0